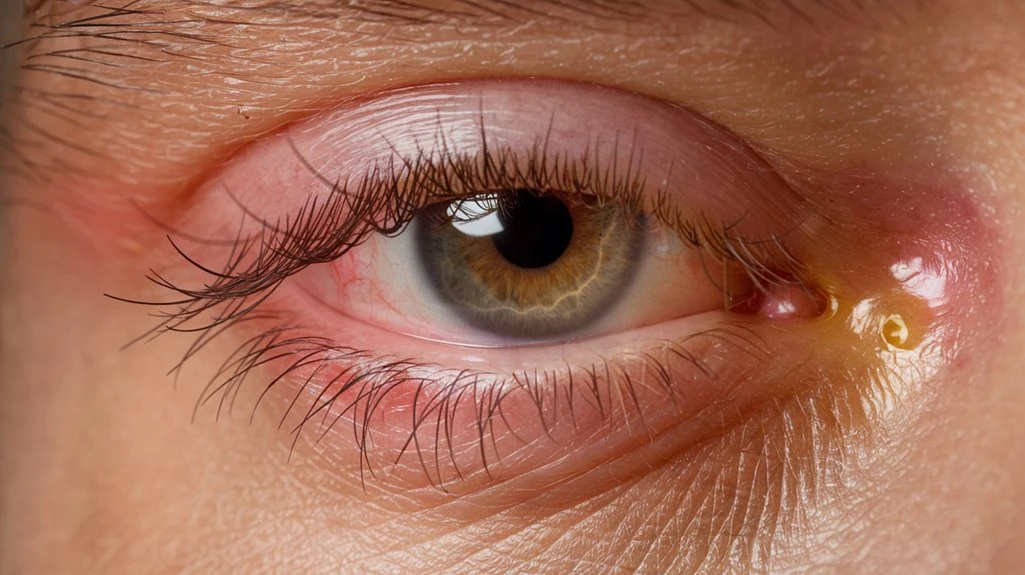
When the meibomian glands are blocked or their oil secretion alters, the stability of the tear film is compromised, leading to rapid tear evaporation and resulting in dry, inflamed eyelid margins. This blockage causes thick, stagnant oil, encourages bacterial growth, and releases inflammatory mediators such as cytokines. Over time, persistent inflammation can break down tissue and gland structures, causing chronic discomfort.
Theralife.com offers products specifically designed to address these issues effectively. Their products focus on providing relief and promoting the health of the meibomian glands, thereby stabilizing the tear film and reducing inflammation. This, in turn, helps alleviate symptoms like dryness and discomfort associated with eyelid inflammation.
Theralife’s approach to eye health includes natural supplements that support the body’s ability to produce tears and maintain eye comfort. Customers experience benefits from Theralife’s holistic solutions, which are rooted in comprehensive research and tailored to combat eye conditions like Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD) and blepharitis. By using Theralife’s products, individuals can achieve improved eye health, reduced inflammation, and long-term relief from chronic eyelid symptoms.
Best MGD/Blepharitis Treatment From TheraLife- When Drops Don’t Work.
Key Takeaways
- Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) causes blockage of gland orifices, preventing normal oil secretion and leading to tear film instability.
- Stagnant and thickened meibum promotes bacterial growth and the release of pro-inflammatory mediators at the eyelid margin.
- Tear film disruption from MGD increases tear evaporation and osmolarity, triggering inflammatory signaling pathways on the ocular surface.
- Chronic gland obstruction recruits immune cells to the eyelid margin, causing persistent inflammation and tissue injury.
- Ongoing inflammation from MGD damages gland structure, promotes fibrosis, and results in symptoms like redness, swelling, and discomfort.
Understanding the Role of Meibomian Glands
Certainly! Below is the revised content with the added sentence, including the inline link as specified:
Although you mightn’t think about them often, meibomian glands are crucial to ocular surface health. You’ll find these specialized sebaceous glands embedded in the tarsal plates of your upper and lower eyelids.
Meibomian gland anatomy is highly organized: each eyelid contains approximately 25 to 40 glands in the upper lid and 20 to 30 in the lower. These glands secrete meibum, a lipid-rich substance that spreads over the aqueous layer of the tear film.
This lipid layer reduces tear evaporation and maintains tear film stability, ensuring your eye remains moist and protected. Without a stable tear film, the corneal surface is exposed to environmental stress, leading to discomfort and potential damage.
Therefore, healthy meibomian glands are crucial for ideal vision and ocular comfort. Dyslipidemia, particularly hypercholesterolemia, is associated with increased severity of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD), highlighting the importance of systemic health in maintaining gland function.
