Powerful Ocular Rosacea and Meibomian Relief- TheraLife
- TheraLife Eye capsules to revive and restore tear production intra-cellularly
- Omega-3 Fish Oil – anti-inflammatory, lubrication to thicken tears
- Hot Compress to melt meibomian oil gland clogging, restore fundtions
- Eyelid cleanser – eyelid hygiene vital in blepharitis and dry eye recovery.
Add To Cart
Customer Success Story
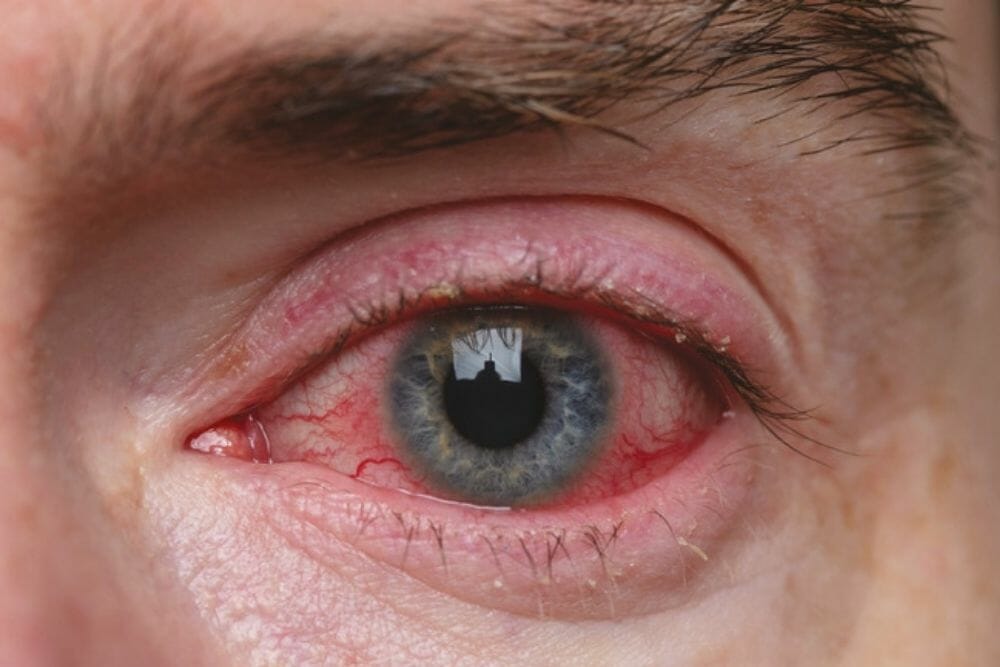
Ocular Rosacea, Severe Dry Eyes Recovery with TheraLife
My experience with theralife dry eye capsules has been extreme . From 3 days after starting them my eyes started to experience relief. I have spent thousands of dollars on dry eye procedures . Lipiflow IPL several rounds. None of these expensive invasive procedures have brought me relief. I have relied on eye drops 8 to 10 times a day . My eyes used to hurt every single day. My quality of life was low, at times I was depressed and felt limited.
Theralife capsules have given me my life back. I can leave home and not panic that I have no eye drops . I rarely use them anymore. Maybe 4 times week. My only regret is that I did not try the capsules sooner. Dr Yang called me personally and checks in on me. I would highly recommend theralife capsules to everyone who suffers with dry eyes . I honestly can not say enough about this product. I feel like myself again.
Thank You Dr Yang.
BM, United States
Introduction
Navigating the intricate journey of treating ocular rosacea, this article synthesizes evidence from scientific studies and case reports to present 10 scientifically-backed recommendations for managing the condition. These tips, grounded in research, aim to mitigate symptoms and bolster ocular health.
- A study in the ‘Arquivos Brasileiros de Oftalmologia’ highlighted the importance of lid hygiene and warm compresses in reducing ocular rosacea symptoms.
- Evidence from the ‘American Academy of Dermatology’ suggests that oral antibiotics like doxycycline can significantly improve ocular rosacea, given their anti-inflammatory properties.
