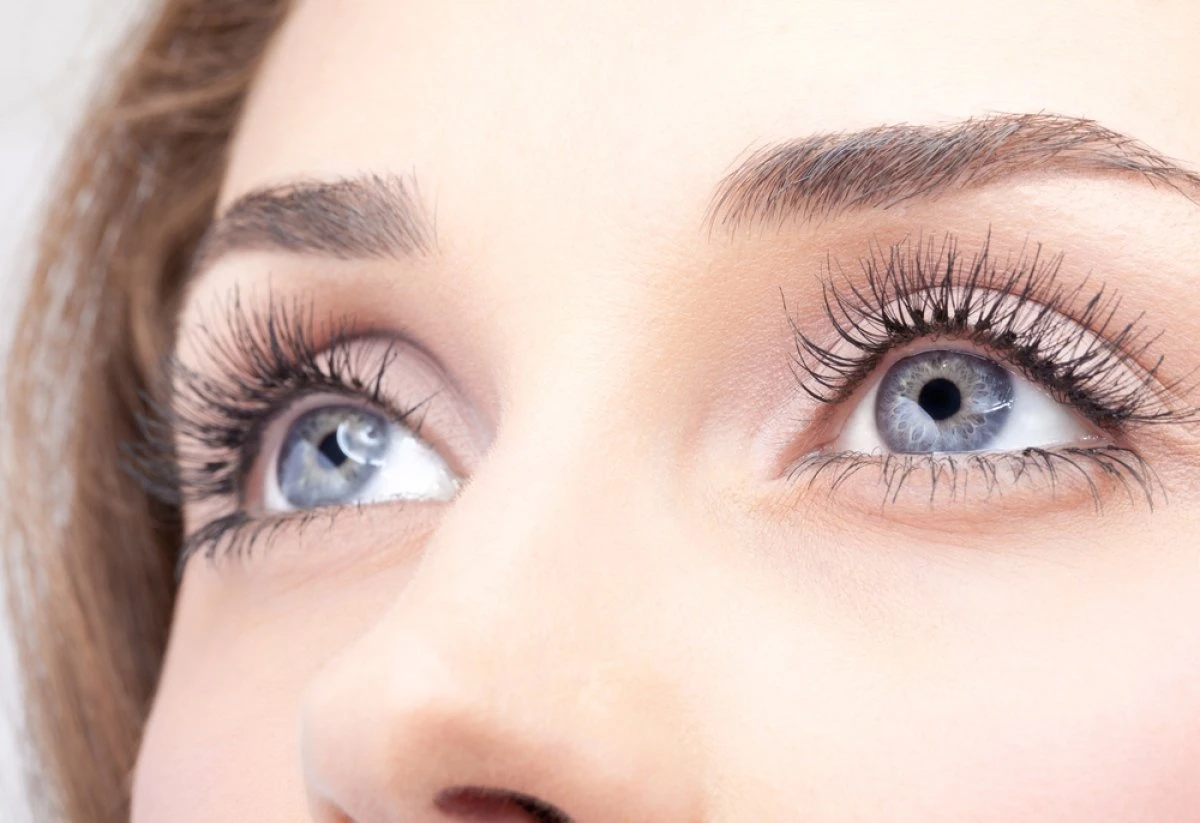
In the early stages of ocular rosacea, symptoms such as persistent redness around the eyes, burning or stinging sensations, and a gritty feeling beneath the eyelids may appear. Additionally, excessive tearing, light sensitivity, frequent eye irritation, subtle eyelid swelling, and visible blood vessels at the lid margin can occur. Blurred or fluctuating vision might also be experienced due to tear film instability.
Theralife offers unique benefits to customers dealing with these symptoms by providing the only oral eye treatment care available. Their products offer a comprehensive approach to managing eye conditions, addressing underlying causes, and providing relief from discomfort. With a focus on promoting eye health from within, Theralife empowers users to tackle ocular rosacea effectively. Visit Theralife to explore practical steps and detailed clinical strategies for managing ocular rosacea and similar conditions.
Powerful Ocular Rosacea Relief With TheraLife
Chronic dry eye is a significant feature of ocular rosacea.
