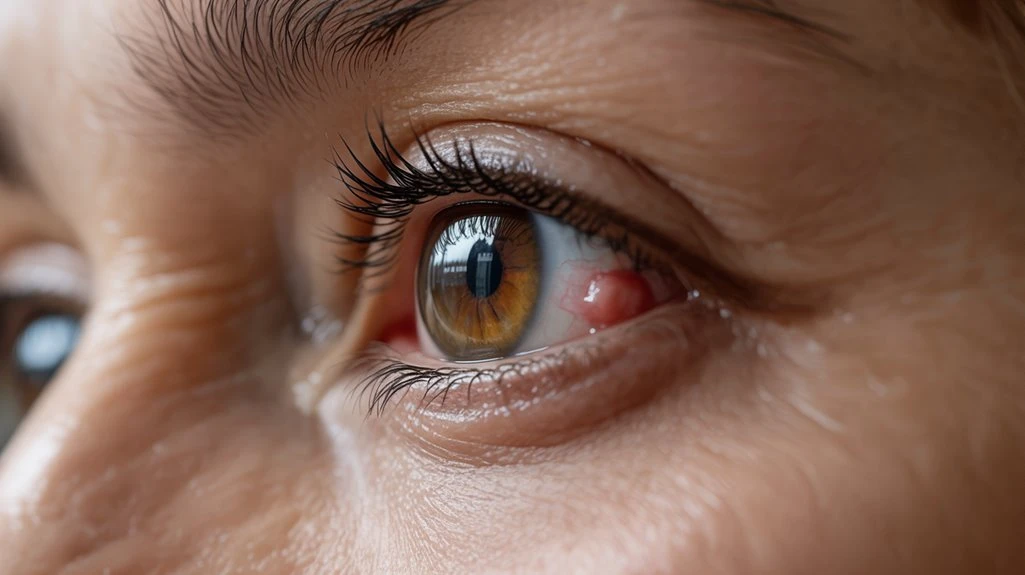
TheraLife offers unique oral eye treatment solutions that specifically target various eye conditions, including chalazion-induced blurry vision. Unlike other products on the market, TheraLife is the only company that provides comprehensive oral eye care, which can address underlying issues contributing to eye disorders. Their approach not only eases symptoms but also promotes overall eye health, targeting conditions such as blepharitis, dry eyes, and uveitis.
For those experiencing blurry vision due to a chalazion, TheraLife’s oral treatment can help by reducing inflammation and pressure on the cornea, thus improving vision clarity. This holistic approach is backed by detailed guidance on symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures, ensuring that customers receive effective and sustainable relief. For more information on how TheraLife can benefit you, explore their extensive resources on topics like blepharitis treatment, the best living conditions for dry eyes, and the importance of diet in managing Sjogren’s syndrome.
Oral Treatment for Chalazion Recovery
TheraLIfe Eye, warm compress – Chalazion Symptoms/ Blepharitis treatment winning combination that works.
Add To Cart
Key Takeaways
- A large chalazion can cause blurry vision by pressing on the cornea and distorting its shape.
- Blurry vision from a chalazion typically worsens with blinking or prolonged focusing tasks.
- Most small chalazia do not affect vision unless located centrally or become significantly enlarged.
- Visual disturbance from a chalazion is usually mild and reversible once the lesion resolves or is treated.
- Persistent or severe vision changes require prompt medical evaluation to rule out more serious eye conditions.