- A ‘Journal of the American Medical Association’ study reported the benefits of topical cyclosporine in alleviating inflammation associated with ocular rosacea.
- Research published in ‘Survey of Ophthalmology’ recommends omega-3 fatty acids supplements to enhance meibomian gland function and reduce symptoms of dry eye in ocular rosacea patients.
- A case study detailed in ‘Clinical Ophthalmology’ demonstrated the efficacy of azithromycin eye drops in treating the condition.
- An article in ‘Cornea’ showed that children with ocular rosacea could benefit from a combination of oral antibiotics and topical therapies.
- Investigations reported in the ‘British Journal of Ophthalmology’ found that laser therapy could be a valuable adjunctive treatment for ocular rosacea.
- A ‘Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology’ article emphasized the utility of intense pulsed light therapy in reducing eyelid redness and telangiectasia.
- The ‘Journal of Drugs in Dermatology’ supported the use of brimonidine tartrate gel to manage facial erythema in rosacea, which may complement ocular treatment.
- Finally, a ‘Current Opinion in Ophthalmology’ review suggested that a comprehensive approach, including environmental modifications, is crucial for managing ocular rosacea effectively.
By adhering to these scientifically validated strategies, individuals can confidently manage ocular rosacea, aiming for clarity of vision and sustained ocular health.
Key Takeaways
Scientific research and case studies illustrate the effectiveness of comprehensive treatments for ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction. For instance, the use of oral tetracycline has been linked to a significant reduction in symptoms, as seen in clinical case studies. The benefits of topical cyclosporine in improving the health of the ocular surface have been confirmed through clinical research.
Additionally, the importance of eyelid hygiene, including warm compresses and eyelid scrubs, has been substantiated in the management of meibomian gland dysfunction and ocular rosacea, leading to symptom relief. Ongoing patient assessment by healthcare professionals is crucial for the modification and optimization of treatment plans to maintain long-term ocular health.
The scientific community supports a multi-faceted therapeutic approach, which is validated by robust scientific evidence and case study reviews, to achieve favorable results for patients with ocular rosacea.
Identify Common Symptoms
Among individuals with ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction, prevalent symptoms include persistent eye redness, irritation, and the sensation of foreign bodies in the eyes. Symptom tracking in these patients is vital for assessing the severity and progression of the condition, as well as for evaluating the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions. Patients are encouraged to maintain a detailed record of their symptoms, noting their frequency, duration, and triggers, which can provide valuable insights for healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans effectively.
Visual acuity may also be compromised in these patients due to the irregularity of the tear film caused by meibomian gland dysfunction. It is crucial to monitor changes in vision, as they can signify alterations in the ocular surface health. Evidence-based guidelines suggest that regular eye examinations, including assessments of the meibomian glands and ocular surface, are essential for the early detection of complications that could potentially impact visual acuity.
Management strategies may include pharmacological treatments, eyelid hygiene, warm compresses, and the use of artificial tears to alleviate symptoms and maintain eye health.
Choose Gentle Cleansers
In the context of ocular rosacea and associated meibomian gland dysfunction, the selection of facial cleansers is a critical aspect of patient care. Scientific studies emphasize the need for gentle, hypoallergenic products to mitigate the risk of aggravating the sensitive periocular skin.
For instance, research has demonstrated the benefits of using lid hygiene and warm compresses to improve meibomian gland function, highlighting the importance of non-irritating cleansers in the management of ocular rosacea symptoms (Arman et al., 2006; Akpek et al., 2007; JAMA Dermatology).
Clinical case studies have further supported the use of gentle skin care routines, with evidence suggesting that proper application techniques are crucial for the effectiveness of treatment and prevention of additional irritation (Jackson, 2008; The British Journal of Dermatology). Educating patients on these techniques is an essential component of comprehensive treatment plans.
