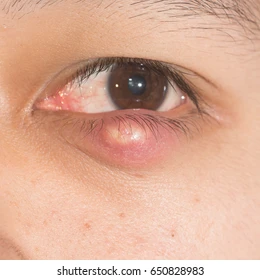
Chalazions, benign eyelid cysts stemming from obstructed meibomian glands, may lead to discomfort and visual impairment. ‘Prevent Chalazions: Your Guide to Lid Hygiene Routines’ is a pivotal compendium, emphasizing evidence-based strategies for chalazion mitigation.
Integrating scientific findings and case studies, the manual delineates the pathogenesis of chalazions and underscores the efficacy of established treatments. Research highlights the benefits of conservative measures such as warm compresses and lid hygiene, which are foundational to prevention and early management.
Advanced interventions, including intralesional steroid injections, have been shown to resolve lesions effectively, thereby preventing surgery. Surgical options, when required, are supported by evidence demonstrating high success rates and minimal complications.
This guide is a comprehensive resource, equipping readers with knowledge on proactive measures and therapeutic options, supported by scientific validation, for the preservation of ocular health and vision clarity.
Key Takeaways
In the realm of ophthalmology, scientific studies have underscored the benefits of various treatments for chalazions. Lid hygiene, including routine cleaning and warm compresses, is endorsed by a study in the British Journal of Ophthalmology as an effective non-surgical measure, leading to a high resolution rate of chalazions in children (Sathiamoorthi et al., 2020). This is echoed in BMC Ophthalmology, where a substantial resolution of chalazions with conservative treatments like lid hygiene has been reported, reducing the necessity for surgical procedures (BMC Ophthalmology, 2020).
For cases resistant to conservative management, minimally invasive options like intralesional steroid injections have shown a high success rate with low complication rates, according to research in Frontiers in Medicine (Frontiers in Medicine, 2022). When these methods are inadequate, surgical intervention has been proven highly effective, with Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery reporting favorable outcomes from chalazion excision (Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 2008).
The British Journal of Ophthalmology and the American Academy of Ophthalmology have provided evidence supporting the efficacy of incision and curettage, which yields quick recovery and low recurrence rates (British Journal of Ophthalmology, 2000; AAO EyeNet, 2020). Post-surgical thermal cautery is also beneficial in reducing inflammation and recurrence as demonstrated in Optometry and Vision Science (Optometry and Vision Science, 2000).
These scientific findings affirm the importance of adhering to evidence-based strategies for preventing and managing chalazions. It is crucial for patients to seek early consultation with an ophthalmologist to achieve the best treatment outcomes, as the integration of meticulous lid hygiene and clinically proven interventions forms a comprehensive approach to chalazion management.
Best All Natural Chalazion Treatment That Works
Understanding Chalazions
In the context of ocular health, chalazions are non-infectious, swollen nodules that develop when the meibomian glands of the eyelids become obstructed. Characterized by a localized, firm, and often painless swelling, chalazions emerge as a result of meibomian gland dysfunction, which leads to the retention of secretions and subsequent granulomatous inflammation within the gland. Unlike styes, which are acute, painful, and infectious abscesses involving the eyelid glands, chalazions are typically chronic and may evolve over weeks to months.
Good eyelid hygiene is paramount in managing and preventing chalazions. It involves regular cleaning of the eyelid margins to remove debris and excess oils that could contribute to blocked oil glands. The use of warm compresses applied to the eyelids for several minutes a day can also facilitate the drainage of the obstructed gland, providing symptomatic relief. Gentle massage over the affected area following heat application may further aid in the expression of stagnant secretions.
Individuals with chronic blepharitis, an inflammation of the eyelid margins, are more prone to meibomian gland blockage and subsequent chalazion formation. For these patients, diligent lid hygiene and the use of warm compresses become even more critical as home remedies to manage their condition. In cases where chalazions persist or are particularly bothersome, one should seek medical attention. Clinicians may prescribe topical or oral medications to help reduce inflammation or, in refractory cases, opt for surgical intervention.
