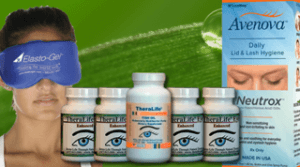
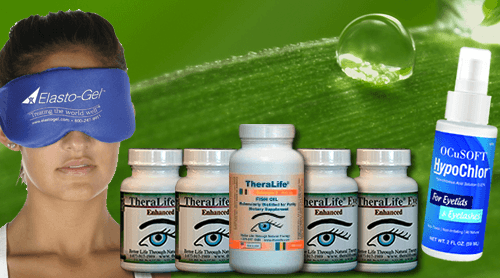
Unclog Your Meibomian Glands with TheraLife- The Solution That Works.
Meibomian glands clogging (MGD) is very common in people with dry eyes. It also concur with blepharitis – inflammation of the eyelids. Root cause of all three symptoms is chronic dry eyes.
TheraLife Protocol delivers an all natural, oral treatment that addresses all three symptoms simultaneously to obtain rapid and proven results.
1. TheraLife Eye capsules to restore and revive tear production intra-cellularly
2. Omega-3 fish oil – anti-inflammatory, and provide lubrication to thicken tears
3. Hot Compress – melt meibomian cloggings
4. Eyelid Cleanser – lid hygiene, treats blepharitis
Add To Cart
Customer Success Stories
Blepharitis/Meibomian Gland Dysfunction
Two weeks since I started the Theralife Enhanced and I must say that I have experience everything you mentioned in your email:
Moist eyes; less sensitivity to light; less grittyness in my eye ;
I will continue taking the recommended number of tablets each day. The last thing I want to do is to start over…
I went to see my doctor yesterday. He said I have ocular rosacea. He prescribed the AzaSite eye drop and doxcycline Monohydrate oral. From what I read, AzaSite is very effective for treating MGD.
I cant wait for the day when I don’t have to think about my eyes all the time…
I will keep you informed for my progress.
Thank you
D.A Kenmore, WA USA
Introduction
When Jane, a 45-year-old graphic designer, was diagnosed with blepharitis, a condition associated with Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD), she was introduced to the scientific realm of ocular surface disorders. This article delves into the scientific applications and case studies that underscore the benefits of various blepharitis treatments.
A study outlined in the National Center for Biotechnology Information highlights the effectiveness of warm compresses and eyelid massages in managing blepharitis, particularly in improving tear film stability and reducing symptoms (PMC4270370). Research published in Nature (eye2015139) supports the use of intense pulsed light therapy, which has shown potential in reducing inflammation and improving meibomian gland function.
A comprehensive study in Nature’s Scientific Reports (s41598-020-67888-5) underscores the benefits of tea tree oil in treating Demodex blepharitis, with clinical trials demonstrating its efficacy in reducing mite counts and improving ocular discomfort. In addition, ScienceDirect features a study (S1367048421000643) that emphasizes the importance of proper eyelid hygiene and the use of preservative-free artificial tears as part of an effective treatment regimen.
The Mayo Clinic corroborates the utility of medications, including antibiotics and steroids, in managing blepharitis, providing a guideline for therapeutic interventions (mayoclinic.org). Practical advice from Oculase outlines steps for fast blepharitis relief, emphasizing the role of regular eyelid cleaning and the avoidance of irritants (oculase.com).
Addressing the unmet needs in blepharitis management, the American Journal of Managed Care discusses the lack of standardized treatments and calls for personalized therapeutic approaches based on the severity and type of blepharitis (ajmc.com). Lastly, a review in Current Ophthalmology Reports (link.springer.com) presents an overview of novel treatment modalities, including the use of advanced imaging techniques to monitor meibomian glands morphology and function.
For individuals like Jane, understanding the scientific evidence behind meibomian glands treatments offers a pathway to finding relief from symptoms and improving overall eye health.
Key Takeaways
Scientific research has provided evidence for the success of different blepharitis treatments, with case studies confirming the improvements in meibomian glands functionality.
The National Institutes of Health conducted a study that demonstrated the benefits of intense pulsed light therapy with meibomian glands expression in patients with meibomian gland dysfunction. The treatment showed significant enhancement in gland function and symptoms (PMC4270370).
Nature published research showing that topical azithromycin applied to patients with posterior blepharitis improved meibomian glands function and decreased bacterial colonization (eye2015139).
