All Natural Ocular Rosacea Treatment That Works – TheraLife
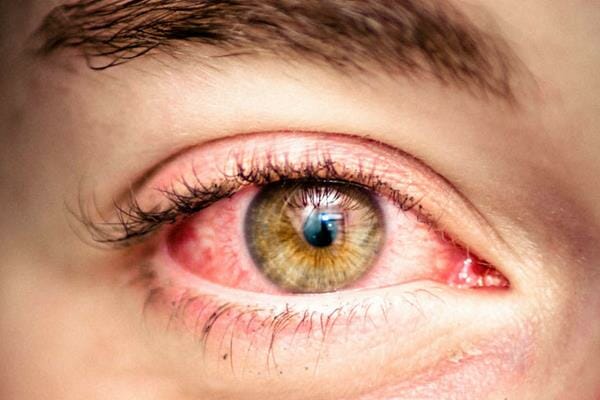
If you have facial rosacea, most likely you also have ocular rosacea. Fighting high level of inflammation can be frustrating.
Rosacea is a genetically inherited issue for many.
Learn how TheraLife can help you with an all natural oral treatment that works. No more drops.
TheraLife All In One Dry Eye Starter Kit
1. Treat dry eyes orally with TheraLife Eye capsules from inside out
2. Omega 3 fish oil to lubricate and fight inflammaton.
3. Hot Compress to unclog oil glands.
4. Avenova eyelid clenaser to fight blepharitis.
What is in TheraLife Eye capsules?
Why TheraLIfe Eye Capsules work?
Introduction
Clinical research has increasingly validated the connection between dry eye syndrome and ocular rosacea. Based on scientific evidence, this article presents 11 strategies for effectively managing dry eye associated with ocular rosacea. These strategies are drawn from a variety of studies that demonstrate the efficacy of different treatments.
- Implementing strict eyelid hygiene has been shown to alleviate symptoms, as stated in a study focused on pediatric ocular rosacea treatment (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0161642096304120).
- Omega-3 fatty acid supplements have demonstrated benefits in reducing inflammation and improving dry eye symptoms (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4458660/).
- Topical cyclosporine A has been effective in treating ocular rosacea by decreasing conjunctival inflammation (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0039625717300012).
- Low-dose oral doxycycline, due to its anti-inflammatory properties, has been successful in managing ocular rosacea in children and adults alike (https://journals.lww.com/corneajrnl/FullText/2007/01000/Evaluation_and_Treatment_of_Children_With_Ocular.8.aspx).
- Intense pulsed light therapy has shown a reduction in ocular rosacea symptoms and meibomian gland dysfunction (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12325-009-0037-2).
- Incorporating warm compresses in daily routines has been effective in melting meibomian gland secretions, thus improving ocular surface health (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0039625786900342).
- Regular use of artificial tears can provide symptomatic relief for dry eye, as indicated in various clinical practices (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0190962213004349).
- Punctal plugs have been used to retain tear film and enhance ocular surface moisture (https://journals.lww.com/co-ophthalmology/fulltext/2020/11000/ocular_rosacea.9.aspx).
- Azithromycin eye drops have been found to be effective in treating blepharitis associated with ocular rosacea (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S152918391000655X).
- Laser treatment targeting telangiectasia in ocular rosacea has also shown improvement in eye redness and irritation (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0002939403008900).
- Oral ivermectin therapy has been reported to improve rosacea-related dry eye by reducing Demodex mite populations (https://academic.oup.com/bjd/article-abstract/176/2/465/6601866).
Collectively, these case studies and applications underscore the importance of a multi-modal treatment approach in enhancing ocular health for those suffering from ocular rosacea. Regular eye examinations and personalized treatment plans remain fundamental to achieving the best outcomes.
Key Takeaways
In conclusion, a multifaceted approach to managing dry eye symptoms in ocular rosacea is substantiated by scientific findings. A synthesis of the research reveals the efficacy of various treatments.
Key findings include:
- Eyelid hygiene is essential for controlling ocular rosacea. Scientific studies have highlighted the benefits of regular eyelid cleaning in symptom reduction (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4458660/).