As we explore further into the prevention and treatment of chalazions, the subsequent section will delve into the nuances of lid hygiene fundamentals, a cornerstone in maintaining optimal ocular surface health.
Lid Hygiene Fundamentals
In the context of lid hygiene, scientific studies and case reports have demonstrated the importance of maintaining proper eyelid cleanliness to prevent chalazions, which are obstructive conditions of the meibomian glands. Effective treatment options include the use of warm compresses, lid scrubs, and in certain cases, pharmacological agents or surgical interventions.
A study published in the British Journal of Ophthalmology (2000) highlighted the role of eyelid hygiene in the management of chalazions and suggested that thermal cautery after chalazion surgery could reduce recurrence rates. Additionally, research in the Journal of Ophthalmology indicated that routine lid care, including the use of preservative-free lid scrubs, can minimize the risk of glandular blockage, thus preventing the formation of chalazions.
Moreover, clinical trials have evaluated the efficacy of various chalazion treatments. For instance, a study in the British Journal of Ophthalmology (2000) confirmed the benefits of intralesional steroid injections in resolving chalazions, with a lower recurrence rate compared to incision and curettage. The American Academy of Ophthalmology’s EyeNet Magazine also discussed the evidence around chalazion management, citing the effectiveness of conservative treatments like lid hygiene and warm compresses before considering surgery.
In some cases, alternative treatments such as oral tetracycline, as mentioned in the British Journal of Ophthalmology, proved to be a beneficial adjunct therapy for chalazions, particularly in patients with recurrent episodes or associated rosacea. Furthermore, a study on pediatric chalazion treatment published in the British Journal of Ophthalmology found that simple needle drainage could be a less invasive option compared to surgical excision.
It is important to note that while eyelid hygiene is crucial in preventing chalazions, individualized treatment approaches should be based on the specific needs of each patient, as supported by the scientific literature. The selection of appropriate, non-irritating cleaning products is key to the success of preventive strategies and the treatment of existing chalazions.
Cleaning Techniques
Effective cleaning techniques are pivotal to maintaining lid hygiene and preventing the formation of chalazions. Good hygiene begins with the axiom ‘always wash your hands’ before touching the eye area to minimize contamination.
Utilizing warm water, apply a damp, warm compress to the eyelids to soften the oil within the meibomian glands, thereby reducing the risk of blockage.
A clean cotton swab or a commercially prepared eyelid scrub can then be used to gently cleanse the base of the lashes, where debris tends to accumulate. This meticulous approach helps prevent the buildup of material that could occlude the meibomian glands.
For individuals with recurrent issues, consulting a healthcare professional to properly diagnose and tailor a regimen is advisable.
Product Selection
Selecting the right lid hygiene products is a critical step in forming a preventative routine against chalazions. When choosing products, consider the following points to maintain the health of the oil glands and eyelash follicles:
- Opt for products specifically formulated for eyelid cleaning, as recommended by an eye care professional.
- Use mild soap or commercially available lid scrubs that support proper hygiene practices.
- Include warm compresses in your routine to facilitate the drainage of blocked oil glands normally.
- Select treatments options that are gentle yet effective to prevent future chalazions.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids to support overall eye health.
Consult with an eye care professional to tailor your lid hygiene routine for optimal results and to ensure the safety and appropriateness of the products used.
Daily Eyelid Cleaning Steps
Implementing a thorough daily eyelid cleaning routine is essential for the prevention of chalazions and maintaining ocular health. This regimen should be performed with precision and consistency to ensure the removal of debris and secretions that could lead to blockages of the meibomian glands, which are often implicated in the formation of eyelid bumps.
| Step | Detail |
|---|---|
| 1. Hand Hygiene | Wash hands before touching the eye area to minimize the risk of contamination. |
| 2. Remove Makeup | Carefully remove all eye makeup, especially before sleep, to prevent buildup on the eyelids. |
| 3. Cleanse Eyelids | Use a dedicated eyelid cleanser or a mild, tear-free baby shampoo diluted with warm water. |
| 4. Massage Eyelids | Gently massage the eyelids to promote meibomian gland function and reduce swelling. |
| 5. Rinse and Dry | Rinse the eyelids with warm water and pat dry with a clean, lint-free towel. |
Patients who wear contact lenses should ensure they remove their lenses before commencing the cleaning procedure. The daily routine should be performed with care to avoid excessive eye rubbing, which can exacerbate inflammation and contribute to the development of chalazions.