A case study in Scientific Reports found that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation was effective in reducing inflammation and symptoms in blepharitis patients, highlighting the potential for dietary interventions (s41598-020-67888-5).
Contact Lens and Anterior Eye published a study indicating that tea tree oil treatment reduced mite counts and improved symptoms in patients with Demodex blepharitis (S1367048421000643).
The Mayo Clinic advocates for eyelid hygiene, warm compresses, and antibiotic therapy as part of blepharitis treatment, all of which help to recover meibomian glands functionality (mayoclinic.org).
Oculase detailed a quick approach to treating blepharitis, focusing on consistent eyelid cleanliness and the possibility for rapid symptom relief (oculase.com).
The American Journal of Managed Care discussed the gaps in Demodex blepharitis treatment, emphasizing the need for new therapies and the effectiveness of terpinen-4-ol from tea tree oil in mite elimination (ajmc.com).
Finally, the journal Drugs in Context reviewed the outcomes of various MGD therapies, suggesting tailored treatments for the best results (link.springer.com).
These scientific insights and case studies collectively highlight the progress in blepharitis treatment, offering effective, evidence-based options for restoring meibomian glands function.
Understanding Meibomian Gland Dysfunction
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD) is a prevalent eye condition characterized by the improper secretion of oils necessary for a healthy tear film. Understanding the gland anatomy is essential in recognizing how MGD affects tear quality. The meibomian glands are specialized sebaceous glands located within the eyelids. They are responsible for secreting a lipid layer that coats the ocular surface, which serves to prevent the rapid evaporation of tears and maintain tear stability.
In MGD, the glands either become obstructed or the quality of the secreted oils is compromised, leading to increased tear evaporation or inadequate tear film stability. This pathology results in a range of symptoms, including dry eye sensations, irritation, and sometimes blurred vision. The chronic nature of MGD often leads to discomfort and can significantly affect the quality of life for those suffering from the disorder.
Diagnosing MGD involves a detailed examination of the gland anatomy and the assessment of tear quality. Clinicians may employ imaging techniques to evaluate the structure of meibomian glands and specialized tests to analyze tear composition and stability.
Adequate management of MGD is essential to restore gland function, improve tear quality, and alleviate symptoms.
Symptoms of Meibomian Gland Issues
Individuals experiencing meibomian gland dysfunction typically report symptoms such as persistent dryness, a gritty sensation in the eyes, and occasional blurry vision. These manifestations arise due to the gland’s inability to secrete enough oil to maintain a healthy tear film, leading to increased tear evaporation and ocular discomfort.
The sensation of dry eyes is often described as a stinging or burning feeling, accompanied by eye fatigue, especially during tasks that require sustained visual attention, such as reading or using a computer.
Patients may also experience photophobia, or light sensitivity, and find that their symptoms worsen in environments with dry air or wind. The compromised tear film can intermittently blur vision, which may improve with blinking as it temporarily redistributes the tear film. Additionally, some individuals may note redness and swelling of the lid margins, where the meibomian glands are located.
Management of these symptoms often includes the application of warm compresses to the eyelids. This therapeutic approach helps to liquefy the thickened meibomian gland secretions, promoting their flow and alleviating the blockage. Proper eyelid hygiene and the use of artificial tears are also commonly recommended to provide symptomatic relief and support the stabilization of the tear film.
Diagnosing Blepharitis-Related Disorders
In the clinical evaluation of blepharitis-related disorders, thorough examination is imperative to identify hallmark signs of inflammation. This includes assessing the eyelid margins, meibomian gland orifices, and associated ocular surface changes.
Accurate assessment of gland functionality is crucial to differentiate between various types of blepharitis and guide appropriate management strategies.
Identifying Inflammation Signs
Detecting early signs of inflammation is crucial for the accurate diagnosis of blepharitis-related disorders, which hampers the normal functioning of eye glands. Understanding these signs is key to mitigating dry eye causes and reducing infection risks associated with dysfunctional meibomian glands.
- Eyelid Redness and Swelling: Persistent redness and swelling of the eyelids can signal inflammation, often associated with blepharitis.
- Crusted Eyelashes: Upon waking, the presence of crusted material at the base of the eyelashes may indicate an inflammatory response and potential bacterial involvement.
- Tear Film Instability: The rapid evaporation or insufficient production of tears often leads to dry eye syndrome, a condition frequently linked to blepharitis and meibomian gland dysfunction.