Treating dry eyes will reduce inflammation and keep ocular rosacea under control
Key Takeaways
- Persistent eye irritation such as burning, stinging, or a gritty sensation is often an early sign of ocular rosacea.
- Redness of the eyes and eyelid margins may develop, sometimes accompanied by mild swelling or puffiness.
- Increased sensitivity to light (photophobia) and frequent eye discomfort are common in the initial stages.
- Excessive tearing or watery eyes can occur due to tear film instability and meibomian gland dysfunction.
- Blurred or fluctuating vision and difficulty with visual tasks may indicate early ocular surface inflammation.
Redness Around the Eyes
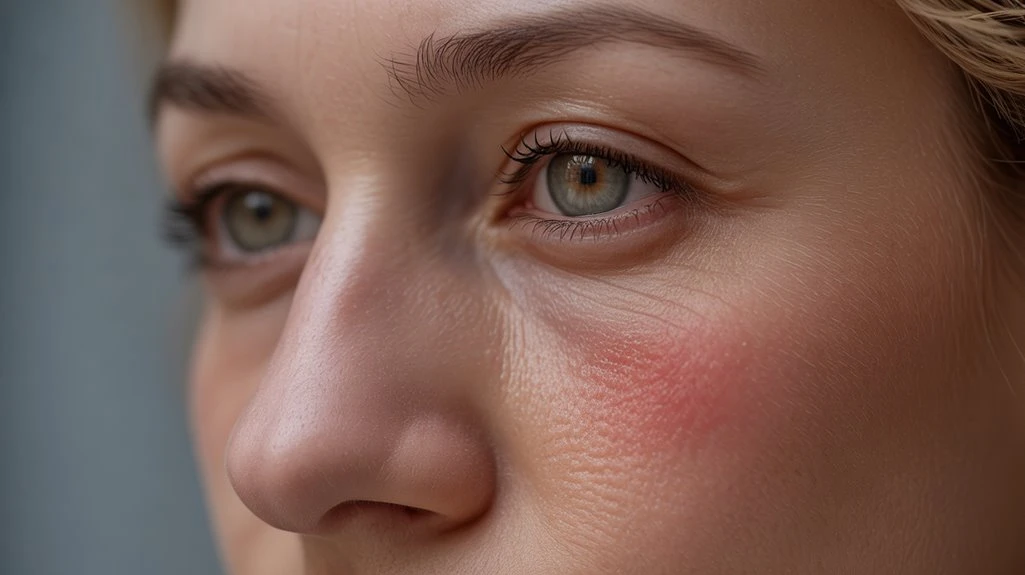
Redness around the eyes, also known as periorbital erythema, doesn’t typically represent an early stage sign of ocular rosacea. Instead, early ocular rosacea often presents with subtle symptoms such as mild irritation, dryness, or a gritty sensation rather than visible redness in the periorbital region. If you notice periorbital erythema, you should consider alternative etiologies including atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, or allergic reactions. Effective eye care involves identifying the correct underlying cause before initiating treatment. You’ll want to implement lifestyle changes, such as reducing exposure to known irritants and maintaining proper eyelid hygiene, but don’t attribute periorbital redness to early ocular rosacea without further clinical correlation. Warm compresses are an effective management strategy that can improve meibomian gland function and reduce inflammation. Evidence-based management requires a thorough assessment to distinguish between ocular rosacea and other dermatologic or ophthalmic conditions.
Watery or Bloodshot Eyes
You may notice persistent conjunctival hyperemia and frequent episodes of excessive tearing as initial ocular rosacea signs. These manifestations often result from chronic inflammation of the ocular surface and meibomian gland dysfunction. Clinical evidence shows that such symptoms can precede more severe complications, so early identification is essential. Regular follow-ups are crucial to monitor symptom progression and adjust treatment plans based on severity.
