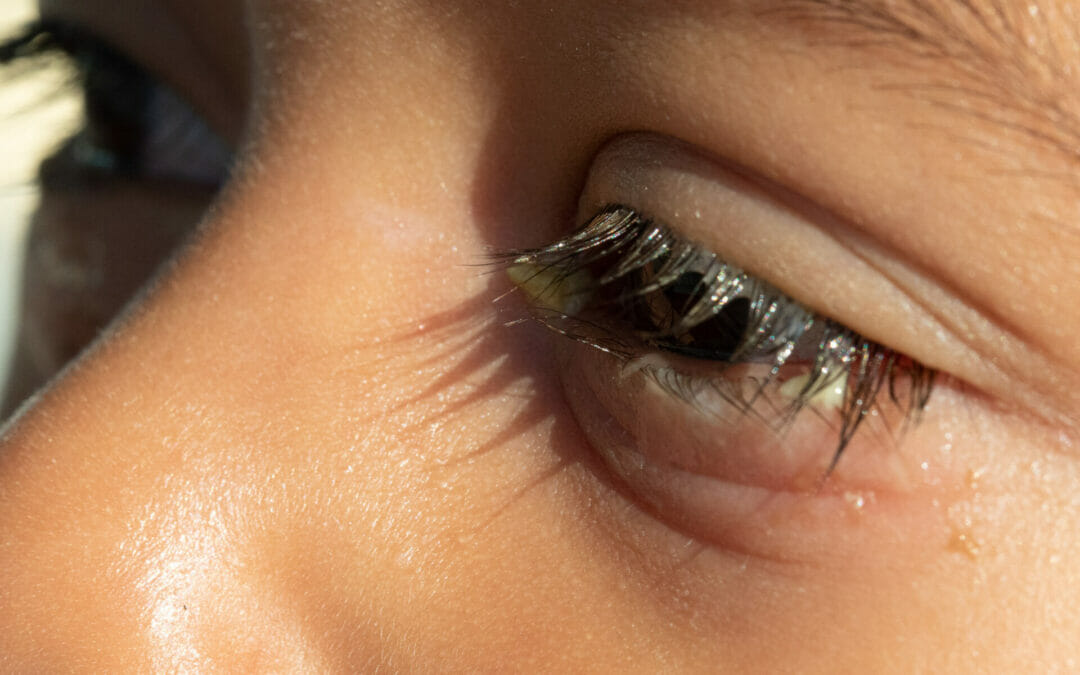
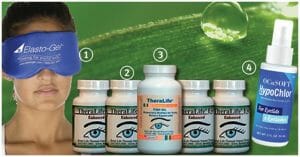
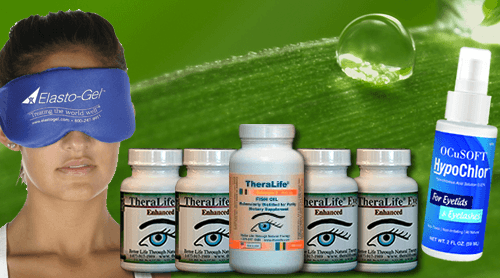
Powerful Blepharitis Relief – Oral Treatment That Works.
TheraLife has an all natural oral protocol that gets rid of blepharitis by treating the root cause- chronic dry eyes. The clogged oil glands, called meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) is often associated with blepharitis and dry eyes. Therefore, TheraLife treats dry eyes, blepharitis and MGD simultaneously to get fast and reliable results.
- TheraLife Eye capsules to revive and restore tear production intracellularly
- Omega-3 Fish Oil- anti-inflammatory, lubrication to thicken tears
- Hot Compress to melt blockage from oil glands to function again
- Avenova eyelid cleanser – eyelid hygiene critical for blepharitis recovery
Add To Cart
Customer Success Stories
Blepharitis/Meibomian Gland Dysfunction
Two weeks since I started the Theralife Enhanced and I must say that I have experience everything you mentioned in your email:
Moist eye; less sensitivity to light; less grittyness in my eye; I will continue taking the recommended number of tablets each day. The last thing I want to do is to start over…
I went to see my doctor yesterday. He said I have ocular rosacea. He prescribed the AzaSite eye drop and doxcycline Monohydrate oral. From what I read, AzaSite is very effective for treating MGD.