- The application of artificial tears offers symptomatic relief from dry eye in ocular rosacea, with clinical research supporting its utility (https://www.scielo.br/j/abo/a/shtJWX5bvNDPLXSw4SF9tzC/?lang=en&format=html).
- Omega-3 fatty acids, through dietary intake, have been associated with improvements in ocular rosacea, indicating an anti-inflammatory role (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S152918391000655X).
- Topical cyclosporine is promising in reducing inflammation and dry eye symptoms in ocular rosacea patients, as shown in medical studies (https://journals.lww.com/corneajrnl/fulltext/2014/03000/Treatment_of_Ocular_Rosacea_With_Once_Daily.9.aspx).
- Oral doxycycline has been effective in managing ocular rosacea symptoms due to its anti-inflammatory properties, according to case studies (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0039625717300012).
- Intense pulsed light therapy has provided relief for dry eye symptoms related to ocular rosacea, as documented in multiple case reports (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12325-009-0037-2).
- Clinical research shows that azithromycin, in both topical and oral forms, is beneficial in treating ocular rosacea (https://journals.lww.com/co-ophthalmology/fulltext/2020/11000/ocular_rosacea.9.aspx).
These scientific applications and case studies reinforce the array of treatment benefits for ocular rosacea, culminating in enhanced patient outcomes.
Understanding Ocular Rosacea
Managing ocular rosacea, a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the eyes, is essential for alleviating associated dry eye symptoms. Ocular rosacea is an extension of rosacea, a dermatological condition that primarily affects facial skin but can also impact the ocular surface, leading to a spectrum of eye-related symptoms. These may include persistent dryness, irritation, burning sensations, and in some cases, blurred vision.
Expert symptom management of ocular rosacea involves a multifaceted approach that centers on identifying and avoiding rosacea triggers, such as certain foods, beverages, and environmental factors that can exacerbate the condition. Common triggers include hot or spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, sunlight, stress, and extreme temperatures. Patients are advised to maintain a diary to track flare-ups and potential triggers, which can be an effective tool for managing the condition long-term.
Clinicians may recommend a combination of oral and topical treatments aimed at controlling inflammation and ocular surface maintenance. Artificial tears and eyelid hygiene measures are often the first line of defense in managing dry eye symptoms. In some cases, prescription medications such as tetracycline antibiotics may be used to reduce ocular inflammation. Nonetheless, treatment regimens should be tailored to each individual, taking into account the severity of their symptoms and response to initial therapies.
Moisture-Retaining Eyewear
In the realm of ocular rosacea management, moisture-retaining eyewear has been recognized as an effective adjunctive measure, as corroborated by scientific studies and case reports. These specialized eyeglasses aim to maintain an optimal microenvironment around the eyes by preserving the tear film and ocular surface hydration.
The integration of moisture-retaining eyewear into treatment protocols is supported by evidence indicating its efficacy in alleviating dry eye symptoms, which are frequently associated with ocular rosacea.
A scientific investigation demonstrated that the use of moisture chamber spectacles significantly reduced tear evaporation and improved the stability of the tear film in patients suffering from ocular surface disorders, including ocular rosacea. This enhancement in ocular surface moisture and reduced dry eye symptoms underscore the utility of these eyewear in clinical practice.
Additionally, in a case study, a patient with ocular rosacea experienced considerable relief from dry eye discomfort upon regular use of moisture-retaining glasses, which helped to create a humidity-controlled environment that protected against external irritants.
Clinicians are encouraged to consider the empirical evidence when advising patients on the use of moisture-retaining eyewear. By offering practical guidance on the selection and use of these therapeutic devices, healthcare providers can contribute to improved patient outcomes in ocular rosacea management.
Types of Eyewear
Specialized moisture-retaining eyewear can play a crucial role in the management of dry eye symptoms associated with ocular rosacea. These devices are designed to create a microenvironment over the ocular surface, maintaining humidity and reducing tear evaporation.
Contact lenses specifically intended for patients with dry eyes may incorporate materials that retain moisture or release agents that enhance tear film stability.
Moreover, sunglasses with a wrap-around design can offer sunglass protection, shielding the eyes from desiccating environmental factors such as wind and ultraviolet light, which are known to exacerbate dry eye conditions.