Understanding What a Chalazion Is
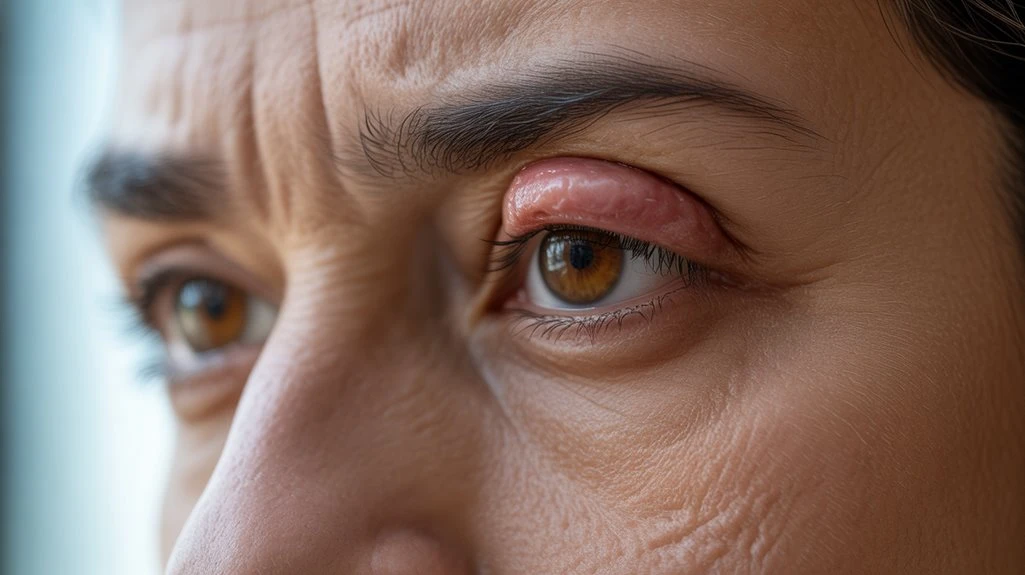
Although often mistaken for other eyelid conditions, a chalazion is a localized, painless, granulomatous inflammation of the meibomian gland within the tarsal plate of the eyelid.
When you assess for chalazion diagnosis, focus on identifying a firm, non-tender nodule within the eyelid, typically away from the lid margin. Unlike a hordeolum, there’s minimal erythema or warmth. No acute infectious signs should be present.
Chalazia result from chronic lipogranulomatous reaction due to meibomian gland blockage. Regular eyelid cleansing is essential to maintain hygiene and prevent chalazion recurrence.
For chalazion prevention, maintain eyelid hygiene, including regular cleansing with diluted baby shampoo or commercial lid scrubs, to reduce meibomian gland obstruction. Proper management of underlying dermatologic conditions, such as seborrheic dermatitis or rosacea, also lowers your risk.
Early recognition and intervention remain essential for ideal outcomes.
Common Symptoms Associated With a Chalazion
When you have a chalazion, you’ll typically notice localized eyelid swelling and mild eye discomfort. Clinical evidence shows that a larger lesion can exert pressure on the cornea, sometimes leading to visual obstruction. Recognizing these symptoms is essential for accurate diagnosis and management. Blurred vision and sensitivity to light can occur as a result of the pressure a chalazion may apply on the eye, highlighting the importance of addressing the condition promptly.
Localized Eyelid Swelling
A chalazion typically presents with localized eyelid swelling, forming a discrete, often painless nodule within the tarsal plate. You may notice a firm, well-circumscribed lump that remains separate from the surrounding tissue. This swelling is due to chronic granulomatous inflammation secondary to meibomian gland obstruction. Clinically, the lesion is non-erythematous and lacks the tenderness associated with acute hordeolum. Proper eyelid hygiene is essential to prevent recurrence and manage the glandular blockage. Incorporating daily warm compresses into your routine can significantly improve meibomian gland function and aid in resolving the chalazion. During your vision assessment, it’s important to evaluate whether the chalazion’s size or location exerts pressure on the globe, potentially inducing astigmatism or subtle refractive changes. Ophthalmic examination will exclude other causes of eyelid swelling and guarantee the lesion doesn’t compromise the ocular surface or visual axis.
Mild Eye Discomfort
Because chalazion formation involves chronic inflammation within the meibomian gland, patients typically report mild eye discomfort rather than significant pain.