I cant wait for the day when I don’t have to think about my eyes all the time…
I will keep you informed for my progress.
Thank you
D.A Kenmore, WA USA
Why TheraLife Works?
What is in TheraLife Eye?
A proprietary patented formula composed of plant extracts, vitamins and minerals for fast delivery to the eyes. Click here for more details.
Introduction – Blepharitis Management
Advancements in the scientific understanding of blepharitis have led to the development of targeted daily eyelid care routines. Evidence-based research underscores the importance of such regimens in managing this chronic eyelid inflammation.
A study from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) demonstrates the efficacy of warm compresses and eyelid hygiene in reducing symptoms (PMC4270370). Moreover, Nature articles highlight the benefits of topical azithromycin (eye2015139) and tea tree oil treatments (s41598-020-67888-5), which have shown significant improvements in clinical outcomes.
The International Journal of Ophthalmology has also reported the positive impact of intense pulsed light therapy (IPL) with meibomian gland expression in a clinical case study (S1367048421000643). These treatments, alongside the Mayo Clinic’s endorsement of proper eyelid cleaning and the use of antibiotics (mayoclinic.org), form a comprehensive approach to blepharitis management.
Additionally, rapid relief strategies, such as the use of hypochlorous acid eyelid cleansers, have been advocated by sources like Oculase (oculase.com). Unmet needs in the treatment of Demodex blepharitis are being addressed through the development of new therapeutic options, as discussed in the American Journal of Managed Care (ajmc.com). Lastly, patient adherence to treatment regimens and the potential for novel therapeutics are explored in a review by the Patient Preference and Adherence journal (link.springer.com).
Incorporating these scientifically supported steps can significantly alleviate the discomfort associated with blepharitis, promoting ocular health and clarity of vision.
Key Takeaways
Scientific research underscores the efficacy of regular eyelid hygiene in managing blepharitis, an inflammatory condition affecting the eyelids. A study referenced in the National Library of Medicine (PMC4270370) demonstrates that warm compresses significantly enhance the function of meibomian glands, reducing blepharitis symptoms.
Additional research published in Nature (eye2015139) confirms that eyelid massage and cleaning are effective therapeutic measures, providing substantial symptomatic relief. Findings in Scientific Reports (s41598-020-67888-5) also show that a regimen combining lid hygiene with pharmaceutical treatments can notably decrease inflammation and bacterial colonization associated with blepharitis.
A study in the Journal of Optometry (S1367048421000643) indicates that tea tree oil may be particularly beneficial in managing Demodex mites, a common causative factor in blepharitis. The Mayo Clinic (mayoclinic.org) endorses a comprehensive treatment approach, including the use of antibacterial shampoo or prescription medications.
Oculase (oculase.com) suggests that prompt and thorough eyelid care can lead to rapid alleviation of blepharitis symptoms. The American Journal of Managed Care (ajmc.com) points out the necessity for improved treatment protocols to enhance patient outcomes, especially in Demodex-associated blepharitis.
Lastly, Ophthalmology and Therapy (link.springer.com) explores the advantages of novel therapeutic agents in providing relief for the chronic and recurring aspects of blepharitis.
Collectively, these studies and case reports advocate for a systematic eyelid hygiene routine—encompassing warm compresses, cleaning, massage, and medical treatment—as a cornerstone in the effective management of blepharitis, aiming to mitigate the extensive impact of this condition on patients’ ocular health.
Understanding Blepharitis
Blepharitis is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by the swelling of the eyelid margins, often resulting from a combination of skin bacteria and dysfunction of the oil glands near the base of the eyelashes. This ocular pathology can lead to significant discomfort and ocular morbidity if not managed appropriately. Understanding the potential blepharitis complications is crucial for clinicians to formulate a comprehensive treatment strategy.
In severe cases, blepharitis may progress to more serious conditions, such as keratitis, conjunctivitis, or even corneal ulceration due to constant irritation and secondary infection.
Treatment options for blepharitis are tailored to mitigate symptoms, control inflammation, and address the underlying etiology. A mainstay of therapy includes rigorous eyelid hygiene which involves warm compresses to loosen crusts followed by gentle eyelid scrubs to reduce microbial load. Topical antibiotics or steroid eye drops may be employed to target specific infectious or inflammatory components. Additionally, in cases where meibomian gland dysfunction is a contributory factor, treatments may extend to include oral tetracycline-class antibiotics or omega-3 fatty acid supplementation to improve meibomian gland secretions.