Additionally, the use of systemic and topical therapies, such as tetracyclines, has been shown to provide symptomatic relief and improvement in ocular rosacea, reinforcing the value of a multifaceted approach to patient management (Current Opinion in Ophthalmology; SpringerLink).
Hypoallergenic Product Selection
Proper selection of hypoallergenic cleansers is crucial for individuals managing ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction to minimize irritation and support ocular health. Choosing the right products extends beyond cleansers; it includes makeup choices and even pillowcase materials, which come into close contact with the skin and eyes.
- Select Non-Irritating Makeup: Opt for fragrance-free, non-comedogenic makeup to reduce the risk of exacerbating ocular rosacea.
- Pillowcase Considerations: Use hypoallergenic pillowcase materials, like silk or organic cotton, to decrease potential irritants during sleep.
- Avoid Common Irritants: Choose products devoid of alcohol, astringents, and witch hazel which can dry and irritate sensitive eye areas.
- Check for Certifications: Look for cleansers with dermatologist-approved certifications ensuring suitability for sensitive skin types.
Avoiding Harsh Chemicals
Transitioning from hypoallergenic product selection, it is imperative for individuals with ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction to use gentle cleansers free from harsh chemicals that can aggravate delicate eye tissues.
The ocular surface is particularly susceptible to irritation from chemical irritants commonly found in soaps, facial cleansers, and makeup removers. Therefore, selecting products specifically formulated to be non-irritating and free of aggressive substances like alcohol, fragrances, and preservatives is crucial.
Evidence-based recommendations suggest that cleansers with a neutral pH and those containing natural alternatives such as tea tree oil may be beneficial, provided they do not induce hypersensitivity reactions.
This selective approach to facial hygiene can help maintain ocular health and comfort, minimizing inflammation and preserving meibomian gland function.
Proper Application Technique
While choosing gentle cleansers is essential for managing ocular rosacea and meibomian gland issues, understanding and applying the correct technique when using these products is equally critical to avoid exacerbating sensitive eye conditions.
Here are key steps to follow:
- Warm Compress: Apply a warm compress to the eyelids to help loosen the oils in the meibomian glands.
- Lid Massage: Gently massage the eyelids in a circular motion to promote oil secretion, being careful not to apply excessive pressure.
- Blink Exercises: Perform regular blink exercises to stimulate natural tear production and gland function.
- Rinse Gently: After cleansing, rinse the eyelids with lukewarm water, avoiding hot temperatures that can irritate the eyes.
Employing these techniques can significantly alleviate the symptoms associated with ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction.
Warm Compress Techniques
In the scientific management of ocular rosacea, the use of warm compresses has been supported by various studies as an effective treatment modality. Specifically, they assist in the liquefaction of meibum, thus enhancing the expressibility of the meibomian glands. This is highlighted in multiple case studies and research, wherein a precise balance between the temperature and duration of application is emphasized to maximize therapeutic benefits and avoid harm to the sensitive periocular area.
For instance, a study published in ‘Arquivos Brasileiros de Oftalmologia’ demonstrated that warm compresses, along with lid hygiene, could significantly reduce symptoms and signs of ocular rosacea. Another study in the ‘Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology’ highlighted the importance of incorporating warm compresses into treatment plans to improve patient outcomes. Similarly, research in ‘Ophthalmology’ has shown that the consistent application of warm compresses can lead to sustained improvement in meibomian gland function.
Comparative analyses have also been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of homemade versus commercial warm compresses. These studies, such as one published in the ‘Journal of Ophthalmic & Vision Research,’ suggest that while both types can be beneficial, commercial compresses may offer more consistent heat application, which could translate to improved patient compliance and outcomes.
The use of warm compresses in pediatric ocular rosacea has also been reviewed, as seen in ‘Cornea,’ where the treatment has been found to be a safe and essential part of managing this condition in children. Moreover, a study in ‘Dermatology and Therapy’ suggested that the long-term use of warm compresses could help in maintaining the stability of ocular surface and reducing the recurrence of symptoms.