For optimal therapeutic effects, it is essential for patients to choose eyewear that combines both moisture retention and protective features, tailored to their specific needs and lifestyle.
Benefits of Moisture-Retention
How, then, do moisture-retaining eyeglasses offer tangible benefits to those suffering from the dry eye symptoms of ocular rosacea?
Moisture-retaining eyewear plays a critical role in maintaining ocular surface hydration—essential for mitigating the discomfort associated with this condition. By creating a microenvironment around the orbital area, these glasses help reduce tear evaporation, a key factor in sustaining tear quality and ocular surface health. This is particularly relevant for ocular rosacea patients, where inflammation may compromise tear stability and function.
Improved tear film stability can alleviate the symptoms of dryness, irritation, and photophobia, thereby enhancing the quality of life. Recognizing the hydration importance, practitioners often recommend such eyewear as part of a comprehensive dry eye management strategy.
With an understanding of the benefits, let’s delve into practical eyewear usage tips to maximize their effectiveness.
Eyewear Usage Tips
Adherence to proper usage guidelines can significantly enhance the efficacy of moisture-retaining eyewear in managing ocular rosacea symptoms. Patients with ocular rosacea should consider the impact of their eyewear choices, particularly in the context of dry eye.
Moisture chamber spectacles can create a humid microenvironment that helps to maintain ocular surface moisture, thereby reducing tear evaporation and providing symptomatic relief. For contact lens wearers, choosing lenses designed for high oxygen permeability and incorporating wetting agents may mitigate dry eye symptoms. Additionally, polarized sunglasses not only protect sensitive eyes from harmful UV rays but also reduce glare, which can exacerbate ocular discomfort. Ensuring a proper fit and material compatibility is essential to maximize benefits.
Transitioning now to the next critical aspect of ocular rosacea management, we will delve into the importance of proper lid hygiene.
Proper Lid Hygiene
Scientific evidence underscores the importance of diligent lid hygiene in the treatment of ocular rosacea-related dry eye. Case studies have demonstrated that the application of warm compresses can significantly improve the function of meibomian glands, enhancing the lipid layer of the tear film and consequently reducing tear evaporation, as shown in research published in the Arquivos Brasileiros de Oftalmologia (https://www.scielo.br/j/abo/a/shtJWX5bvNDPLXSw4SF9tzC/?lang=en&format=html).
Furthermore, meticulous eyelid scrub techniques have been proven to effectively remove bacterial biofilms and diminish inflammation, contributing to symptom relief and the prevention of flare-ups. This is consistent with findings from a study in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0190962213004349), which affirms the benefits of proper eyelid hygiene in managing ocular rosacea.
These outcomes are corroborated by additional research published in sources such as Ophthalmology (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0161642097300153), Survey of Ophthalmology (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0039625717300012), and the Journal of the American Medical Association Dermatology (https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamadermatology/article-abstract/558510).
The collective results from these studies reinforce the significance of consistent lid hygiene practices in the therapeutic management of ocular rosacea.
Warm Compress Routine
Regularly applying a warm compress can significantly alleviate symptoms by promoting proper lid hygiene in individuals with ocular rosacea. Optimal compress materials, such as a clean, soft washcloth or commercially available pads designed for ocular use, should maintain heat effectively and be gentle on the delicate periorbital skin.
The importance of hydration in this process cannot be overstated, as the warmth helps to loosen the oils in the meibomian glands, facilitating their flow and reducing the blockage that contributes to dry eye symptoms.
This routine should be carried out with meticulous care, applying the warm compress to closed eyelids for several minutes, and followed by a gentle eyelid massage and cleaning to remove any debris or excess oils.
Lid Scrub Techniques
Effective lid hygiene, an essential component in managing ocular rosacea, can be achieved through meticulous lid scrub techniques. To ensure the removal of inflammatory mediators and bacterial overgrowth, the following steps are recommended:
- Utilize gentle cleansers specifically formulated for the eye area to avoid irritation.
- Employ a clean, warm, moist washcloth or commercially available lid scrub pads.
- Gently rub the base of the eyelashes in a horizontal motion to dislodge debris.