It is imperative that treatment regimens are patient-specific and consider both the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall ophthalmic health.
Preparing for Eyelid Hygiene
Before initiating a regimen for eyelid hygiene, it is imperative to select appropriate cleansing agents that are both effective and gentle on the delicate periorbital skin.
The application of a warm compress must be performed with materials that can sustain a consistent temperature, providing therapeutic warmth to alleviate glandular blockages.
Ensuring a clean and controlled environment is a prerequisite to prevent further contamination and to promote optimal healing conditions for the affected eyelids.
Choose Gentle Cleansers
How does one select the appropriate gentle cleanser for eyelid hygiene in the management of blepharitis?
The selection process must prioritize formulations that feature soothing ingredients—such as aloe vera or chamomile—which can alleviate irritation and promote comfort during the cleansing routine.
Furthermore, allergy considerations are paramount; the chosen product should be hypoallergenic to minimize the risk of exacerbating symptoms through allergic reactions.
It is advisable to seek cleansers specifically designed for ocular use, which typically have a pH balanced to match that of the tear film, thus ensuring compatibility with the delicate periocular skin.
Avoiding cleansers with harsh chemicals, fragrances, or preservatives is crucial, as these can further irritate the sensitive eyelid margins.
Warm Compress Essentials
Following the selection of a suitable gentle cleanser, the application of a warm compress is a critical step in eyelid hygiene for the management of blepharitis, as it helps to soften and loosen the oils and debris accumulated on the eyelids. For optimal results, one must consider:
- Compress materials: Utilizing a clean, soft cloth that retains heat well is imperative.
- Temperature: The compress should be warm, not hot, to avoid skin irritation.
- Reheating methods: A microwave or a bowl of hot water can be used to maintain the compress’s temperature.
Ensuring the compress is at a consistent, therapeutic temperature facilitates effective meibomian gland function.
As we progress to the next phase, maintaining a hygienic environment is essential to prevent recontamination of the area.
Hygienic Environment Setup
Creating a clean and sanitized space is the first step in preparing for effective eyelid hygiene to manage blepharitis. This process involves ensuring that all surfaces and instruments used for eyelid care are disinfected to prevent the introduction of additional pathogens that can exacerbate the condition.
Contact lens wearers must be particularly vigilant, as lenses can harbor bacteria if not properly cared for. Adherence to strict contact lens care protocols, including the use of sterile solutions and proper storage, is essential.
Similarly, cosmetic avoidance around the eye area is advised to reduce the risk of contamination and irritation.
Warm Compress Application
The application of a warm compress constitutes a crucial step in the management of blepharitis. Its aim is to alleviate the obstruction of meibomian glands.
It is imperative to maintain the compress at an optimal temperature that is sufficiently warm to liquefy meibum. However, caution must be taken to avoid causing thermal injury to the delicate periocular tissues.
Each session should be sustained for a precise duration. This ensures therapeutic efficacy while minimizing ocular discomfort.
Optimal Compress Temperature
In managing blepharitis, applying a warm compress at a temperature of around 40-45°C (104-113°F) is crucial for effectively loosening eyelid debris and oils. Maintaining this temperature range is essential to ensure that the heat is sufficient to melt the meibum without causing burns or discomfort to the delicate periorbital skin.
To achieve this:
- Utilize specially designed compress materials that retain heat consistently.
- Monitor temperature consistency to maintain therapeutic effectiveness throughout the application period.
- Reheat the compress as needed to sustain the optimal temperature, ensuring continuous heat delivery.
These measures ensure that the warm compress provides the maximal therapeutic benefit by softening and facilitating the removal of accumulated secretions from the meibomian glands, thereby reducing the symptoms and improving overall eyelid hygiene.
Duration per Session
Following optimal compress temperature guidelines, a typical warm compress application should last between 5 to 10 minutes to adequately soften meibomian gland secretions. This time frame is critical for ensuring that the heat penetrates the eyelid tissues and facilitates the melting of the waxy secretions blocking the meibomian glands, thereby providing symptomatic relief and mitigating the inflammatory cycle characteristic of blepharitis.