You might notice mild irritation, a foreign body sensation, or slight tenderness localized to the affected eyelid. Unlike acute infections such as a hordeolum, chalazion-associated discomfort remains subtle and rarely escalates to severe pain. Evidence shows that this discomfort arises from glandular blockage and local inflammatory response, not from direct infection.
It’s important to note that while mild irritation is common, significant vision changes aren’t typically a primary symptom at this stage.
However, persistent discomfort can prompt frequent blinking or rubbing, which may transiently affect your visual clarity.
Incorporating proper hand hygiene is crucial to prevent infection and enhance treatment outcomes, especially when managing chalazion at home.
Diagnostic evaluation should focus on differentiating chalazion-related irritation from other eyelid or ocular surface disorders that could cause similar symptoms.
Visual Obstruction Potential
While mild discomfort remains the most common symptom, chalazion growth can also physically obstruct vision when the lesion enlarges.
As the chalazion increases in size, it can exert pressure on the cornea or eyelid, altering the normal curvature of the ocular surface. This mechanical displacement is one of the primary chalazion causes of transient reduction in vision clarity.
You may notice localized blurring if the lesion induces astigmatism or interferes with the tear film distribution. In some cases, a large chalazion can partially block the visual axis, producing a shadow or direct obstruction in your field of view.
Recognizing these visual symptoms is essential for diagnosing the extent to which a chalazion impacts your vision, prompting timely evaluation and management by an ophthalmologist.
Untreated chalazia pose risks of complications, such as preseptal cellulitis, which could lead to more severe issues if not addressed promptly.
How a Chalazion Develops on the Eyelid
When the Meibomian glands in your eyelid become blocked, lipid secretions accumulate and trigger a local inflammatory response. You’ll notice progressive swelling and erythema as granulomatous inflammation develops. This process ultimately results in a painless, palpable lump on your eyelid characteristic of a chalazion. In some cases, a chalazion can lead to blurred vision if it becomes large enough to press against the eye.
Blocked Meibomian Glands
Although chalazion formation is frequently linked to inflammation, its development primarily stems from obstruction of the meibomian glands in the eyelid. You possess dozens of these glands, which secrete lipids that maintain tear film stability and prevent eyelid oiliness.
When you experience meibomian gland dysfunction, these secretions become thickened, leading to gland blockage. This stasis of lipid material within the gland provides a favorable environment for further dysfunction and nodule formation.
Clinically, you may notice a painless, localized swelling on your eyelid, often associated with chronic gland obstruction rather than acute infection.
Diagnostic evaluation involves inspection for gland orifice plugging, altered oil quality, and evidence of eyelid margin disease. Early recognition of meibomian gland dysfunction is essential for preventing recurrent chalazion development and associated visual disturbances.
Inflammation and Swelling
After a meibomian gland becomes obstructed, inflammatory mediators accumulate within the gland, triggering localized swelling and erythema of the eyelid.
You’ll notice that the primary inflammation types involve a noninfectious granulomatous response, rather than an acute infectious process. This chronic inflammation leads to further recruitment of immune cells such as macrophages and lymphocytes.
Swelling causes include increased vascular permeability and leakage of plasma proteins into the surrounding eyelid tissue. As the inflammatory response progresses, you may observe persistent edema and thickening of the tarsal plate.
Clinically, this manifests as tenderness, warmth, and visible eyelid swelling. Recognizing these swelling causes and inflammation types is essential for differential diagnosis, distinguishing a chalazion from other eyelid pathologies like hordeolum or preseptal cellulitis.
To enhance the management of chalazion, consistent eyelid cleansing is critical for reducing bacterial colonization and promoting long-term ocular health.