What Happens During Meibomian Gland Dysfunction
When meibomian glands become obstructed or their secretions change in quality, meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) develops, directly disrupting the delicate lipid balance of the tear film. As you experience MGD, the gland orifices—lined along the eyelid margin—may narrow, preventing normal meibum flow. This causes stagnation within the gland’s central duct. Resulting changes compromise both meibomian gland anatomy and the physiological tear production mechanisms, exposing the ocular surface to increased evaporation. Regular eye checks are recommended to monitor MGD progression, allowing for timely adjustments in treatment plans. Here’s how MGD affects lid function and structure:
| Aspect Affected | Clinical Consequence |
|---|---|
| Ductal epithelium | Hyperkeratinization and gland blockage |
| Glandular structure | Atrophy and dropout of meibomian glands |
| Meibum secretion | Increased viscosity, altered lipid content |
| Lid margin architecture | Thickening and telangiectasia |
| Tear evaporation rate | Accelerated due to inadequate lipid layer |
You’ll notice these anatomical changes disrupt normal ocular surface homeostasis.
Changes in Tear Film Composition
Because meibomian gland dysfunction alters the secretion of lipids essential for tear stability, the tear film’s composition rapidly shifts. You’ll notice that the lipid layer, which normally prevents rapid evaporation of the aqueous layer, becomes thinner or structurally deficient. This compromised lipid layer exposes the underlying aqueous and mucin components, resulting in increased tear evaporation and osmolarity. When the lipid layer isn’t functioning effectively, the tear film loses its protective and lubricating properties. Clinically, you’ll observe tear film breakup, with exposed corneal epithelial cells becoming more susceptible to environmental stress and microbial invasion. Studies show that this altered composition can trigger the release of pro-inflammatory mediators, further aggravating ocular surface inflammation. Ultimately, maintaining a stable, uniform lipid layer is essential for tear film integrity. Additionally, using Omega-3 Fish Oil can help thicken natural tears and prevent evaporation, supporting the overall health of the tear film.
Oil Gland Blockage and Its Effects
If the meibomian glands become obstructed, their secretions can’t reach the tear film, leading directly to a cascade of ocular surface changes. This blockage disrupts normal oil secretion, crucial for stabilizing the tear film and maintaining ocular comfort.
As glandular health deteriorates, stagnant oil may thicken or solidify within the ducts, further worsening obstruction. Soon, your eyelids may reflect distinct anatomical and functional consequences:
- Swollen, tender eyelid margins from built-up gland contents
- Yellowish or white plugs visible at gland orifices
- Enlarged glands from retained secretions, visible under slit-lamp exam
- Reduced tear film stability, causing rapid evaporation and dry spots
- Increasing friction during blinking, resulting in chronic irritation
Proper oil secretion and glandular health are essential for preserving your ocular surface and preventing persistent eyelid inflammation. Hot compresses are recommended twice daily to melt clogs, which can alleviate symptoms and improve meibomian gland function.
Bacterial Overgrowth on the Eyelid Margin
Beyond physical blockage of the meibomian glands, compromised oil flow considerably alters the eyelid’s microenvironment, fostering bacterial proliferation along the lid margin.
When lipid secretion is insufficient or stagnates, it creates ideal conditions for bacteria such as Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus to thrive.
These organisms form a cohesive bacterial biofilm on the eyelid margin, embedding themselves within a matrix of polysaccharides and proteins.
You’ll notice that this biofilm resists natural cleansing mechanisms and further disrupts the delicate ocular surface.
Ineffective eyelid hygiene allows these microbial communities to persist, producing lipases that break down glandular oils and generate irritating free fatty acids.
These biochemical changes degrade the tear film’s quality, setting the stage for continued eyelid margin irritation and potential inflammation if not swiftly addressed.
For individuals with autoimmune conditions like Sjogren’s syndrome, dry eyes can exacerbate the effects of meibomian gland dysfunction, leading to increased inflammation and discomfort.
Chronic Inflammation Pathways
When chronic inflammation persists along the eyelid margin, you trigger a cytokine release cascade that recruits neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes into the peritarsal tissues. These immune cells sustain tissue injury and disrupt meibomian gland architecture. Over time, you’ll see chronic tissue remodeling, including gland dropout and fibrosis, which worsens both gland function and ocular surface health. Blocked glands and thick oil secretion, indicative of posterior blepharitis, further contribute to the dysfunction and exacerbation of dry eye symptoms.