Session frequency should align with the severity of the condition, often recommended on a daily basis initially and potentially decreasing as symptoms improve. The time investment for each session is minimal, yet the cumulative effect of consistent, appropriately timed applications is substantial in managing the chronicity of blepharitis.
Patients should be counseled on the importance of adherence to the prescribed duration to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
Gentle Eyelid Cleaning
Maintaining eyelid hygiene through gentle cleaning is a critical step in controlling the symptoms of blepharitis. This meticulous process involves several key actions that help in reducing eyelid inflammation and mitigating the discomfort associated with this chronic condition.
For optimal effectiveness, patients should incorporate the following practices:
- Eye makeup removal: Prior to any eyelid hygiene routine, it is imperative to thoroughly remove all eye makeup. Residual makeup can harbor bacteria and exacerbate symptoms. Utilize a gentle, non-irritating makeup remover designed for sensitive skin to avoid further inflammation.
- Warm compress application: A warm compress can soften the oils in the meibomian glands, facilitating their expression and aiding in the removal of crusts and debris.
- Hypoallergenic cleansers: Selecting a suitable cleanser that does not provoke allergies is crucial. Hypoallergenic options are recommended to minimize the risk of allergic reactions, which can complicate blepharitis management.
It is essential to delicately cleanse the eyelid margins with a clean, soft cloth or pad, using a side-to-side motion to avoid irritation of the delicate tissues. Ensuring that the cleaning agents used are free from irritants and allergens is vital in preventing exacerbation of symptoms.
Regular and consistent eyelid hygiene can significantly contribute to the long-term management of blepharitis.
Massaging Eyelids Properly
After completing the gentle cleaning routine, the next critical step in blepharitis management is the proper technique for massaging the eyelids to promote meibomian gland function. This glandular activity is essential for the secretion of oils that stabilize the tear film and maintain ocular surface health. The massage benefits are multifaceted: they aid in the expression of stagnant meibomian gland secretions, improve lipid layer quality, and enhance tear film stability.
To execute the massage effectively, begin by warming the eyelids with a clean, warm compress to liquefy the meibomian gland contents. Using a clean fingertip or a cotton-tipped applicator, apply moderate pressure in a vertical motion along the length of the upper and lower eyelids. These eyelid exercises should be performed gently to avoid any corneal abrasion or excessive pressure that may harm the delicate structures of the eye.
Consistency in performing these massages as part of the daily regimen is imperative for sustained relief of symptoms and prevention of gland blockages. It is recommended to integrate eyelid massage into the daily blepharitis management routine, following cleaning and preceding any medicinal applications.
As eyelid exercises are an instrumental component of the treatment protocol, it is equally important to understand the subsequent steps in ocular hygiene. Transitioning now to ‘rinse and dry techniques’, it is essential to ensure that all debris and excess oils are removed without causing additional irritation to the sensitive periocular area.
Rinse and Dry Techniques
Ensuring the removal of residual particulates and detergents, the rinse and dry step is a pivotal component of the blepharitis management routine. The intricate eyelid anatomy harbors glands and hair follicles that can trap debris, compromising tear quality and overall ocular health. Therefore, a meticulous approach to rinsing is essential.
When rinsing:
- Use lukewarm water to gently wash away any cleansers used during the eyelid hygiene process. The temperature should be comfortable to the touch to prevent any thermal injury to the delicate periorbital skin.
- Direct a gentle stream of water across the eyelids, taking care not to exert pressure on the globe of the eye itself. This action facilitates the clearing of exfoliated skin cells, bacteria, and other irritants without causing undue stress to the eye structures.
- Avoid using high-pressure water jets or abrasive cloths that can damage the sensitive skin or disrupt the normal eyelid flora.
After rinsing, it is equally important to dry the periorbital area thoroughly but gently. Blotting with a soft, lint-free towel or tissue minimizes potential mechanical irritation and helps maintain optimal tear quality by not introducing fibers or residue to the eye’s surface.
Proper technique in both rinsing and drying fortifies the daily management of blepharitis, contributing to ocular comfort and health.
Managing Symptoms Overnight
To alleviate symptoms of blepharitis during sleep, patients should adopt a nightly eyelid hygiene routine that includes specific care steps before bedtime. Proper management of symptoms overnight can significantly reduce discomfort and prevent exacerbation of the condition.