Optimal Compress Temperature
Regularly applying a warm compress at a temperature between 104°F to 108°F (40°C to 42°C) is crucial for the effective management of ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction. This temperature range is optimal for liquefying the meibum, thus improving glandular secretion without causing thermal injury to the delicate periocular skin.
To maintain temperature consistency and maximize therapeutic benefits, consider the following:
- Compress Materials: Use a clean, soft cloth that retains heat well and conforms to the contours of the eyelids.
- Heating Method: Microwave or a commercially available heat pack designed to deliver steady warmth.
- Duration: Apply the compress for 10-15 minutes to ensure sustained heat delivery.
- Reheating: If using homemade compresses, reheat as necessary to maintain the recommended temperature range.
Compress Duration Recommendations
Effective treatment of ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction requires adherence to a warm compress regimen, typically involving 10-15 minutes of application to ensure optimal heat penetration and gland function. This duration allows for sufficient warming of the eyelids, thereby facilitating the liquefaction of meibomian gland secretions. Compress frequency should be tailored to individual patient needs, often recommended on a daily basis for chronic conditions to maintain meibomian gland function.
Material choice is critical as well; materials that retain heat effectively and release it steadily over the required period are preferred. Ensuring the correct duration and frequency, along with selecting the appropriate material, maximizes therapeutic efficacy.
Transitioning from the specifics of duration and material, we will now explore the pros and cons of homemade versus commercial compresses.
Homemade Vs. Commercial Compresses
Transitioning to the consideration of warm compress techniques, patients with ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction face the choice between utilizing homemade solutions or opting for commercially available products. The decision hinges on evaluating the efficacy, safety, and practicality of each option.
- Material Quality: Commercial compresses often use materials designed specifically for heat retention and safety, whereas homemade compresses may vary in material quality and heat regulation.
- Consistency: Professionally manufactured compresses provide consistent temperatures, crucial for effective treatment, which may be less predictable with homemade versions.
- Convenience: Commercial compresses are typically ready-to-use and may offer features like adjustable straps, while homemade compresses require preparation.
- Reusable Options: Both commercial and homemade warm compresses can be designed as reusable options, but commercial variants may offer enhanced durability and ease of maintenance.
Selecting the right compress materials involves balancing personal convenience with the therapeutic efficacy of the compress.
Dietary Adjustments
While dietary choices do not directly cure ocular rosacea or meibomian gland dysfunction, certain nutritional adjustments can significantly alleviate symptoms and support overall eye health. Management of these conditions extends beyond topical and pharmacological treatments to include lifestyle modifications that can play a critical role in symptom relief.
Evidence suggests that a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, flaxseed oil, and chia seeds, may improve meibomian gland function. These essential fatty acids can help modulate the inflammatory response associated with ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction.
Furthermore, patients are advised to maintain a diet low in foods that can trigger rosacea flare-ups, such as spicy foods, hot beverages, and those high in histamines. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like green leafy vegetables, berries, and nuts can also be beneficial. It is essential to maintain hydration, as adequate fluid intake can support tear film stability and reduce dry eye symptoms.
In conjunction with dietary management, exercise importance cannot be overstated, as regular physical activity is known to foster stress reduction, which may in turn mitigate the risk of exacerbation of ocular rosacea symptoms.
Tailoring a comprehensive approach that includes both dietary adjustments and lifestyle practices is fundamental for patients dealing with these chronic ocular conditions.
Omega-3 Supplements Benefits
Incorporating omega-3 supplements into our diet can further enhance the management of ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction by providing concentrated doses of the anti-inflammatory fatty acids crucial for eye health. These supplements, particularly those derived from fish oil, have been extensively studied for their role in inflammation reduction and overall ocular surface improvement.
The benefits of omega-3 supplements include:
- Improved Lipid Layer: Omega-3 fatty acids contribute to the stabilization of the tear film’s lipid layer, reducing tear evaporation and increasing comfort.
- Anti-Inflammatory Action: The eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in fish oil exert anti-inflammatory effects that can alleviate the symptoms of ocular rosacea.