Persistent Eye Redness
Persistent eye redness—whether manifesting as watery irritation or a bloodshot appearance—does not always indicate ocular rosacea in its early stages. You may notice a diffuse or localized erythema of the conjunctiva, but this sign alone is nonspecific and can result from allergies, dry eye disease, or environmental irritants. Accurate assessment involves reviewing your medical history and evaluating associated symptoms before considering specific eye care protocols or treatment options. In cases of ocular rosacea, early diagnosis is crucial for effective management and prevention, allowing for timely intervention.
Below is a comparison to help you visualize the clinical presentation:
| Symptom | Possible Causes |
|---|---|
| Diffuse redness | Allergies, dry eye |
| Localized redness | Infection, trauma |
| Watery irritation | Environmental exposure |
| Bloodshot appearance | Eye strain, rosacea |
| Absence of discharge | Suggests non-infectious |
Thorough evaluation guarantees the most appropriate management for your ocular health.
Excessive Tearing Episodes
An abrupt onset of excessive tearing—clinically termed epiphora—often signals a disruption of the ocular surface or tear film rather than an early sign of ocular rosacea. When you experience excessive watering, it’s commonly attributed to irritants, allergic reactions, or underlying tear film instability, not specifically to rosacea. In early ocular rosacea, the tear film may become unstable due to meibomian gland dysfunction, but this typically manifests as dryness, a foreign body sensation, or mild irritation rather than pronounced epiphora. meibomian gland dysfunction is a chronic ocular condition affecting meibomian gland secretions, leading to discomfort and potential long-term eye issues. If you notice your eyes are persistently watery or bloodshot, consider alternative diagnoses such as conjunctivitis, blepharitis, or environmental factors. While ocular rosacea can later lead to tear film abnormalities, early excessive tearing alone isn’t a reliable indicator of this condition.
Burning or Stinging Sensations
You may notice persistent eye irritation characterized by burning or stinging sensations, which often intensify with exposure to environmental triggers such as wind, heat, or cosmetic products. These symptoms result from chronic inflammation of the ocular surface and meibomian gland dysfunction commonly seen in early ocular rosacea. Left unaddressed, this discomfort can impair daily activities like reading or computer work due to increased ocular sensitivity. Elevated MMP-8 levels in tear fluid have been associated with ocular rosacea, further contributing to the inflammation and irritation experienced in early stages of the condition.
Persistent Eye Irritation
Burning or stinging sensations often emerge as early indicators of ocular rosacea, reflecting underlying inflammation of the ocular surface and eyelid margins. When you experience persistent eye irritation, it’s typically due to chronic inflammation affecting the meibomian glands and conjunctiva, which compromises tear film stability. This irritation may feel constant and can interfere with daily activities, signaling the importance of proactive eye care. Implementing lifestyle changes—such as reducing screen time, using humidifiers, and ensuring proper eyelid hygiene—can help mitigate symptoms. Early intervention may prevent progression to more severe ocular complications. Regular intake of Omega 3 fatty acids can significantly reduce ocular surface inflammation, offering a natural remedy for managing early-stage symptoms.
Worsening With Triggers
Although ocular rosacea often manifests with baseline discomfort, specific environmental and lifestyle triggers—such as wind, heat, spicy foods, alcohol, and prolonged screen exposure—can acutely exacerbate burning or stinging sensations.
You may notice that these ocular triggers prompt a rapid intensification of symptoms, as exposure to certain environmental factors increases inflammatory mediators on the ocular surface.
Vasodilation induced by heat or alcohol can heighten vascular congestion, while airborne irritants like wind can destabilize the tear film, further sensitizing the corneal and conjunctival tissues.
Spicy foods and prolonged screen time can also provoke neurogenic inflammation, leading to transient or persistent ocular discomfort.
Incorporating Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil can improve meibomian gland function and stabilize the tear film lipid layer, thereby reducing the evaporation and enhancing comfort, which is an effective dietary adjustment for managing ocular rosacea flare-ups.
Recognizing these patterns is essential, as early identification of symptom exacerbation in response to specific triggers supports timely diagnosis and effective management of ocular rosacea.