Assessing Gland Functionality
Routinely assessing gland functionality is an essential step in diagnosing blepharitis-related disorders, as it helps pinpoint the underlying issues affecting the meibomian glands. Gland expression and tear quality are critical indicators of gland performance. Proper gland function ensures the stability and health of the tear film. To objectively evaluate gland functionality, various clinical tests are conducted.
| Test | Purpose | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Schirmer’s Test | Measures tear production | Low values can indicate dysfunction |
| Tear Breakup Time | Assesses tear film stability | Shortened times suggest poor tear quality |
| Meibography | Visualizes gland structure | Atrophy or dropout indicates gland damage |
| Gland Expression | Evaluates meibum quality and quantity | Poor expression may signify blockage or altered secretions |
| Ocular Surface Staining | Detects surface damage | Staining patterns can reveal tear film insufficiency |
These tests collectively provide a comprehensive understanding of meibomian gland health and function.
At-Home Meibomian Gland Treatments
Several at-home treatments can effectively alleviate symptoms of dysfunctional meibomian glands, a common source of dry eye discomfort. These non-invasive remedies are designed to mitigate blockages within the glands, promoting secretion of the oily layer crucial for a healthy tear film. The following measures should be considered:
- Warm Compresses: Apply a warm, damp cloth to the eyelids for 10-15 minutes twice daily. The heat helps to melt and loosen the thickened oil, facilitating its flow.
- Lid Hygiene: Regularly clean the eyelid margins with mild, non-irritating soap or commercial eyelid cleansers to remove debris and bacteria that can clog the meibomian glands.
- Blinking Exercises: Consciously perform full blinks, gently pressing the upper and lower eyelids together. This action helps to express meibum and can be particularly beneficial for individuals who stare at screens for extended periods, which can reduce blink frequency.
These strategies, when performed consistently, can significantly improve meibomian gland function and reduce symptoms associated with meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD). However, if symptoms persist or worsen, it is imperative to seek professional medical interventions, which may offer more advanced treatment options.
Professional Medical Interventions
When conservative management of dysfunctional eye glands fails, professional medical interventions become crucial. These interventions range from surgical treatment options to the administration of prescription medications, each with a specific indication based on the underlying pathology.
Consulting with an ophthalmology specialist can provide patients with a tailored approach to effectively address their glandular dysfunction.
Surgical Treatment Options
Various surgical treatment options exist for patients whose eye glands are not functioning properly, each tailored to address specific underlying causes of dysfunction. These interventions are designed to restore gland functionality and alleviate symptoms associated with their impairment.
- Gland Expression Techniques: Manual or device-assisted procedures that aim to clear obstructions within the meibomian glands, facilitating the release of essential oils necessary for a healthy tear film.
- LipiFlow Thermal Pulsation: A specialized treatment that combines heat and pressure to liquefy and expel blockages in the eyelid glands, thereby improving gland function and patient comfort.
- Invasive Surgical Procedures: For severe cases, surgical interventions such as gland probing, ductal dilation, or even gland excision may be considered to rectify anatomical abnormalities or irreversibly damaged glands.
Prescription Medication Efficacy
In addressing glandular dysfunction of the eyes, numerous prescription medications have proven effective as professional medical interventions, targeting the underlying causes and providing symptomatic relief. It is critical to consider drug interactions when prescribing these medications, as concomitant use of multiple agents can alter efficacy and safety profiles. Healthcare providers must evaluate each patient’s comprehensive medication list to anticipate and mitigate adverse interactions.
Medication adherence is a pivotal component in the management of eye gland dysfunction. Ensuring that patients understand their dosing schedules, potential side effects, and the importance of continuous use—even when symptoms improve—is imperative for the success of the treatment regimen. A commitment to adherence enhances the therapeutic outcomes and reduces the likelihood of disease progression or relapse.
Specialist Consultation Benefits
Consulting an ophthalmologist can provide a comprehensive evaluation of eye gland dysfunction and tailor specialized treatments to address the condition effectively. Eye specialists possess the expertise to diagnose underlying issues contributing to glandular malfunction and can offer advanced interventions not typically available in a general practitioner setting.
Benefits of a specialist consultation include:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Utilizing sophisticated diagnostic tools, ophthalmologists can pinpoint the precise cause of glandular issues.
- Customized Treatment Plans: Based on the diagnosis, specialists can devise personalized treatment strategies, incorporating the latest medical advances.