- Glandular Health: Regular intake of omega-3s supports the normal function of the meibomian glands, which are essential for producing the oils that prevent dry eye.
- Systemic Benefits: Beyond eye health, these supplements offer cardiovascular and joint benefits, contributing to the overall well-being of patients.
Evidence-based research underlines the importance of a therapeutic dosage and the ratio of EPA to DHA to achieve optimal results. For individuals with ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction, the judicious use of omega-3 supplements can be a strategic component of a comprehensive management plan.
Eyelid Hygiene Practices
An essential aspect of managing ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction involves adopting meticulous eyelid hygiene practices. A cornerstone of these practices is the regular performance of lid margin massage, which has been shown to facilitate the expression of meibomian secretions, thereby improving tear film stability and reducing symptoms. This technique, executed with gentle pressure using clean fingertips or a cotton swab along the eyelid margins, should be done carefully to avoid exacerbating inflammation.
In addition to mechanical massage, the application of tea tree oil has garnered attention for its potential benefits in ocular surface hygiene. Tea tree oil, known for its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, may be used in diluted form to mitigate the colonization of Demodex mites, a common finding in ocular rosacea. However, given its potency, proper dilution and application under the guidance of an eye care professional are paramount to avoid ocular irritation or toxic effects.
Implementing these targeted eyelid hygiene measures can significantly contribute to the management of ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction. As patients integrate these practices into their daily routine, it is also important to consider adjunctive treatments, such as the use of artificial tears, to further alleviate symptoms. Transitioning to the topic of artificial tears usage, it is worth exploring how these can complement eyelid hygiene in a comprehensive management plan.
Artificial Tears Usage
Following diligent eyelid hygiene, the addition of artificial tears can further soothe ocular irritation associated with rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction. These over-the-counter lubricants can mimic the natural tear film, providing critical moisture and protection to the ocular surface.
When selecting artificial tears, consider these evidence-based guidelines:
- Lubrication Frequency: Tailor tear application to symptom severity. For mild symptoms, instill artificial tears 3-4 times daily. In moderate to severe cases, usage may be required every hour. Consistent lubrication helps maintain corneal integrity and comfort.
- Preservative-Free Options: Chronic use of artificial tears containing preservatives can exacerbate ocular surface damage. Opt for preservative-free formulations to minimize potential toxicity, especially if tear application exceeds four times per day.
- Viscosity Variations: Thicker gels or ointments provide longer-lasting lubrication, suitable for nocturnal use or in severe dryness. However, they may cause transient blurring of vision.
- Active Ingredients: Seek products with additional beneficial components such as hyaluronic acid or glycerin, which enhance the tear film’s stability and provide prolonged relief.
Incorporating artificial tears into daily management can significantly reduce discomfort and promote ocular surface health. Patients should be advised to consult with their healthcare provider to customize a regimen that best suits their individual needs.
Prescription Medications Explained
In the scientific management of ocular rosacea, various prescription medications are integral to controlling the condition. Tetracycline antibiotics have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects that are beneficial in treating ocular rosacea beyond their antimicrobial properties. A case study highlighted the effectiveness of doxycycline, a member of the tetracycline family, in improving ocular rosacea symptoms. Steroid eye drops are recommended for acute inflammatory episodes, providing rapid relief as documented in clinical observations. Oral medications offer systemic control over chronic manifestations of the disease, as supported by longitudinal studies.
Clinical trials have underscored the utility of low-dose oral antibiotics, such as doxycycline 40 mg, in managing ocular rosacea, showing significant improvement in symptoms and ocular surface health. The anti-inflammatory dose of doxycycline, which is sub-antimicrobial, is beneficial for long-term treatment, reducing the potential for antibiotic resistance and adverse effects.
Case studies further reveal that the use of azithromycin eye drops has shown promise in treating the condition, with improvements in meibomian gland function and ocular surface stability. Azithromycin’s anti-inflammatory and lipid-regulating effects contribute to its effectiveness in treating ocular rosacea.