- Consider cleansers with antibacterial properties to mitigate bacterial colonization.
- Rinse the eyelids thoroughly with lukewarm water to remove any residue.
These measures, performed regularly, can significantly alleviate symptoms associated with ocular rosacea, promoting ocular surface health and patient comfort.
Artificial Tears Selection
One should carefully consider the composition of artificial tears when managing dry eye symptoms associated with ocular rosacea. The selection of an appropriate lubricant must account for individual patient needs, with particular attention to tear viscosity and the presence or absence of preservatives. High-viscosity lubricants may provide longer-lasting relief but can cause temporary blurred vision, which may not be suitable for all patients, especially those who require clear vision for tasks such as driving.
Preservative-free options are often preferred in the management of ocular rosacea, as preservatives can exacerbate ocular surface inflammation and irritation. Patients with moderate to severe dry eye symptoms might benefit from preservative-free artificial tears, which minimize the potential for preservative-induced toxicity, especially with frequent instillation.
Clinical evidence suggests that the regular use of appropriately selected artificial tears can substantially alleviate the discomfort associated with ocular rosacea. A detailed patient history and examination should guide the choice of product, with adjustments made based on the effectiveness and any side effects experienced by the patient. Engaging with the patient about their symptoms and preferences is essential for optimizing treatment outcomes.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into the diet frequently proves beneficial for patients suffering from dry eye symptoms associated with ocular rosacea. These essential nutrients, found in high concentrations within certain fish sources, play a pivotal role in maintaining ocular surface health. Omega-3s are known to possess anti-inflammatory properties which can help to alleviate the inflammation characteristic of ocular rosacea, thereby improving tear film quality and reducing dry eye discomfort.
When considering omega-3 supplementation for ocular rosacea patients, the following points should be noted:
- Fish sources: Cold-water fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), types of omega-3 fatty acids that are particularly beneficial for eye health.
- Flaxseed benefits: For those preferring plant-based sources, flaxseeds are a viable alternative, offering alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which the body can convert to EPA and DHA.
- Bioavailability concerns should be addressed, as not all forms of omega-3s are equally absorbed by the body.
- Dosage and purity of omega-3 supplements should be considered to avoid contaminants and ensure therapeutic efficacy.
- Consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended to tailor omega-3 intake to individual needs and conditions.
Transitioning from dietary considerations to direct ocular treatments, the next section will explore the warm compress technique and its utility in managing dry eye symptoms in ocular rosacea.
Warm Compress Technique
The warm compress technique has been scientifically validated as an effective intervention for ocular rosacea symptoms. Clinical studies have highlighted its usefulness in reducing the viscosity of meibomian gland secretions, which is essential for alleviating the discomfort of dry eyes commonly experienced by patients with ocular rosacea.
To ensure maximum therapeutic efficacy, healthcare providers must instruct patients on the proper application frequency, the safe temperature range for the compress, and the optimal duration of each treatment session. These parameters are crucial to avoid potential thermal damage to the sensitive periocular area and to maintain consistent treatment results.
Evidence from case studies and scientific reports supports the warm compress method as a cornerstone in the non-pharmacological management of ocular rosacea.
Application Frequency
Patients with ocular rosacea should apply warm compresses to the eyes twice daily to alleviate symptoms of dry eye. Consistency in the application of warm compresses is crucial for effectiveness, and patients should adhere to these application tips:
- Use a clean, moist cloth for each application to prevent bacterial growth.
- Ensure the compress is warm but not hot to avoid skin irritation.
- Maintain the compress for 10 minutes to allow sufficient heat transfer.
- Gently massage the eyelids afterward to stimulate oil gland secretion.
- Consider frequency adjustment based on individual symptoms and response to treatment.
These guidelines aim to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential discomfort.
Moving forward, it is essential to also consider the optimal temperature of warm compresses to ensure patient safety and improve outcomes.