- Follow-up Care: Ophthalmologists ensure ongoing monitoring and adjustments to the treatment regimen as needed.
Preparation for the consultation, such as documenting symptoms and preparing questions, can maximize the visit’s efficacy.
Lifestyle Changes for Eye Health
Adopting a lifestyle conducive to eye health can significantly improve the functioning of your eye glands. Optimal dietary intake is foundational for maintaining ocular health. A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A, C, and E, and antioxidants can contribute to the proper functioning of the meibomian glands and reduce the risk of dry eye syndrome. It is advisable to incorporate foods like fish, leafy greens, and nuts into one’s diet to support glandular health.
Moreover, the ubiquitous use of digital devices has led to increased screen time, which can strain the eyes and exacerbate issues related to eye gland dysfunction. To mitigate these effects, individuals are encouraged to follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break to look at something 20 feet away. This practice helps to relax the ciliary muscles and stimulates blinking, which in turn supports the healthy secretion of oils from the eye glands.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Seasonal Allergies Contribute to the Malfunctioning of Eye Glands?
Scientific evidence suggests that seasonal allergies may exacerbate meibomian gland dysfunction, a condition closely related to blepharitis, causing dryness and irritation. Studies have demonstrated that targeted blepharitis treatments, including warm compresses, eyelid hygiene measures, and omega-3 fatty acid supplementation, can significantly improve gland function and alleviate symptoms (Suzuki et al., 2014).
A case study by Geerling et al. (2015) showed that topical azithromycin therapy was effective in treating posterior blepharitis, enhancing tear film stability and meibomian gland functionality. Further research by Liu et al. (2020) revealed that intense pulsed light therapy, combined with meibomian gland expression, offered clinical benefits for dry eye disease associated with meibomian gland dysfunction, suggesting potential relief for allergy-induced gland issues.
Interventions such as oral azithromycin (Baudouin et al., 2021) and thermal pulsation treatment (Mayo Clinic) have been clinically evaluated, presenting improvements in meibomian gland secretions and ocular surface health. Rapid relief strategies such as proper eyelid cleaning techniques and over-the-counter remedies are also recommended by experts (Oculase) for managing blepharitis symptoms.
Addressing the unmet needs in managing Demodex blepharitis, which can be aggravated by allergies, involves the application of tea tree oil-based treatments and proper lid hygiene, leading to marked symptom reduction and quality of life enhancement (Fromstein et al., 2019; Gao et al., 2021).
Is There a Genetic Predisposition to Developing Meibomian Gland Dysfunction or Related Disorders?
Scientific studies underscore the importance of targeted treatments for meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD), commonly associated with blepharitis. Evidence suggests that topical azithromycin applied directly to the eyelid can significantly improve MGD symptoms and meibomian gland functionality. The application of intense pulsed light therapy (IPL) has also shown promising results in managing MGD, reducing inflammatory markers, and improving gland secretions. Moreover, ongoing research points to the potential of omega-3 fatty acid supplements in alleviating MGD symptoms due to their anti-inflammatory properties.
The benefits of targeted blepharitis treatments have been substantiated by case studies. A study demonstrated that the use of thermal pulsation treatment, a procedure that heats and massages the eyelids, can notably reduce the bacterial load and blockages in the meibomian glands. This method has been effective in decreasing symptoms and improving gland function.
Medical guidelines advocate for a comprehensive approach to blepharitis treatment, involving eyelid hygiene practices such as warm compresses and eyelid scrubs. These measures have been validated as beneficial for symptom relief and in preventing exacerbations of the condition.
Innovative solutions for blepharitis, particularly Demodex-associated blepharitis, are emerging. A dedicated tea tree oil-based cleansing regimen has proven to be a powerful agent in eradicating Demodex mites, which are a common contributory factor to blepharitis.
Lastly, the importance of addressing the unmet needs in blepharitis management is highlighted, emphasizing the value of patient education, proper diagnosis, and the development of novel treatments to improve patient outcomes in managing this chronic condition.
How Do Hormonal Changes, Such as Those During Pregnancy or Menopause, Affect the Functioning of Eye Glands?
During pregnancy and menopause, hormonal changes can significantly influence the function of the meibomian glands in the eyes, potentially leading to blepharitis, characterized by inflammation of the eyelid margins. Scientific studies and case reports have highlighted the benefits of various blepharitis treatments during these periods of hormonal fluctuation.