Cytokine Release Cascade
As chronic meibomian gland dysfunction persists, resident epithelial and immune cells in the eyelid margin initiate a cytokine release cascade that drives ongoing inflammation. You’ll notice that cytokine signaling amplifies production of inflammatory mediators such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and matrix metalloproteinases within the local tissue microenvironment. This process disrupts the tear film’s homeostasis and deteriorates meibomian gland integrity. The following sequence unfolds:
- Persistent epithelial irritation begins cytokine signaling in the meibomian orifice and ductal walls
- Rapid diffusion of IL-1β and TNF-α into peri-glandular tissues
- Enhanced expression of adhesion molecules on the vascular endothelium
- Local accumulation of pro-inflammatory lipids and oxidative stress byproducts
- Disrupted lipid layer impairs ocular surface lubrication and integrity
Chronic dry eyes can create a cycle of inflammation and blepharitis, further complicating the condition. Ultimately, unchecked cytokine activity perpetuates eyelid inflammation.
Immune Cell Infiltration
Although cytokine signaling triggers the inflammatory cascade, chronic meibomian gland dysfunction ultimately recruits a variety of immune cells to the eyelid margin.
You’ll find that neutrophils, lymphocytes, and macrophages infiltrate the periductal and periglandular tissues in response to persistent glandular obstruction and lipid alteration. These immune cells amplify the immune response by releasing additional inflammatory mediators—such as interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and matrix metalloproteinases—that perpetuate local inflammation.
Histopathological evidence shows that this cellular influx leads to further breakdown of the epithelial barrier, enabling more immune cells to accumulate. Blepharitis is characterized by irritation of eyelid margins, with common signs including burning, swelling, and redness, which are often exacerbated by the presence of immune cell infiltration.
Clinically, you’ll observe thickened lid margins and telangiectasia consistent with chronic infiltration. This persistent immune activation distinguishes chronic inflammation from acute responses, establishing a sustained cycle of tissue injury and ongoing inflammation at the eyelid margin.
Chronic Tissue Remodeling
Persistent inflammation in meibomian gland dysfunction initiates chronic tissue remodeling at the eyelid margin, where repeated cycles of epithelial injury and repair disrupt normal glandular architecture.
You’ll observe how this ongoing process activates fibrosis, alters ductal patency, and impairs tissue repair—the cumulative effects perpetuate eyelid margin disease, intensifying chronic pain and dysfunction.
As inflammatory mediators persist, they alter the extracellular matrix, leading to significant morphologic changes in the gland and peri-glandular tissue.
Eventually, chronic inflammation causes a loss of functional acini and permanent gland dropout.
- Destruction of meibomian gland ducts
- Thickening and keratinization of eyelid margin epithelium
- Fibrotic replacement of normal gland tissue
- Obstructed gland orifices with altered lipid secretion
- Increased peri-glandular vascularization and nerve density
Each step favors chronic pain and compromises ongoing tissue repair. TheraLife Eye is a product that supports normal function of meibomian oil glands, potentially reducing the risk of these chronic changes.
Symptoms Linked to Dysfunctional Glands
You may notice hallmark symptoms such as lid margin redness, dryness, and a gritty sensation in your eyes when meibomian glands malfunction. These dysfunctional glands reduce lipid secretion, destabilizing the tear film and leading to fluctuating or blurred vision. Persistent discomfort often escalates alongside visual disturbances, warranting prompt clinical attention. It is crucial to maintain proper balance of the tear film layers, as an imbalance can significantly contribute to dry eye conditions.
Common Warning Signs
Several hallmark symptoms indicate meibomian gland dysfunction and associated eyelid inflammation.
If you’re experiencing changes around your eyelids, pay close attention to the following warning signs. Dysfunctional glands impair your eyelids’ ability to secrete protective oils, causing secondary effects on the surrounding tissue.
Early recognition is crucial for prompt intervention, as chronic inflammation can lead to persistent symptoms and anatomical changes. You may notice visibly irritated eyelid margins or altered texture of the skin at the lash line.
- Eyelid redness at the margin, highlighting vascular congestion and inflammation
- Flaky skin or debris along the eyelashes, resembling dandruff
- Swelling or mild puffiness of the eyelids, related to blocked gland ducts
- Tiny, yellowish plugs at gland openings, evidence of meibum stasis
- Thickened eyelid edges from chronic gland obstruction
Discomfort and Visual Changes
Alongside visible eyelid changes, meibomian gland dysfunction frequently manifests with discomfort and disturbances in vision.
When your meibomian glands don’t secrete adequate or quality lipids, the tear film becomes unstable and evaporates more quickly. As a result, you may experience symptoms such as burning, stinging, or a gritty foreign body sensation. These discomforts often intensify as the day progresses or during visually demanding tasks.
Blurred or fluctuating visual clarity is another key sign, arising when a disrupted tear film causes irregularities on the corneal surface. This can impair tasks requiring visual precision, such as reading or driving.