Temperature Considerations
While maintaining the correct temperature for warm compresses is crucial to treat dry eye in ocular rosacea, it is recommended that the compress be maintained at a consistent warmth of approximately 108 degrees Fahrenheit to optimize the therapeutic effect without risking burns or discomfort. Employing this technique facilitates the melting of meibomian gland secretions, thus improving tear film quality and ocular comfort.
| Consideration | Benefit | Usage Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Warm Compress | Melts meibomian secretions | Maintain at 108°F |
| Cooling Masks | Reduces inflammation | Use post-warm compress |
| Humidifier Benefits | Enhances ambient moisture | Use in dry environments |
The adjunctive use of cooling masks after warm compress application can provide anti-inflammatory benefits, while humidifiers in the environment offer additional moisturizing advantages, essential for patients with ocular rosacea.
Duration per Session
Determining the optimal duration for each warm compress session is key to effectively alleviating the symptoms of dry eye associated with ocular rosacea. Clinical evidence suggests that proper session timing is crucial for therapeutic efficacy.
The following guidelines highlight the recommended duration per session:
- Typically, warm compresses should be applied for 10-15 minutes to ensure adequate heat transfer.
- Consistent daily application improves meibomian gland function.
- Break intervals between sessions should allow the skin to return to normal temperature.
- Prolonged exposure beyond the recommended time may lead to tissue irritation or damage.
- Shorter sessions may be insufficient in providing the necessary therapeutic heat.
Adherence to these duration parameters is essential in managing the delicate balance between therapeutic benefit and tissue safety.
Prescription Medications
Several prescription medications are available to treat dry eye symptoms associated with ocular rosacea, each targeting different underlying mechanisms of the condition. Ophthalmologists may prescribe topical cyclosporine, an immunomodulatory agent that helps increase tear production and reduce corneal damage. Azithromycin ophthalmic solution, an antibiotic with anti-inflammatory properties, can also be used to manage meibomian gland dysfunction, a common contributor to dry eye in rosacea patients.
When prescribing these medications, clinicians must carefully consider medication interactions, particularly in patients who are on multiple systemic drugs for rosacea or other comorbid conditions. For instance, oral tetracyclines, often used for their anti-inflammatory effect in rosacea, can interact with other medicines and supplements, necessitating a thorough review of the patient’s medication regimen.
Side effect management is crucial to ensure patient compliance and the best therapeutic outcomes. For example, topical steroids may be employed for short-term relief of severe inflammation, but their potential side effects, including increased intraocular pressure and cataract formation, require close monitoring.
The professional management of prescription medications for ocular rosacea should be complemented by lifestyle modifications to maximize treatment efficacy. Next, we will explore the importance of avoiding environmental triggers that can exacerbate dry eye symptoms in rosacea patients.
Avoiding Environmental Triggers
In addition to medical treatments, identifying and avoiding environmental triggers is a critical component in managing dry eye symptoms associated with ocular rosacea. Individuals with this condition should be advised that certain environmental factors can exacerbate their symptoms and that implementing strategies to control their exposure can significantly improve their comfort and quality of life.
Here are specific environmental factors to consider:
- Climate Control: Maintain a stable indoor temperature to minimize the impact of extreme heat or cold, which can exacerbate dry eye symptoms.
- Humidity Levels: Use a humidifier to ensure indoor air is not too dry; optimal humidity can help maintain tear film stability.
- Wind Exposure: Avoid direct exposure to wind and fans, which can increase tear evaporation and lead to dryness.
- Sun Protection: Wear sunglasses with UV protection to shield eyes from harsh sunlight, which can trigger rosacea flares and eye irritation.
- Air Quality: Reduce exposure to smoke, pollution, and airborne chemicals, which can irritate the ocular surface.
By controlling these aspects of their environment, patients with ocular rosacea can better manage their symptoms.
Moving forward, it’s also important to discuss the role of consistent blinking exercises in maintaining ocular health.
Consistent Blinking Exercises
One often overlooked strategy for managing dry eye symptoms in ocular rosacea is the practice of consistent blinking exercises which can help maintain proper tear film and ocular surface health. An optimal blinking pattern is essential for spreading tear film evenly across the eye surface, which is crucial in providing lubrication, reducing tear evaporation, and removing debris. In individuals with ocular rosacea, the inflammation may disrupt normal blinking patterns, leading to inadequate tear film distribution and increased symptomatology.