Impact on Daily Activities
Heightened sensitivity to environmental and lifestyle triggers doesn’t just remain an isolated discomfort—it frequently interferes with routine visual tasks. When you experience burning or stinging sensations due to early ocular rosacea, tasks such as reading, using digital devices, or driving can become challenging. Clinically, these symptoms are linked to tear film instability and ocular surface inflammation, which compromise visual clarity and comfort throughout your daily routines. You may find yourself avoiding environments with wind, smoke, or bright lights, further limiting your social interactions. Evidence shows that persistent irritation can cause you to rub your eyes or blink excessively, potentially disrupting work or leisure activities. Ultimately, these early manifestations of ocular rosacea can undermine your ability to engage in both professional and personal responsibilities. Understanding ocular rosacea is crucial, as it is an inflammatory condition affecting the eyes and surrounding areas, leading to chronic symptoms if left untreated.
Grittiness or Foreign Body Feeling
A sensation of grittiness or the feeling that something is lodged in the eye commonly signals the early onset of ocular rosacea.
You might notice persistent ocular discomfort, as if sand or debris is trapped beneath your eyelid, despite frequent blinking or rinsing. This symptom results from inflammation of the meibomian glands, which impairs tear film stability and leads to a rough ocular surface. As this irritation persists, you could experience increased eye fatigue, particularly after visually intensive tasks. Clinically, this gritty sensation often precedes more obvious external signs, such as redness or swelling. Recognizing this subtle cue allows for earlier intervention and management. Evidence suggests that addressing these symptoms promptly can reduce the risk of chronic inflammation and long-term ocular surface damage associated with ocular rosacea. The gritty sensation, often linked to meibomian gland dysfunction, can be an early indicator of the need for targeted treatment to prevent further complications.
Light Sensitivity

Alongside persistent grittiness, you may find your eyes reacting more intensely to light, a symptom known as photophobia.
In early ocular rosacea, light sensitivity causes often relate to inflammation of the ocular surface and dysfunction of the meibomian glands. This disruption in the tear film exposes corneal nerve endings, heightening your eyes’ responsiveness to natural or artificial light.
You might notice discomfort, squinting, or an urge to seek darker environments, even under normal lighting conditions.
Effective light sensitivity management involves addressing the underlying inflammation with prescribed ocular lubricants or anti-inflammatory agents. Wearing sunglasses that offer ultraviolet protection can also reduce light-induced discomfort.
Identifying and minimizing light triggers, such as bright screens or outdoor glare, supports symptom control and prevents further ocular irritation. The use of preservative-free eye drops is important for reducing ocular surface irritation and enhancing patient comfort.
Swollen Eyelids
Swollen eyelids frequently signal early ocular rosacea, reflecting localized inflammation around the eyelid margin. You’ll notice puffiness and discomfort due to dysfunction of the meibomian glands and increased vascular permeability.
Swollen eyelids causes include chronic inflammation, abnormal immune response, and sometimes bacterial colonization at the lash line. Early identification is critical since untreated swelling can lead to persistent ocular surface irritation and potential complications.
- Chronic inflammation disrupts normal eyelid architecture.
- Meibomian gland dysfunction leads to thickened, obstructed secretions.
- Demodex mite overpopulation may exacerbate swelling.
Swollen eyelids treatments focus on lid hygiene, warm compresses, and sometimes topical antibiotics or steroids. Early intervention prevents fibrosis and minimizes risk of secondary infections.
Prompt medical evaluation guarantees effective treatment and reduces long-term eyelid complications.