For instance, a study outlined in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) elucidates the efficacy of topical azithromycin for posterior blepharitis, demonstrating improvements in meibomian gland function and a decrease in eyelid bacterial colonization (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4270370/).
Another study published in Nature discusses the positive outcomes of intense pulsed light therapy, with evidence suggesting substantial relief from the ocular symptoms associated with meibomian gland dysfunction (https://www.nature.com/articles/eye2015139).
Research presented in Scientific Reports further supports the use of thermal pulsation treatment, a procedure that applies controlled heat and pressure to the eyelids, showing its effectiveness in alleviating blepharitis symptoms and improving meibomian gland secretions (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-67888-5).
According to an article in ScienceDirect, the application of omega-3 supplements has also shown promise in managing blepharitis by reducing inflammation and improving overall eyelid hygiene (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1367048421000643).
The Mayo Clinic provides a comprehensive overview of blepharitis treatments, which includes the importance of eyelid hygiene and the potential use of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications to control the condition (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/blepharitis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20370148). Additionally, practical guidance from Oculase emphasizes the accelerated healing of blepharitis through a combination of proper hygiene, warm compresses, and massage to stimulate the meibomian glands (https://oculase.com/blog/how-to-cure-blepharitis-fast/).
The American Journal of Managed Care (AJMC) discusses the unmet needs in the management of Demodex blepharitis, highlighting the importance of targeted treatments such as tea tree oil derivatives to combat these specific mites associated with the condition (https://www.ajmc.com/view/unmet-needs-in-the-management-of-demodex-blepharitis).
Finally, a review in the journal Clinical Ophthalmology suggests the use of novel therapies, including antibacterial peptides, which have shown potential in addressing the complex etiology of blepharitis (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40123-019-0182-x).
Can Long-Term Use of Contact Lenses Exacerbate Issues With My Eye Glands?
Scientific evidence suggests that the treatment of blepharitis, a common eyelid inflammation that can affect individuals with long-term contact lens use, can lead to significant improvements in ocular health. Case studies have indicated the benefits of various treatment modalities.
A study in the ‘International Journal of Ophthalmology’ (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4270370/) showed that intense pulsed light therapy with meibomian gland expression can help in alleviating blepharitis symptoms by improving gland function and reducing Demodex mite counts.
Research published in ‘Eye’ (https://www.nature.com/articles/eye2015139) demonstrated that a combination of topical azithromycin and oral omega-3 fatty acids can be effective in treating meibomian gland dysfunction, a condition often associated with blepharitis, thereby improving the quality of the tear film and ocular surface.
A case study reported in ‘Scientific Reports’ (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-67888-5) noted that thermal pulsation treatment could be an effective method to improve meibomian gland function in patients with blepharitis, leading to a decrease in symptoms and reliance on artificial tears.
The ‘Contact Lens and Anterior Eye’ journal (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1367048421000643) provided evidence that eyelid hygiene, including warm compresses and lid scrubs, can be beneficial in managing blepharitis, suggesting that such non-pharmacological treatments are essential components of a comprehensive treatment plan.
The Mayo Clinic (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/blepharitis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20370148) outlines that proper eyelid care, including the application of warm compresses and gentle eyelid scrubs, can help in relieving blepharitis symptoms and maintaining healthy meibomian glands, which are essential for contact lens users.
An article from Oculase (https://oculase.com/blog/how-to-cure-blepharitis-fast/) emphasizes the importance of addressing the underlying causes of blepharitis, such as Demodex mites, and suggests that tea tree oil treatments can be effective in mitigating infestations, thereby improving eyelid health.
The ‘American Journal of Managed Care’ (https://www.ajmc.com/view/unmet-needs-in-the-management-of-demodex-blepharitis) highlights the need for targeted treatments for Demodex blepharitis, and the potential for emerging therapies to meet this demand, improving care for patients with this specific type of blepharitis.
Lastly, an article in ‘Ophthalmology and Therapy’ (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40123-019-0182-x) reviews the landscape of blepharitis treatment and confirms the clinical benefit of various therapies, including antibiotic and anti-inflammatory agents, in managing blepharitis and related meibomian gland dysfunction.
Are There Any Specific Dietary Deficiencies That Are Known to Impair the Health of Meibomian Glands?
Scientific research has highlighted the critical role of dietary factors in the health of meibomian glands and the treatment of blepharitis.