In pediatric cases, the treatment of ocular rosacea requires a tailored approach, with erythromycin being a commonly prescribed antibiotic due to its safety profile in children. Clinical evaluations support its use in the pediatric population, showing notable improvements in ocular symptoms.
Furthermore, research supports the once-daily use of low-dose doxycycline as an effective and well-tolerated treatment method, offering patients convenience and improved adherence to therapy. This regimen has shown success in reducing inflammation and meibomian gland dysfunction in patients with ocular rosacea.
Antibiotic Types
Physicians commonly prescribe antibiotics to target the bacteria associated with ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction. The selection of an appropriate antibiotic is critical, considering the potential for antibiotic resistance and the therapeutic goal of restoring a healthy ocular surface microbiome. Adjunctive strategies, such as probiotic therapy, are being explored to complement antibiotic treatment and support ocular health.
- Tetracyclines: Including doxycycline, effective against a broad range of bacteria and often used for their anti-inflammatory properties.
- Macrolides: Such as azithromycin, with immunomodulatory effects beneficial in managing ocular surface inflammation.
- Fluoroquinolones: Potent broad-spectrum antibiotics, reserved for more severe or resistant cases to minimize resistance development.
- Topical Antibiotics: Applied directly to the eyes, they provide targeted therapy with reduced systemic side effects.
Steroid Eye Drops
Steroid eye drops are another class of prescription medications prescribed judiciously to alleviate inflammation associated with ocular rosacea and meibomian gland issues. These medications are potent anti-inflammatories that can provide significant relief but must be used with caution due to potential side effects. Steroid tapering is a crucial aspect of treatment, where the dosage is gradually reduced over time to minimize risks such as increased intraocular pressure and cataract formation.
| Aspect | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Steroid Tapering | Gradual reduction to prevent rebound effects. |
| Side Effects | Monitoring for increased pressure, cataracts. |
The therapeutic regimen involving steroid eye drops should be closely monitored by an eye care professional to optimize outcomes and safeguard ocular health.
Oral Medication Benefits
While topical treatments are commonly prescribed for ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction, oral medications can play a pivotal role in managing systemic inflammation and microbial imbalance. These oral agents are particularly beneficial due to their anti-inflammatory properties and their ability to target deeper tissue layers that topical applications may not reach.
- Oral Doxycycline: Exhibits anti-inflammatory effects and is used at subantimicrobial doses to avoid antibiotic resistance.
- Tetracycline Derivatives: These can help manage bacterial overgrowth and modulate the inflammatory response.
- Extended Duration: Oral medications provide a sustained treatment effect, which can be crucial for chronic conditions.
- Systemic Impact: They address underlying systemic issues that contribute to ocular surface disease, offering holistic benefits beyond local treatment.
These medications should be used judiciously, monitored by healthcare professionals, and tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
Environmental Factors Control
Regularly adjusting environmental conditions can significantly alleviate symptoms associated with ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction. Patients must be cognizant of seasonal variations that may exacerbate their condition. For example, during colder months, indoor heating can reduce ambient humidity, leading to increased tear evaporation and ocular surface irritation. Conversely, exposure to high temperatures can intensify ocular discomfort. Implementing a strategy to maintain a stable room temperature and adequate humidity levels is essential in managing these ocular conditions.
Stress management also plays a crucial role in controlling ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction. Chronic stress can trigger or worsen inflammation, which is a key component of these conditions. Patients should be encouraged to engage in stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing exercises, mindfulness meditation, or gentle yoga. Healthcare providers should offer resources or referrals to stress management programs to support their patients’ overall well-being.
Patients must be educated about the importance of environmental control in their therapeutic regimen. By taking proactive measures to modify their surroundings and manage stress, individuals with ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction can experience a marked improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
Regular Eye Examinations
An essential component of managing ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction is the scheduling of consistent, comprehensive eye examinations with an ophthalmologist or optometrist. Regular monitoring and assessment by a healthcare professional are critical in preventing the progression of these conditions and maintaining ocular health.