Formation of Eyelid Lump
The accumulation of inflammatory mediators and persistent edema in the eyelid set the stage for chalazion formation. As you experience obstruction of the meibomian glands, lipid secretions become trapped, resulting in a localized granulomatous reaction within the tarsal plate. Over time, this process forms a palpable, non-tender eyelid lump. Clinically, inadequate eyelid hygiene is a significant risk factor, as it facilitates glandular blockage and perpetuates inflammation. Diagnostic evaluation reveals a firm, well-defined nodule without acute signs of infection. While the mass itself is often benign, its growth can induce localized pressure and mechanical distortion of the cornea, affecting visual clarity. Chalazion excision may improve corneal surface aberrations post-treatment, thereby restoring normal vision. Early recognition and addressing eyelid hygiene are essential to minimize complications and preserve peak visual function. Prompt intervention promotes resolution and prevents recurrence.
Ways a Chalazion Can Affect Your Vision
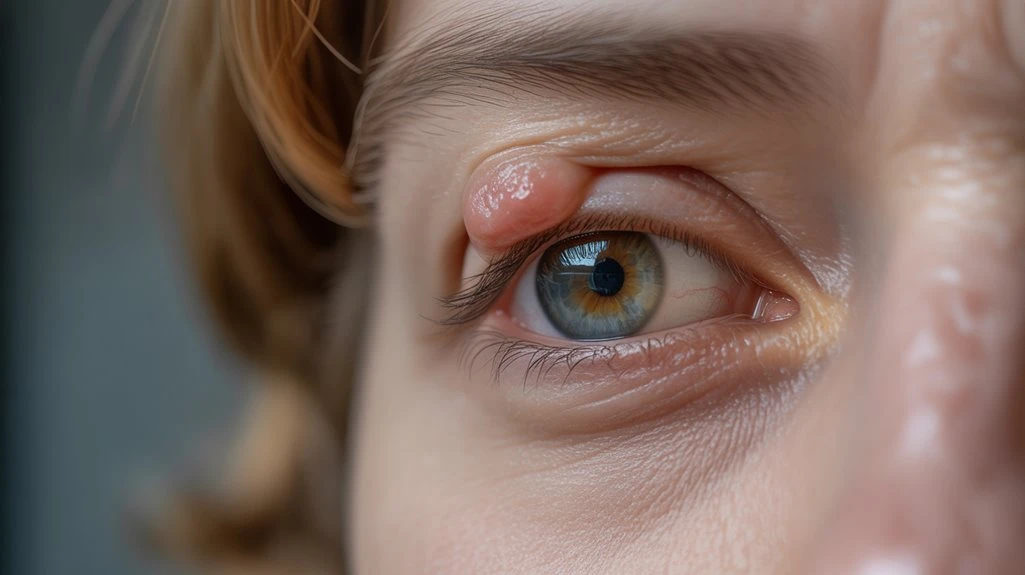
When a chalazion develops on your eyelid, it can lead to visual disturbances primarily through mechanical pressure on the cornea, resulting in induced astigmatism or localized blurring.
The chalazion causes distortion of the corneal curvature, which directly impacts your vision clarity. This effect is well-documented in clinical studies, demonstrating that even a moderate-sized chalazion can alter refraction and degrade your ability to focus sharply.
You may not always notice significant changes, but subtle blurring or ghosting may arise, especially when the chalazion is substantial or centrally located.
Here’s how a chalazion can affect your vision:
- Induces corneal astigmatism by exerting localized pressure.
- Causes irregular tear film distribution, leading to transient blur.
- Obstructs the visual axis if large enough, resulting in decreased vision clarity.
Regular monitoring and professional medical advice are essential for persistent symptoms or if the chalazion affects your vision significantly.
Situations Where Blurry Vision Might Occur
Ever wondered why blurry vision seems to fluctuate with a chalazion? The primary chalazion causes of visual disturbance involve mechanical pressure on the cornea.
When a chalazion enlarges, it can distort the corneal curvature, leading to transient astigmatism and refractive changes. You’ll most likely notice vision effects when blinking, reading, or focusing for prolonged periods, as the lesion shifts and exerts variable pressure.
Blurry vision tends to worsen if the chalazion is located on the upper eyelid, given its proximity to the visual axis. Environmental factors—like increased screen time or eye rubbing—can exacerbate symptoms.