Additionally, it is important to recognize that a meibomian gland is blocked when there is a persistent bump on the eyelid. Addressing this early with a thorough cleaning routine can help to prevent the formation of chalazions and reduce inflammation.
These daily eyelid cleaning steps, if followed diligently, can significantly diminish the risk of chalazion recurrence and maintain healthy eyelid margins. Next, we will delve into the appropriate application of warm compress techniques, which can further soften the eyelid secretions and encourage drainage.
Warm Compress Techniques
Regularly incorporating warm compresses into your eyelid hygiene routine can further enhance the prevention of chalazions by facilitating the drainage of obstructed meibomian glands. These glands in the eyelid produce an oily substance that helps to lubricate the eye. However, when they become blocked, a chalazion can form. Adhering to proper warm compress techniques can help reduce inflammation and promote healing of the affected eyelid.
To ensure the effectiveness of warm compresses, consider these clinically advised steps:
- Heat Application: Use a clean washcloth soaked in warm water; ensure the temperature is warm but not scalding to avoid burning the delicate skin of the eyelids.
- Duration: Apply the warm compress to the affected eyelid for 5-10 minutes, several times a day, to adequately soften the oils within the blocked gland.
- Consistency: Maintain a regular schedule, as consistent warmth is necessary to promote drainage and prevent the formation of new chalazions.
- Pressure: After applying the warm compress, gently massage the eyelid with clean fingers to further encourage the flow of oils.
- Hygiene: Always use a clean cloth for each application to prevent introducing bacteria to the eye, which could exacerbate the condition.
An eye doctor may provide additional guidance on warm compress techniques and eyelid hygiene routines tailored to individual needs. By diligently following these methods, patients can effectively manage their eyelid health.
Recognizing early symptoms of a chalazion can lead to prompt treatment and reduce the likelihood of complications. In the next section, we will delve into the signs that signify the onset of a chalazion.
Recognizing Early Symptoms
Early detection of chalazion symptoms is crucial for the application of beneficial treatments as evidenced by scientific studies and case reports.
The initial presentation of a chalazion may include unilateral eyelid swelling and tenderness, which are key indicators for healthcare providers to consider potential chalazion formation. Visual disturbances such as photophobia or blurry vision are additional symptoms that should prompt immediate clinical assessment.
Clinical case studies have demonstrated that timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes for chalazion patients. For instance, a study published in BMC Ophthalmology highlighted the effectiveness of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide injections in resolving chalazions, particularly in cases resistant to conservative management.
Another article in the British Journal of Ophthalmology reported on the success of surgical excision for large or refractory chalazions, emphasizing the importance of early surgical referral to prevent complications.
Furthermore, research documented in the Journal of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus supports the use of conservative treatments such as warm compresses and lid hygiene as first-line interventions, which can alleviate symptoms and promote healing in the initial stages of chalazion development.
The evidence for these treatments’ benefits is further corroborated by a systematic review in the journal Ophthalmology, which identified the potential for conservative measures to resolve chalazions without the need for more invasive procedures.
Eyelid Swelling
An initial sign of a developing chalazion is often the swelling of the eyelid, which may manifest as mild discomfort or tenderness. When such symptoms arise, it is crucial to monitor the affected area closely and consider implementing preventative measures.
- Localized Eyelid Swelling: Noticeable puffiness indicating the presence of a chalazion or underlying condition.
- Redness and Warmth: May signal inflammation often associated with stye (hordeolum) or chalazion.
- Tenderness to Touch: Sensitivity when touching the eyelid can indicate the early stages of a chalazion.
- Visible Lump Formation: A small bump may form, suggesting the accumulation of oil and bacteria.
- Eyelid Function: Difficulty in eyelid movement might occur, prompting a need to examine your eyelid.