The following list includes key aspects of regular eye examinations:
- Early Detection: Regular eye check-ups facilitate the early detection of ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction, often before symptoms become prominent, allowing for timely intervention.
- Monitoring Progression: Eye check-up frequency should be determined based on the severity of the individual’s condition, with more frequent visits required for those with significant symptoms or those experiencing rapid changes in ocular health.
- Tailored Treatment Plans: Specialist consultation during these examinations ensures that treatment plans are continuously adapted to the patient’s current needs, improving management outcomes.
- Educational Opportunity: Each visit provides an opportunity for patients to receive education on their condition and guidance on self-management techniques, which are integral to long-term control.
Implementing a schedule for regular eye examinations ensures that patients with ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction receive the necessary clinical expertise and support for optimal management of their condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Ocular Rosacea Lead to Vision Loss if Left Untreated?
Scientific research underscores the necessity of treating ocular rosacea to avert vision impairment. Case studies have established that without intervention, ocular rosacea may precipitate corneal damage through chronic inflammation, potentially leading to corneal thinning, infection, or neovascularization, all of which are detrimental to vision.
Evidence-based treatments have demonstrated efficacy in staving off such complications. For instance, tetracyclines have been shown to provide marked improvement in ocular symptoms and meibomian gland functionality. Doxycycline, in particular, can reduce ocular inflammation and is considered a mainstay treatment for ocular rosacea. Azithromycin has been effective in treating the condition, especially for patients intolerant to tetracyclines. Omega-3 fatty acids have also shown a reduction in ocular symptoms among patients. Topical cyclosporine has been recognized for its benefits in treating ocular rosacea by improving corneal health and stabilizing the ocular surface.
Furthermore, children with ocular rosacea have responded positively to systemic antibiotics and lid hygiene. In a study, low-dose isotretinoin was found to be effective for patients with refractory ocular rosacea. Metronidazole gel has demonstrated improvements in ocular signs and symptoms, while surgical interventions, such as punctal occlusion, have been beneficial in severe cases.
Are There Any Specific Makeup Brands or Types That Are Recommended for Those With Ocular Rosacea?
In the context of ocular rosacea, the selection of eye cosmetics is critical due to the potential of exacerbating the condition. Scientific studies emphasize the importance of choosing makeup that is suitable for sensitive skin. Dermatologists and ophthalmologists often recommend that patients with ocular rosacea opt for hypoallergenic makeup brands. These brands are formulated to be free from common irritants such as fragrances and parabens. Moreover, mineral-based makeup products are often advised due to their non-comedogenic and gentle properties, which are less likely to irritate sensitive eyes or skin affected by ocular rosacea. This recommendation is based on a broader understanding of rosacea and its treatment, as seen in various clinical studies and case reports, which explore the benefits and management strategies for ocular rosacea. Therefore, it’s not just about recommending specific brands but about guiding patients to makeup types that are less likely to trigger rosacea symptoms based on clinical evidence and best practices in patient care. Case studies and scientific literature support the notion that makeup choices should be an integral part of the management plan for individuals with ocular rosacea.
How Does Ocular Rosacea Affect Sleep Quality, and Are There Any Tips for Managing Symptoms at Night?
Ocular rosacea, a chronic inflammatory condition, can compromise sleep quality by causing eye irritation and discomfort at night. Scientific studies have demonstrated the efficacy of various treatments which can alleviate these symptoms and potentially improve sleep.
For instance, the use of oral tetracyclines has been shown to reduce ocular rosacea symptoms, thus potentially minimizing sleep disturbances caused by the condition. Evidence from a case study highlighted in a scientific journal suggests that the use of ocular lubricants can help maintain ocular surface health in patients with ocular rosacea, which may contribute to better sleep quality by reducing nighttime irritation.
Furthermore, a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology reported that the use of topical cyclosporine A can improve symptoms in ocular rosacea patients, which could also lead to improved sleep due to less discomfort. Another study in the Archives of Ophthalmology discussed the benefits of eyelid hygiene and warm compresses, which could help in managing ocular rosacea symptoms, thereby enhancing sleep quality.