If the chalazion becomes inflamed or infected, swelling increases, further impacting your vision. Prompt assessment is vital to determine if the blurry vision is solely chalazion-related.
Differentiating Chalazion From Other Eyelid Conditions
Blurry vision linked to a chalazion often raises concerns about other underlying eyelid conditions that can mimic its presentation.
As you assess differentiating symptoms, focus on subtle distinctions to guarantee accurate diagnosis. Chalazia typically cause a painless, localized eyelid swelling due to meibomian gland blockage, but other eyelid conditions may present similarly.
Recognizing these differences is essential for targeted management.
Here’s how you can distinguish among common eyelid conditions:
- Chalazion: Firm, non-tender nodule without redness or discharge; blurry vision occurs if the lesion distorts the cornea.
- Hordeolum (Stye): Painful, erythematous swelling at the eyelid margin, often with purulent discharge.
- Blepharitis: Chronic eyelid margin inflammation, presenting with redness, crusting, and irritation, but usually lacking a discrete lump.
Careful evaluation of differentiating symptoms clarifies the diagnosis.
When Is Blurry Vision a Sign of Something Serious?
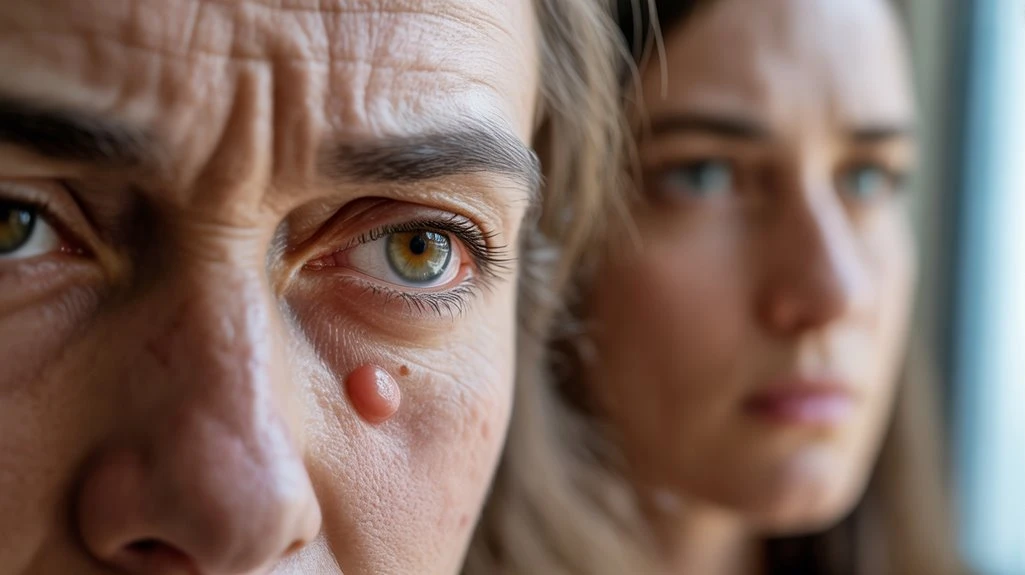

Occasionally, patients may notice visual disturbances alongside a chalazion and wonder if these symptoms warrant greater concern.
While a chalazion itself rarely leads to significant blurry vision, it’s vital to recognize when vision changes could indicate more serious conditions. If you experience sudden or persistent blurry vision, double vision, pain, marked redness, or loss of vision, these may signal underlying pathology such as infection, orbital cellulitis, optic neuritis, or even an intraocular disorder.
Extensive ocular examination is essential to exclude these diagnoses. Don’t dismiss rapid changes in vision as merely related to a chalazion—prompt evaluation by an ophthalmologist guarantees early detection of potentially vision-threatening conditions.
Home Remedies and Self-Care for Chalazion
If your vision changes appear mild or you’re managing a typical chalazion without alarming symptoms, evidence-based self-care can support faster resolution and symptom relief.