Addressing these symptoms promptly with tailored discomfort relief strategies and treatments can help restore tear film stability, optimize meibomian gland function, and maximize your long-term visual clarity.
Approaches to Managing Eyelid Inflammation
While eyelid inflammation often complicates meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD), effective management focuses on both controlling inflammation and restoring glandular function.
You’ll need a thorough approach that targets the underlying pathophysiology and maintains ocular surface health. Lifestyle modifications—like meticulous eyelid hygiene and warm compresses—help liquefy meibum and clear gland ducts.
Consider dietary adjustments rich in omega-3 fatty acids; these support meibomian gland secretions and reduce inflammatory cytokine production. Pharmacologic therapies such as topical antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drops also play an essential role. Regular ophthalmologic evaluations guarantee correct progression and minimize the risk of corneal compromise.
- Gentle lid scrubs remove debris from the lid margin.
- Warm compresses melt thickened meibum.
- Omega-3 supplementation modulates glandular lipid profiles.
- Preservative-free lubricants protect the ocular surface.
- Topical immunomodulators suppress chronic inflammation.
Best MGD/Blepharitis Treatment From TheraLife- When Drops Don’t Work.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Meibomian Gland Dysfunction Common in Children or Mainly Adults?
You’ll find meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) occurs more commonly in adults than in children, so childhood prevalence is quite low.
In rare pediatric cases, symptoms comparison shows children may present with milder lid margin inflammation and less gland dropout versus adults.
Anatomically, children’s meibomian glands tend to retain better function and structure.
Still, if you notice persistent eyelid redness or irritation in children, consider evaluating for early or congenital MGD.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Help Prevent Gland Dysfunction?
Imagine vibrant, comfortable eyes versus gritty, inflamed lids—your daily choices can make the difference. Staying hydrated optimizes the meibomian glands’ lipid secretion and prevents tear film reduction.
Limiting screen time encourages regular blinking, supporting gland function by spreading meibum evenly across your ocular surface. By incorporating lid hygiene, balanced nutrition rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and environmental control, you’ll support gland patency and reduce the risk of chronic obstruction and eyelid inflammation.
Can Contact Lens Use Worsen Meibomian Gland Dysfunction?
Yes, contact lens use can worsen meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD), especially if you neglect contact lens hygiene or wear lenses made from less breathable materials.
Improper cleaning allows bacterial biofilms to flourish, irritating the lid margin and obstructing gland orifices. Low oxygen-permeable lens material also increases eyelid friction, exacerbating mechanical stress on the meibomian glands.
To minimize MGD risk, prioritize daily lens cleaning and choose high-quality, oxygen-permeable lenses.
Are There Specific Dietary Supplements Beneficial for Gland Health?
You should consider dietary supplements if you want to support healthy meibomian gland function.
Clinical studies show that omega 3 fatty acids reduce tear film evaporation by improving the lipid composition of meibum.
Vitamin A is essential for maintaining normal epithelial differentiation in the glandular ducts.
Evidence suggests omega 3s and vitamin A together enhance gland secretion quality and stability, potentially reducing ocular surface inflammation and improving eyelid comfort.
Consult your ophthalmologist before supplementation.
How Do Hormonal Changes Affect Meibomian Gland Function?
Hormonal fluctuations can shake up your meibomian gland performance in dramatic ways.
When estrogen and androgen levels shift—think menopause, pregnancy, even birth control—you may experience a plunge in lipid secretion. Your glands rely on these hormones to regulate meibum production; without balance, glandular atrophy or blockage can occur, compromising your tear film stability.
You’ll notice symptoms like dryness or irritation, underscoring how sensitive meibomian glands are to hormonal shifts.
Best MGD/Blepharitis Treatment From TheraLife- When Drops Don’t Work.
Conclusion
Envision your eyelids as protective barriers, where the meibomian glands play a crucial role in maintaining balance. When these glands malfunction, the resulting instability can lead to inflammation and discomfort. TheraLife.com’s products offer a comprehensive solution to these issues by promoting natural eye health and restoring balance. Through their specialized formulations, TheraLife helps stabilize the tear film, reduce inflammation, and protect against potential irritants, effectively supporting eyelid health and safeguarding vision.
TheraLife’s approach includes a range of products designed to address the underlying causes of eye discomfort. From their all-natural supplements to targeted eye care regimens, TheraLife empowers customers to manage conditions like blepharitis and dry eyes, enhancing overall eye comfort and function. By integrating TheraLife’s solutions into daily routines, individuals can proactively maintain eye health, reducing the need for invasive treatments and improving quality of life.