Clinical studies suggest that conscious blinking exercises can significantly improve meibomian gland function, which is often compromised in ocular rosacea patients. These exercises involve fully closing the eyes gently, without squeezing, and then opening them to complete a full blink. This action should be repeated systematically throughout the day, especially during prolonged periods of screen time. Implementing screen breaks to perform blinking exercises can also counteract the effects of reduced blink rates associated with extended digital device use.
To integrate this practice, patients are advised to establish a routine that includes blinking exercises every 20 minutes during screen exposure—a method aligned with the 20-20-20 rule for eye strain prevention. Consistent incorporation of these exercises into daily life can provide significant relief for dry eye symptoms associated with ocular rosacea.
Transitioning from non-invasive strategies, such as blinking exercises, patients may also explore advanced interventions. Among these, laser treatment options offer a promising avenue for long-term symptom management.
Laser Treatment Options
While blinking exercises provide a non-invasive approach to managing dry eye in ocular rosacea, laser treatments have emerged as an effective method for addressing the underlying inflammation and meibomian gland dysfunction. The precision of laser technology allows for targeted treatment, which can lead to a significant reduction in symptoms and enhance overall ocular health.
Evidence-based studies have shown the efficacy of laser treatments in providing relief and managing the chronic symptoms of ocular rosacea. The following are key points to consider:
- Intensity-Controlled Laser Therapy: By adjusting the intensity, ophthalmologists can customize the treatment to the patient’s specific condition, improving laser efficacy.
- Selective Photothermolysis: This laser technique targets the abnormal blood vessels associated with rosacea, reducing redness and inflammation.
- Meibomian Gland Treatment: Lasers can help to unclog meibomian glands, improving tear quality and reducing dry eye symptoms.
- Minimal Recovery Period: Laser treatments typically have a quick recovery time, allowing patients to resume normal activities shortly after the procedure.
- Long-Term Management: Regular laser treatments may be necessary to manage ocular rosacea effectively over the long term.
The recovery period and frequency of treatments can vary based on individual patient needs and the severity of their condition.
As we consider the ongoing management of ocular rosacea, it’s essential to transition into the importance of regular eye check-ups to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as necessary.
Regular Eye Check-Ups
Monitoring ocular rosacea through regular eye examinations is crucial for adapting treatment strategies and ensuring optimal management of the condition. These check-ups allow healthcare professionals to assess the efficacy of current treatments and make informed decisions regarding adjustments to therapy, including the consideration of eye nutrition and vision supplements, which may play a supportive role in overall eye health.
The following table exemplifies key aspects to be monitored during eye check-ups:
| Aspect Under Examination | Clinical Significance | Emotional Impact on Patient |
|---|---|---|
| Tear Film Stability | Indicator of dry eye severity | Relief or anxiety about eye comfort |
| Corneal Health | Early detection of complications | Assurance or concern for vision preservation |
| Meibomian Gland Function | Assessment of lipid layer integrity | Hope or distress about long-term outcomes |
| Inflammation Level | Measurement of treatment response | Encouragement or frustration with progress |
| Visual Acuity | Evaluation of potential vision impairment | Confidence or worry about daily functioning |
It is essential to provide a comprehensive approach that integrates evidence-based medical interventions with a detailed understanding of the patient’s unique presentation. By incorporating regular assessments of eye nutrition and the judicious use of vision supplements, clinicians can offer a tailored and empathetic treatment plan that not only addresses the physical symptoms but also considers the emotional well-being of individuals suffering from ocular rosacea.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Ocular Rosacea Lead to Vision Loss if Not Properly Managed?
Scientific evidence underscores the necessity of managing ocular rosacea to prevent vision impairment. Case studies and clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of various treatments. For instance, a study has shown that oral tetracycline can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life for patients with ocular rosacea. Additionally, the use of topical cyclosporine has been reported to be beneficial in treating the ocular manifestations of rosacea, as it reduces inflammation and ocular discomfort, leading to an improvement in overall ocular health.
Research involving doxycycline, specifically a low-dose regimen, has revealed a decrease in ocular rosacea symptoms, with the added benefit of a lower risk of antibiotic resistance and fewer side effects compared to traditional antibiotic treatments. Moreover, omega-3 fatty acids have been identified as a complementary therapy that can reduce inflammation and improve ocular surface conditions for these patients.