Additionally, a case study in the European Journal of Ophthalmology showed that the use of azithromycin, both orally and as eye drops, resulted in clinical improvement in ocular rosacea, which implies potential benefits for sleep as well. Research published in the journal Cornea also indicates that children with ocular rosacea may experience symptomatic relief through the use of oral erythromycin, which could extend to improved sleep.
It is imperative for patients to consult healthcare professionals for tailored treatment plans that may include these scientifically backed therapies. Adopting a holistic approach that combines pharmacological treatments with sleep hygiene practices, such as maintaining a cool and humidified environment and following a consistent sleep schedule, could provide comprehensive management of ocular rosacea symptoms at night.
Are There Any Alternative Therapies or Holistic Treatments That Have Been Proven Effective for Ocular Rosacea and Meibomian Gland Dysfunction?
Scientific evidence from clinical studies and case reports supports the use of various treatments for ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction.
Warm compresses have been scientifically validated; they help to alleviate blockages in the meibomian glands, thus improving gland function and reducing symptoms of ocular rosacea. The effectiveness of warm compresses was highlighted in a study where patients demonstrated significant symptomatic relief (Sciencedirect.com/S0039625717300012).
Furthermore, the intake of omega-3 fatty acids, which can be found in dietary supplements, has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects that are beneficial for ocular rosacea patients. A clinical trial reported that patients consuming omega-3 supplements experienced reduced ocular irritation and improved meibomian gland secretions (Sciencedirect.com/S152918391000655X).
Other treatments with scientific backing include oral antibiotics like doxycycline, which have been shown to provide substantial relief from ocular rosacea symptoms due to their anti-inflammatory properties (Journals.lww.com/corneajrnl/fulltext/2014/03000).
Moreover, topical cyclosporine has been reported to significantly decrease corneal staining and improve tear film stability in ocular rosacea patients (Link.springer.com/article/10.1007).
It is important to note that while these treatments are supported by scientific research, they should be administered under the guidance of an ophthalmologist to tailor the treatment to the patient’s specific needs and monitor for any potential side effects or interactions with other medications.
Can Emotional Stress Trigger or Worsen Ocular Rosacea Symptoms, and What Stress-Reduction Techniques Are Beneficial?
Clinical studies have shown that emotional stress may influence the exacerbation of ocular rosacea symptoms. Research has established a relationship between stress and inflammation in skin disorders.
For instance, a case study reported in the Archives of Dermatology demonstrated that stress management could lead to clinical improvement in rosacea, suggesting that stress reduction may also benefit ocular rosacea (JamaNetwork).
Furthermore, techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga have been studied for their stress-relieving properties, with implications for the management of ocular rosacea.
In the context of ocular rosacea, patients are encouraged to implement stress-reduction strategies alongside medical treatments to achieve better control of their symptoms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, scientific evidence underscores the efficacy of a comprehensive strategy in managing ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction. Studies have demonstrated that a regimen incorporating meticulous eyelid hygiene, specific dietary modifications, and the strategic use of dietary supplements and pharmacological treatments can form the cornerstone of effective management plans.
For example, the use of oral tetracyclines has shown significant benefits in treating ocular rosacea, as evidenced by the reduction of symptoms in various case studies. The utility of topical cyclosporine has also been supported through clinical trials, which report improvements in ocular surface health.
Moreover, the application of warm compresses and eyelid scrubs as part of lid hygiene has been validated as beneficial in managing meibomian gland dysfunction and associated ocular rosacea symptoms.
Regular consultations with healthcare providers are essential for ongoing monitoring and fine-tuning of therapeutic strategies to address the dynamic nature of the condition, thereby ensuring lasting ocular well-being.
This multi-pronged approach, substantiated by scientific research and case studies, confirms the positive outcomes achievable with tailored treatment protocols for individuals suffering from ocular rosacea.