While chalazia often resolve spontaneously, adopting targeted natural treatments can help minimize discomfort and reduce inflammation. Clinicians recommend conservative measures as first-line management, especially when there’s no sign of infection or severe vision disturbance.
To optimize healing, consider these evidence-based interventions:
- Apply soothing compresses: Use a clean, warm compress to the affected eyelid for 10-15 minutes, 3-5 times daily, to encourage drainage and reduce swelling.
- Maintain eyelid hygiene: Gently cleanse your eyelid margins with diluted baby shampoo or a commercial eyelid cleanser to prevent further blockage.
- Avoid manipulation: Don’t squeeze or attempt to drain the chalazion, as this increases irritation and risk of infection.
Medical Treatments for Persistent Chalazion
If your chalazion persists despite conservative measures, you might need medical interventions such as intralesional steroid injections, incision and curettage, or topical antibiotic ointments.
Your ophthalmologist evaluates the lesion’s chronicity and size to determine the most appropriate evidence-based treatment.
These procedures aim to resolve inflammation, reduce recurrence, and restore clear vision.
Steroid Injections Overview
When conservative management fails to resolve a chalazion, steroid injections offer an evidence-based alternative to surgical intervention. Your ophthalmologist may recommend an intralesional corticosteroid, such as triamcinolone acetonide, to reduce inflammation and hasten lesion resolution.
The injection techniques typically involve transconjunctival or transcutaneous approaches, depending on the size and location of the chalazion. Precision in technique minimizes trauma and optimizes drug delivery.
Consider these aspects:
- Efficacy: Clinical studies show significant reduction in chalazion size within 2–3 weeks post-injection.
- Steroid Side Effects: Be aware of potential complications, including local skin depigmentation, increased intraocular pressure, or rare infection.
- Diagnostic Focus: Your physician will assess lesion characteristics and patient suitability to determine if steroid injection is the best next step.
Surgical Removal Process
Although many chalazia resolve with conservative measures or steroid injections, persistent lesions often require surgical removal to restore eyelid function and comfort.
Your ophthalmologist will assess the chalazion’s size, duration, and impact on vision before recommending excision. Surgical techniques typically involve a small incision on the inner eyelid, allowing the lesion’s contents to be curetted under local anesthesia. This approach minimizes scarring and preserves eyelid anatomy.
In rare cases, an external incision may be necessary for larger or atypical lesions. The recovery process generally includes mild swelling and discomfort for a few days, managed with cold compresses and analgesics.
Most patients experience rapid improvement in both eyelid appearance and visual symptoms, underscoring the efficacy of surgical intervention for chronic chalazia.
Antibiotic Ointment Application
Despite the common misconception, antibiotic ointment application doesn’t effectively treat persistent chalazion, since this lesion is primarily an inflammatory, not infectious, process.
When you consider medical treatments, it’s essential to understand the pathophysiology—chalazia result from blocked meibomian glands and granulomatous inflammation, not bacterial infection. As a result, antibiotic effectiveness in these cases is minimal unless secondary infection develops.
Here’s how ointment application might be used in clinical scenarios:
- Preventing secondary infection: If the overlying skin is compromised, antibiotic ointment can reduce infection risk.
- Adjunct to lid hygiene: Sometimes prescribed alongside warm compresses to support overall eyelid health.
- Post-surgical care: Following incision and curettage, ointment application may prevent postoperative infection.
Ultimately, don’t expect resolution of chalazion through antibiotic ointment alone without addressing the underlying inflammation.