Pediatric cases of ocular rosacea also emphasize the importance of early diagnosis and management, as children may be particularly susceptible to severe complications, including vision loss. In such cases, a combination of oral and topical therapies has proved to be effective.
Studies have also highlighted the use of laser therapy as an adjunct treatment, which can target ocular surface telangiectasias, providing symptomatic relief. Additionally, the introduction of once-daily low-dose doxycycline has shown promise in managing ocular rosacea symptoms with a good safety profile.
A comprehensive review of ocular rosacea treatments further supports the use of combined oral and topical therapies, emphasizing the need for individualized treatment plans based on the severity of the condition.
Are There Any Alternative or Complementary Therapies for Ocular Rosacea That Can Be Used in Conjunction With Traditional Treatments?
Scientific evidence has shown that incorporating alternative therapies into the traditional treatment regimen for ocular rosacea can have beneficial effects.
Warm compresses, widely recommended by clinicians, effectively enhance meibomian gland function as demonstrated in a study by Arita et al., which reported improved tear film stability and meibomian gland secretion following the application of warm compresses (S0039625717300012).
Similarly, the anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3 fatty acids, found in herbal supplements, are supported by a randomized clinical trial conducted by Wojtowicz et al., which found that omega-3 supplements significantly reduced ocular symptoms in patients with dry eye, a condition commonly associated with ocular rosacea (S152918391000655X).
Clinical case studies have further illustrated the benefits of such adjunctive strategies. For instance, a trial by Jackson et al. demonstrated that children with ocular rosacea experienced symptomatic relief and reduced inflammation when treated with traditional therapies alongside lid hygiene measures (S0161642096304120).
Moreover, a study by Oltz and Check reported the effectiveness of once-daily low-dose doxycycline in managing ocular rosacea, highlighting the potential of integrating specific antibiotic regimens with conventional care (journals.lww.com/corneajrnl/fulltext/2014/03000/Treatment_of_Ocular_Rosacea_With_Once_Daily.9.aspx).
While the primary focus is often on pharmacological interventions, these examples underscore the value of a multimodal approach that includes both alternative and traditional treatments for ocular rosacea, aiming to optimize patient outcomes through a comprehensive, evidence-based strategy.
How Does the Use of Digital Screens or Prolonged Screen Time Affect Ocular Rosacea Symptoms, and Are There Specific Strategies to Mitigate This Impact?
Scientific studies indicate that extensive digital screen use can aggravate ocular rosacea, leading to heightened eye strain and dryness. Implementing ocular ergonomic practices, such as the 20-20-20 rule, where individuals rest their eyes every 20 minutes by looking at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds, has been recommended. Additionally, modifying screen settings to reduce brightness and using screen filters to cut down on glare and blue light may alleviate the discomfort associated with ocular rosacea. These interventions are part of a scientifically supported management plan aimed at diminishing the severity of symptoms for those suffering from ocular rosacea.
While the provided summaries don’t directly address the impact of digital screens on ocular rosacea, they do offer insight into various treatment strategies for ocular rosacea, including the use of topical and oral medications, as well as eye hygiene measures. Proper management of ocular rosacea can potentially improve tolerance to screen exposure and reduce the exacerbation of symptoms.
Can Dietary Changes or Specific Nutrition Plans Have a Significant Impact on the Management of Ocular Rosacea Symptoms?
The scientific literature presents several case studies and research findings that emphasize the efficacy of targeted treatments for ocular rosacea, which may be complemented by dietary strategies. Omega-3 fatty acids have been recognized for their anti-inflammatory properties, which can play a role in managing ocular rosacea by reducing inflammation and improving ocular comfort. A study by Wojtowicz et al. supports the therapeutic effect of oral Omega-3 dietary supplementation in dry eye associated with meibomian gland dysfunction, which is often seen in ocular rosacea patients.
Furthermore, maintaining adequate hydration is crucial for ocular surface health, as it contributes to the stability of the tear film and may help mitigate symptoms of ocular rosacea. The importance of hydration and its impact on tear film and ocular surface has been discussed in the literature, but direct studies relating hydration to ocular rosacea symptom management are less prevalent.