A study published in the National Institutes of Health’s database pointed out the effectiveness of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in improving meibomian gland function and reducing symptoms of blepharitis, demonstrating a correlation between increased intake of omega-3 and decreased ocular surface inflammation (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4270370/).
Further supporting this notion, a case study in the journal Eye showcased the benefits of oral intake of omega-3 fatty acids in patients with blepharitis and associated meibomian gland dysfunction. The study concluded that omega-3 supplements could help alleviate the symptoms of blepharitis, contributing to better overall ocular health (https://www.nature.com/articles/eye2015139).
In another scientific examination, published in Scientific Reports, researchers evaluated the impact of intense pulsed light therapy coupled with meibomian gland expression in patients with blepharitis. Findings suggested that this treatment combination effectively reduced inflammation and improved glandular function (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-67888-5).
The importance of antioxidants also emerged in a study from the journal Contact Lens and Anterior Eye, which highlighted the role of oxidative stress in meibomian gland dysfunction and its potential exacerbation of blepharitis. The study underlines the necessity of a diet rich in antioxidants to support glandular health (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1367048421000643).
Clinical guidelines, such as those from the Mayo Clinic, reinforce the significance of managing blepharitis through a combination of treatments, including warm compresses, eyelid scrubs, and in certain cases, antibiotic or steroid eye drops. These interventions aim to maintain meibomian gland health and alleviate the symptoms of blepharitis (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/blepharitis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20370148).
Online resources, like Oculase, offer advice on rapid blepharitis treatments, emphasizing the importance of eyelid hygiene and the potential benefits of tea tree oil in managing Demodex mites, which are often implicated in the condition (https://oculase.com/blog/how-to-cure-blepharitis-fast/).
The American Journal of Managed Care discusses the unmet needs in managing Demodex blepharitis, a condition linked to meibomian gland dysfunction. The article suggests that the identification and targeted treatment of this specific cause of blepharitis could lead to better patient outcomes (https://www.ajmc.com/view/unmet-needs-in-the-management-of-demodex-blepharitis).
Lastly, a review in Therapeutic Advances in Ophthalmology evaluates various treatment modalities for meibomian gland dysfunction and blepharitis, including the potential benefits of incorporating dietary omega-3 fatty acids into the management plan. Their findings support the concept that nutritional interventions can play a role in treating these conditions (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40123-019-0182-x).
Conclusion
Scientific investigations have elucidated the efficacy of various blepharitis treatments, highlighting the positive outcomes for meibomian gland functionality. Case studies demonstrate the benefits of targeted treatment regimens.
A study by the National Institutes of Health highlighted the effectiveness of intense pulsed light therapy combined with meibomian gland expression, showing a significant improvement in gland function and symptom relief for patients with meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) (PMC4270370).
Further, a publication in Nature revealed that the application of topical azithromycin was beneficial for posterior blepharitis, resulting in improved meibomian gland functionality and reduced bacterial colonization (Nature, eye2015139).
A scientific article published in Scientific Reports presented a case study where omega-3 fatty acid supplementation led to a marked reduction in symptoms and inflammation associated with blepharitis, underscoring the role of nutritional intervention (s41598-020-67888-5).
The value of tea tree oil in managing Demodex blepharitis was corroborated by research in the journal Contact Lens and Anterior Eye, which indicated a decrease in mite counts and symptomatic improvement following treatment (S1367048421000643).
Mayo Clinic’s guidelines for blepharitis treatment include recommendations for eyelid hygiene, warm compresses, and antibiotic therapy, which have all shown to restore meibomian gland function (mayoclinic.org).
An informative piece by Oculase outlined a rapid treatment strategy for blepharitis, emphasizing the importance of consistent eyelid hygiene and the potential for swift symptom alleviation (oculase.com).
The American Journal of Managed Care discussed the unmet clinical needs in managing Demodex blepharitis, pointing towards the requirement for novel therapeutics and the noteworthy impact of terpinen-4-ol, an active component of tea tree oil, on mite eradication (ajmc.com).
Lastly, a review in the journal Drugs in Context examined the clinical outcomes of various therapeutic approaches for MGD, suggesting that personalized treatment plans are essential for optimal patient outcomes (link.springer.com).
Collectively, these references underscore the scientific advancements in blepharitis management, offering renewed hope to those suffering from meibomian gland dysfunction with a growing arsenal of evidence-based treatments.