Preventing Recurrence and Protecting Your Eyesight
To minimize the risk of chalazion recurrence and safeguard your visual acuity, prioritize meticulous eyelid hygiene and early intervention at the first sign of eyelid inflammation. Evidence supports daily lid scrubs with diluted baby shampoo or commercial cleansers as a cornerstone of chalazion prevention and ideal eye health. If you notice recurrent lesions, consult an ophthalmologist to assess for underlying meibomian gland dysfunction. Incorporate warm compresses to promote glandular secretion and prevent ductal blockage. Maintain consistent follow-up to monitor for early signs of recurrence, which can compromise vision when left untreated.
| Preventive Measure | Diagnostic Rationale |
|---|---|
| Daily lid hygiene | Reduces debris and bacterial colonization |
| Warm compresses | Enhances meibomian gland function |
| Early clinical evaluation | Allows prompt intervention |
| Regular ophthalmic exams | Monitors ocular surface and visual acuity |
Oral Treatment for Chalazion Recovery
TheraLIfe Eye, warm compress – Chalazion Symptoms/ Blepharitis treatment winning combination that works.
Add To Cart
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Children Get Chalazions as Often as Adults?
Children can develop chalazions just as often as adults, especially if they’ve conditions like blepharitis or poor eyelid hygiene.
You should watch for chalazion symptoms such as a painless eyelid lump, redness, or mild tenderness.
Treatment options include warm compresses, lid hygiene, or, in persistent cases, referral for incision and curettage.
Always consult a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and to discuss the best chalazion treatment options for your child.
Is a Chalazion Contagious to Others?
You won’t spread a chalazion by sharing towels, touching eyes, or sitting close to someone.
Chalazions aren’t contagious because they result from blocked meibomian glands, not infection.
While chalazion symptoms include swelling, tenderness, and a lump on your eyelid, no evidence suggests transmission.
Treatment options focus on warm compresses, lid hygiene, or, in persistent cases, minor surgery.
Don’t worry about isolation; instead, focus on proper diagnosis and effective symptom management.
Can Wearing Contact Lenses Cause a Chalazion?
If you wear contact lenses and neglect proper contact lens hygiene, you increase your risk of developing a chalazion.
Poor cleaning practices can introduce bacteria or debris, leading to blockage of the meibomian glands.
Evidence shows that following eye care tips—like washing your hands before handling lenses, using sterile solutions, and adhering to recommended wear schedules—reduces this risk.
If you notice eyelid swelling, consult an eye care professional for diagnostic evaluation.
How Long Does It Take for a Chalazion to Heal Naturally?
If you have a chalazion, healing time typically ranges from two to six weeks without medical intervention.
Natural remedies, such as applying warm compresses several times daily, can accelerate resolution by promoting drainage.
Evidence shows that most chalazia resolve spontaneously, though persistent or recurrent cases may require further diagnostic evaluation.
Always monitor for signs of infection or vision changes, as these warrant prompt medical consultation to rule out more serious conditions.
Are There Any Dietary Factors Linked to Chalazion Development?
When evaluating chalazion development, you should consider your dietary habits and potential nutritional deficiencies.
Evidence suggests diets high in saturated fats and low in omega-3 fatty acids may contribute to meibomian gland dysfunction, increasing chalazion risk.
Additionally, vitamin A deficiency can impair glandular health.
While no direct causality is confirmed, determining your nutritional status and correcting imbalances plays a diagnostic role in reducing recurrence and supporting ideal eyelid gland function.
Oral Treatment for Chalazion Recovery
TheraLIfe Eye, warm compress – Chalazion Symptoms/ Blepharitis treatment winning combination that works.
Add To Cart
Conclusion
When it comes to eye health, being proactive is key. TheraLife’s range of products offers unique benefits, providing comprehensive oral eye treatment care that is unmatched by other companies. A chalazion can occasionally lead to blurry vision if it becomes large enough to exert pressure on the eye. Addressing such issues promptly is vital, as evidence supports that timely diagnosis and treatment significantly reduce complications. TheraLife’s products are designed to support both self-care and medical interventions, ensuring optimal eye health. If blurry vision persists or worsens, consulting a healthcare provider is crucial to safeguard your eyesight and exclude more severe conditions. TheraLife is dedicated to enhancing your eye health with its specialized treatments, ensuring you receive the best care possible.