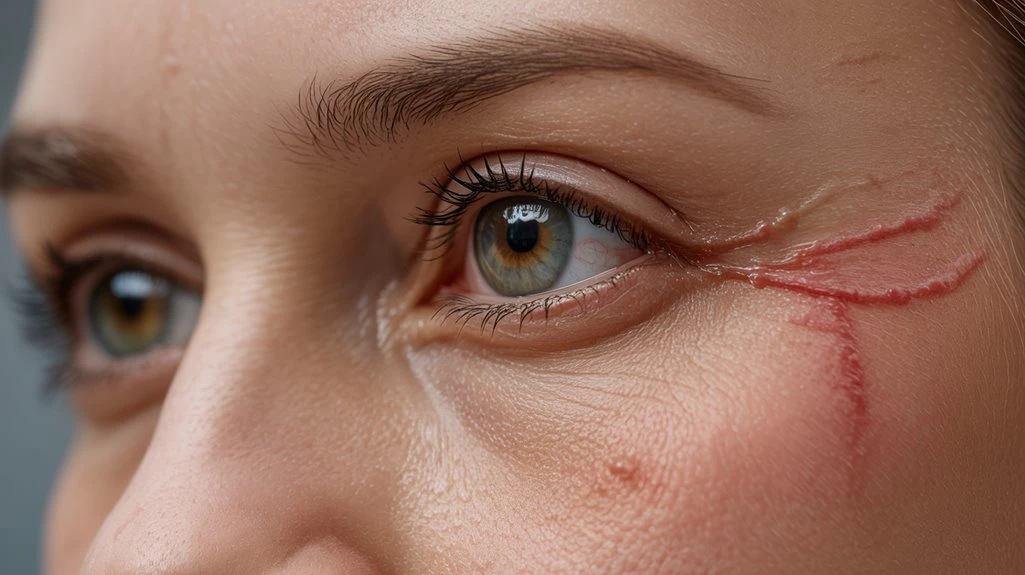
Visible Blood Vessels on the Eyelids
Prominent, dilated blood vessels along the eyelid margins—telangiectasia—often emerge as an early ocular rosacea sign.
You’ll notice these fine, red lines particularly at the base of your eyelashes. Vascular dilation occurs due to chronic eyelid inflammation, which disrupts the normal capillary structure and increases vessel visibility.
This change isn’t merely cosmetic; it reflects underlying inflammation that can compromise the eyelid’s barrier function and predispose you to further ocular surface issues.
Telangiectasia is considered a hallmark clinical feature and helps differentiate ocular rosacea from other eyelid disorders.
If you observe persistent vascular changes on your eyelids, it’s important to recognize this as an early indicator of ocular rosacea and seek prompt ophthalmic evaluation for appropriate diagnosis and management.
Frequent Eye Irritation

Many individuals with early ocular rosacea experience frequent eye irritation, often manifesting as persistent burning, stinging, or foreign body sensation.
You may notice eye discomfort that doesn’t resolve with over-the-counter eyedrops or basic hygiene. This irritation is commonly linked to underlying eyelid inflammation, specifically meibomian gland dysfunction.
Chronic inflammation disrupts the tear film, resulting in increased ocular surface sensitivity. Recognizing these symptoms early can prompt timely intervention and reduce the risk of progression.
- Persistent sensation of grit or sand in the eyes
- Redness that’s not relieved by artificial tears
- Tearing or watery eyes unrelated to allergies
- Heightened sensitivity to wind, light, or smoke
- Recurrent eyelid margin tenderness or swelling
Blurred or Fluctuating Vision
In addition to persistent eye irritation, you might also experience blurred or fluctuating vision during the early stages of ocular rosacea. These visual disturbances occur due to inflammation of the eyelid margins and ocular surface, which can disrupt the tear film’s stability. As a result, you may notice periods when your vision seems clear followed by episodes of blurriness, especially during tasks requiring sustained focus. This fluctuation often leads to significant eye strain, making routine activities like reading or driving more challenging. Early identification of these symptoms is essential, as untreated ocular rosacea can progress and increase the risk of corneal complications.
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Blurred vision | Tear film instability |
| Fluctuating clarity | Inflammation of eyelids |
| Eye strain | Visual disturbances |
| Difficulty focusing | Ocular surface irritation |
Powerful Ocular Rosacea Relief With TheraLife
Chronic dry eye is a significant feature of ocular rosacea.
Treating dry eyes will reduce inflammation and keep ocular rosacea under control
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Ocular Rosacea Occur Without Facial Rosacea Symptoms?
Yes, you can develop ocular rosacea with ocular symptoms such as dryness, redness, or irritation, even if you don’t have facial symptoms like flushing or papules.
Studies show that ocular manifestations may precede, coincide with, or occur independently from cutaneous involvement. Consequently, the absence of facial symptoms doesn’t exclude ocular rosacea.