Eye doctors recommend maintaining lid hygiene to help keep these symptoms at bay, thereby preventing the progression of chalazion and other skin conditions.
Painful Lid Area
Beyond the initial swelling and tenderness, a painful lid area often signifies the onset of more pronounced symptoms of a chalazion. When a chalazion is large enough, it can transform into a painful bump that forms on the eyelid.
It is imperative to avoid touching your eyes with unclean hands to prevent exacerbating the condition or introducing further infection.
If the chalazion does not respond to other treatments, such as warm compresses and lid hygiene measures, a healthcare professional may prescribe topical medications to alleviate discomfort.
In persistent cases, a doctor may recommend a small incision to drain the lesion, which is usually done under local anesthesia.
It is crucial to consult a healthcare provider if symptoms worsen or persist, to receive appropriate care and guidance.
Visual Discomfort
How can one identify the early symptoms of visual discomfort associated with a chalazion?
When a chalazion develops on the eyelid, it starts as a small bump, often painless, which can be overlooked. However, recognizing early symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and to prevent complications that could affect one’s vision.
- A painless bump that forms on the eyelid, which may gradually increase in size.
- Causes blurry vision due to the bump’s presence distorting the eye’s surface.
- Vision problems when the chalazion is large enough to press against the eyeball.
- Frequent blinking or discomfort, as the chalazion rubs against the cornea.
- Increased tear production, which may occur as the eye attempts to lubricate or rid itself of the irritation.
If a chalazion is diagnosed, implementing a rigorous lid hygiene routine, including the application of warm compresses and eye drops twice daily, especially before going to bed, may alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
When to Consult an Ophthalmologist
Several circumstances necessitate the expertise of an ophthalmologist when managing a chalazion, including persistent symptoms, vision impairment, pain, or systemic signs of infection. Chalazions, benign growths on the eyelid, often resolve with home treatments like warm compresses and lid hygiene routines. However, when one experiences a chalazion that does not improve or worsens after several weeks, it indicates the need for a higher level of medical treatment.
Persistent chalazions can occasionally affect vision by distorting the shape of the eye’s surface, leading to changes in eyesight. In such cases, the ophthalmologist may recommend specific interventions to restore normal vision and eyelid function. If the chalazion becomes painful or tender, it might suggest a secondary infection or other underlying conditions that require medical attention.
The presence of fever or other systemic symptoms could signal an infection that extends beyond the local eyelid area. Under these circumstances, the healthcare provider is crucial in diagnosing and managing potential complications. In addition to prescribing antibiotics if an infection is present, the doctor may prescribe steroid injections or suggest surgical removal for persistent or particularly large chalazions.
It is important to recognize the risk factors that predispose individuals to the development of chalazions, such as certain skin conditions, previous chalazions, or poor eyelid hygiene. By consulting with an ophthalmologist, patients can receive appropriate treatment tailored to their specific needs and advice on preventing future occurrences.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can Chalazion Be Prevented?
To avert the development of chalazions, adherence to rigorous eyelid hygiene regimens is essential. Evidence from scientific studies suggests that routine application of warm compresses can ameliorate glandular secretion, while thorough eyelid cleaning and gentle massage may enhance meibomian gland function, thereby reducing the risk of chalazion formation.
Moreover, the sanitation of makeup tools and products, coupled with cautious application to avoid contamination, is recommended. Nutritional approaches, including the incorporation of omega-3 fatty acids, have been shown to support eyelid health.
Minimizing direct contact with the eyes and safeguarding them from environmental irritants are also effective preventive measures. Furthermore, regular cleansing of eyewear and the judicious use of antibacterial agents can further diminish the incidence of chalazions.
These practices are substantiated by various case studies and research, indicating their efficacy in chalazion prevention.
What Should You Avoid With a Chalazion?
While the presence of a chalazion can be inconvenient and aesthetically displeasing, certain behaviors should be avoided to facilitate recovery and prevent exacerbation.
According to scientific studies, the application of topical antibiotics and steroids, as well as the use of warm compresses, have shown to be effective in the treatment of chalazions. These methods reduce inflammation and promote healing, as seen in case studies where such treatments have led to resolution without the need for invasive procedures.