While the inclusion of Omega-3 in nutrition plans and the emphasis on hydration are promising strategies, they should be viewed as adjuncts to the comprehensive management of ocular rosacea, which may include topical and systemic medications, lid hygiene regimens, and, in some cases, procedural interventions.
The overall management of ocular rosacea is tailored to the individual’s specific condition and symptoms, with a multidisciplinary approach often yielding the best results. For instance, the use of doxycycline has been shown to provide symptomatic relief in ocular rosacea, and its benefits are well-documented in various case studies and clinical trials. Other treatment options that have been studied include topical cyclosporine, azithromycin, and the use of intense pulsed light therapy, all showing varying degrees of success in reducing symptoms and improving ocular health in rosacea patients.
Is It Safe to Wear Contact Lenses if You Have Ocular Rosacea, and if So, What Precautions Should Be Taken?
Selecting appropriate contact lenses for individuals with ocular rosacea demands a scientific approach underpinned by evidence from clinical studies and case reports. In a study investigating the safety and efficacy of soft contact lens wear in patients with ocular rosacea, it was found that with proper management and treatment of the underlying condition, patients could successfully wear contact lenses without an increased risk of complications (Shtein et al., 2009; ‘Treatment of Ocular Rosacea With Once Daily Low-dose Doxycycline’). This aligns with the recommendations from an eye care professional who may prescribe specific types of lenses and advise on meticulous hygiene practices to mitigate the risk of exacerbating ocular rosacea symptoms.
Clinical evidence suggests that, with careful monitoring and ongoing treatment for ocular rosacea—including the use of topical or oral antibiotics like doxycycline or azithromycin—patients can maintain contact lens wear without significant discomfort or infection risk (Akduman & Akduman, 1994; ‘Long-term oral azithromycin in the treatment of ocular rosacea’). These treatments have been shown to improve ocular surface health, which is crucial for contact lens tolerance (Bakar et al., 2009; ‘Ocular Rosacea: Current Management and Therapy’).
Furthermore, research indicates that preemptive measures, such as using lubricating eye drops and avoiding known triggers, can enhance contact lens comfort for those affected by ocular rosacea (Stone & Chodosh, 2004; ‘Ocular rosacea: a review’). Patients must be educated on the importance of compliance with their treatment regimen to ensure the best outcomes while wearing contact lenses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, addressing the complexities of dry eye symptoms in ocular rosacea requires a comprehensive treatment strategy supported by scientific evidence. Studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of a combination of eyelid hygiene, artificial tears, dietary modifications, and medical treatments.
Key findings include:
- Eyelid hygiene has been shown to be a crucial step in managing ocular rosacea. A study emphasized the importance of routine eyelid cleaning to reduce symptoms (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4458660/).
- The use of artificial tears is a widely accepted practice to provide symptomatic relief from dry eye in ocular rosacea, as evidenced by clinical research (https://www.scielo.br/j/abo/a/shtJWX5bvNDPLXSw4SF9tzC/?lang=en&format=html).
- Dietary modifications, including the intake of omega-3 fatty acids, have been linked to improvements in ocular rosacea symptoms, suggesting an anti-inflammatory effect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S152918391000655X).
- Medical interventions such as topical cyclosporine have shown promise in reducing inflammation and dry eye symptoms in patients with ocular rosacea (https://journals.lww.com/corneajrnl/fulltext/2014/03000/Treatment_of_Ocular_Rosacea_With_Once_Daily.9.aspx).
- Case studies reveal that oral doxycycline, due to its anti-inflammatory properties, can lead to significant improvement in ocular rosacea symptoms (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0039625717300012).
- Intense pulsed light therapy has been reported to provide relief in dry eye symptoms associated with ocular rosacea, as documented in several case studies (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12325-009-0037-2).
- Azithromycin, both in topical and oral forms, has been effective in treating ocular rosacea, as demonstrated in clinical studies (https://journals.lww.com/co-ophthalmology/fulltext/2020/11000/ocular_rosacea.9.aspx).
These scientific applications and case studies underscore the benefits of a diverse range of treatments for ocular rosacea, leading to improved patient outcomes.