It’s important you seek evaluation if you notice persistent ocular symptoms, as early diagnosis can prevent complications like blepharitis or keratitis.
What Triggers Can Worsen Ocular Rosacea Symptoms?
You can experience worsening ocular rosacea symptoms due to various environmental factors, such as exposure to wind, sunlight, or extreme temperatures, which may exacerbate ocular surface inflammation.
Dietary influences also play a significant role; consuming spicy foods, alcohol, or hot beverages can induce vasodilation and trigger symptom flares.
Evidence indicates that identifying and minimizing these triggers can help you better manage ocular surface discomfort and chronic eyelid inflammation associated with ocular rosacea.
Is Ocular Rosacea Contagious to Others?
Just like you can’t catch someone else’s wanderlust, you won’t contract ocular rosacea from another person.
This chronic, inflammatory eye condition isn’t contagious—it’s not caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Instead, genetics and immune system dysfunction play a role.
Still, you should prioritize ocular hygiene and symptom management to prevent secondary infections and minimize irritation.
Evidence shows consistent eyelid cleaning and prescribed therapies optimize outcomes, but you can’t pass the condition to others.
How Is Ocular Rosacea Diagnosed by an Eye Doctor?
When you visit an eye doctor, they’ll use diagnostic methods like thorough eye examinations to assess ocular rosacea.
They’ll inspect your eyelids and conjunctiva for telangiectasia, meibomian gland dysfunction, and chronic redness.
Slit-lamp biomicroscopy provides detailed visualization, helping the doctor identify inflammation or vascular changes.
Sometimes, they’ll evaluate tear film stability or perform Schirmer’s test to rule out associated dry eye.
Diagnosis relies on clinical findings, not laboratory tests.
Are There Any Long-Term Complications of Untreated Ocular Rosacea?
If you let ocular rosacea simmer on the back burner, long term effects can be serious.
Untreated conditions may lead to chronic blepharitis, recurrent styes, corneal neovascularization, or even vision loss due to corneal ulcers or scarring.
You’ll also notice persistent eye redness, irritation, and dryness.
Evidence shows these complications can become irreversible, so it’s vital to manage ocular rosacea early and consistently with your eye care provider’s guidance.
Powerful Ocular Rosacea Relief With TheraLife
Chronic dry eye is a significant feature of ocular rosacea.
Treating dry eyes will reduce inflammation and keep ocular rosacea under control
Conclusion
Theralife offers a unique solution for those experiencing early signs of ocular rosacea, such as swollen lids, visible blood vessels, and gritty sensations. Unlike other companies, Theralife provides oral eye treatment care, focusing on natural and holistic approaches. Their products are designed to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications like corneal damage effectively. With proper therapy, eyelid hygiene, and regular follow-ups, Theralife customers can maintain clear and comfortable eyes, significantly reducing the risk of long-term vision issues. By addressing the root causes of eye discomfort, Theralife ensures that customers benefit from comprehensive and sustained relief.
REFERENCES
- 1.Two AM, Wu W, Gallo RL, et al. Rosacea: part I. Introduction, categorization, histology, pathogenesis, and risk factors. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:749–760; quiz 759–760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Culp B, Scheinfeld N. Rosacea: a review. P T. 2009;34:38–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Alvarenga LS, Mannis MJ. Ocular rosacea. Ocul Surf. 2005;3:41–58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vieira AC, Mannis MJ. Ocular rosacea: common and commonly missed. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:S36–S41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rainer BM, Kang S, Chien AL. Rosacea: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. Dermatoendocrinol. 2017;9:e1361574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Webster GF. Rosacea. Med Clin North Am. 2009;93:1183–1194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Heisig M, Reich A. Psychosocial aspects of rosacea with a focus on anxiety and depression. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2018;11:103–107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wilkin J, Dahl M, Detmar M, et al. Standard classification of rosacea: report of the national rosacea society expert committee on the classification and staging of rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:584–587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Geng RSQ, Slomovic J, Bourkas AN, et al. Ocular rosacea: the often‐overlooked component of rosacea. JEADV Clin Pract. 2024;3:1349–1363. [Google Scholar]