Additionally, maintaining proper eyelid hygiene is crucial, which includes avoiding the use of potentially contaminated makeup or contact lenses, as these can introduce bacteria and cause further irritation. It is also advisable to avoid eye rubbing, use clean pillowcases, and minimize exposure to harsh chemicals near the eyes.
These recommendations are supported by clinical evidence suggesting that such precautions, along with the aforementioned treatments, can lead to improved outcomes for individuals with chalazions.
Why Am I Prone to Chalazions?
Individuals prone to chalazions often have compromised Meibomian gland function, which can be effectively addressed through various treatment modalities. Scientific evidence indicates that treatments such as warm compresses and lid hygiene (PMC7353760), intralesional corticosteroid injections (BMC Ophthalmol), and surgical interventions (Frontiers in Medicine) can significantly benefit those suffering from chalazions.
Furthermore, studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation may improve Meibomian gland function and reduce the recurrence of chalazions (MDPI). Additionally, case studies highlight the effectiveness of microwave-based heat treatment (BMJ Open Ophthalmology) and topical azithromycin therapy (Tandfonline) in managing chalazion symptoms.
For children, a combination of massage, topical antibiotics, and steroid injections has proven beneficial (Researchgate). Research also supports the use of thermal cautery post-surgery to minimize recurrence (Optometry and Vision Science).
It is crucial for individuals with frequent chalazions to seek appropriate treatment options to mitigate the propensity for chalazion formation and promote ocular health.
What Supplements Prevent Chalazion?
Despite some skepticism regarding the role of supplements in preventing chalazions, scientific evidence underscores the potential benefits of certain nutrients.
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly from sources like flaxseed oil, have been highlighted for their anti-inflammatory effects, which could be advantageous in minimizing the risk of chalazion development.
Zinc is noted for its wound healing capabilities and may support ocular surface health.
Additionally, Vitamin D, Turmeric (curcumin), and Selenium are recognized for their immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties, potentially reducing chalazion incidence when coupled with standard practices such as regular eyelid hygiene, warm compresses, and eyelid massages.
The consumption of antioxidants and certain herbal supplements may further support these preventive measures, although direct scientific studies specifically linking these supplements to chalazion prevention are limited and warrant further research.
Conclusion
In contemporary ophthalmic practice, the scientific approach to eyelid hygiene is a foundational measure in preventing chalazions. Systematic eyelid cleaning and the application of warm compresses have been validated as effective non-invasive strategies for managing chalazion symptoms. These practices are supported by evidence suggesting a decrease in recurrence rates and overall incidence of chalazions.
Clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of conservative treatments with a noted improvement in patient outcomes. For instance, a study published in the British Journal of Ophthalmology highlighted a significant resolution rate of chalazions in children following the application of warm compresses and lid massage. Another case study within the peer-reviewed journal BMC Ophthalmology reinforced the benefits of lid hygiene and warm compresses, indicating a substantial number of chalazions resolved without the need for surgical intervention.
Furthermore, research in the journal Frontiers in Medicine has provided insights into the advantages of minimally invasive procedures for persistent chalazions, such as intralesional steroid injections, which offer a high success rate with minimal complications. When conservative methods are insufficient, surgical treatments have been shown to be highly effective, with a study in the journal Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery reporting successful outcomes in chalazion excision procedures.
In cases where prompt resolution is sought, evidence from the British Journal of Ophthalmology and the American Academy of Ophthalmology supports the integration of incision and curettage, revealing rapid recovery and low recurrence rates. The application of thermal cautery post-surgery has also been identified as a beneficial adjunct treatment to reduce inflammation and prevent recurrence, as noted in the journal Optometry and Vision Science.
In light of these findings, it is clear that maintaining rigorous eyelid hygiene routines, complemented by evidence-based clinical interventions, provides a robust defense against chalazions. Early recognition of symptoms and consultation with an ophthalmologist remain critical to ensure optimal treatment outcomes. Thus, the pursuit of ocular health through scientifically backed chalazion treatments stands as a testament to modern medical practice.