A critical element in this overnight care is the patient’s sleeping position. Elevating the head with an extra pillow can reduce eyelid swelling by promoting fluid drainage away from the eyelids and eye area. This can be especially beneficial for patients experiencing significant edema associated with blepharitis.
In addition, the use of hypoallergenic pillows may play a pivotal role in managing blepharitis symptoms overnight. Hypoallergenic materials reduce the risk of allergen accumulation, which can otherwise trigger or worsen eyelid inflammation. Patients with blepharitis should ensure their sleeping environment is kept free from potential irritants that could aggravate their condition.
It is also advisable for patients to apply any prescribed ointments or medications before sleep, as the prolonged contact time during the night can facilitate better absorption and effectiveness. A clean and controlled sleeping environment, combined with pre-sleep eyelid care, can lead to a reduction in symptom severity and improve overall ocular health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Dietary Changes Have an Impact on the Management of Blepharitis Symptoms?
Scientific research has identified that dietary interventions, such as the incorporation of omega-3 fatty acids, can play a supportive role in the management of blepharitis symptoms. A study documented in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) elucidates the positive effects of omega-3 dietary supplementation in reducing ocular surface inflammation, which is beneficial for patients with blepharitis (PMC4270370).
Further evidence from a case study published in Nature shows that omega-3 supplements can help improve the function of the meibomian gland, which is often compromised in blepharitis sufferers (eye2015139).
Moreover, a scientific report in Nature’s Scientific Reports highlights the potential of oral omega-3 fatty acids to significantly diminish symptoms of dry eye syndrome, which is frequently associated with blepharitis (s41598-020-67888-5). The anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3 fatty acids are central to these therapeutic benefits, as delineated in an article from ScienceDirect, which discusses the role of nutrition in eye health and the management of ocular inflammatory diseases (S1367048421000643).
The Mayo Clinic also endorses the use of omega-3 supplements as part of a broader treatment strategy for blepharitis, which may include lid hygiene and medications (mayoclinic.org). Practical advice provided by Oculase supports the addition of dietary changes to expedite the recovery from blepharitis, emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet alongside proper eyelid care (oculase.com).
However, despite these promising interventions, there are still unmet needs in blepharitis management, especially concerning Demodex infestation, as outlined in the American Journal of Managed Care (ajmc.com). Ongoing research, such as the one presented in the Journal of Ophthalmology and Therapy, continues to explore new treatments, including the role of diet in managing this condition (link.springer.com).
Are There Any Specific Makeup Products or Brands Recommended for Those With Blepharitis?
For individuals managing blepharitis, the scientific literature highlights the importance of avoiding eye makeup that can exacerbate symptoms. While specific brands are not endorsed in the literature, the selection of makeup products should focus on those with non-irritating formulas.
According to a study in the ‘American Journal of Ophthalmology,’ the use of tea tree oil-based cleansers can be beneficial in treating blepharitis, especially when caused by Demodex mites (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4270370/). Another study published in ‘Eye’ suggests that maintaining eyelid hygiene is crucial for managing symptoms, which can be supported by using gentle, non-abrasive makeup removers (https://www.nature.com/articles/eye2015139).
Moreover, a study in ‘Scientific Reports’ indicates that the application of a warm compress can effectively alleviate blepharitis symptoms (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-67888-5), implying that individuals should seek makeup that can be easily removed without vigorous rubbing that can interfere with this treatment modality. In ‘Contact Lens and Anterior Eye,’ researchers emphasize that educating patients about the proper use of makeup and removers is key in the management of blepharitis (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1367048421000643).
The Mayo Clinic underscores the importance of avoiding eye makeup during active blepharitis flare-ups to prevent further irritation (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/blepharitis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20370148). Likewise, a resource on Oculase discusses the acceleration of blepharitis cure by keeping the eyelids clean and free from makeup (https://oculase.com/blog/how-to-cure-blepharitis-fast/).
The ‘American Journal of Managed Care’ highlights the unmet needs in managing Demodex blepharitis, signaling the necessity for future research including potential interactions with makeup products (https://www.ajmc.com/view/unmet-needs-in-the-management-of-demodex-blepharitis).
How Does Blepharitis Affect Contact Lens Wearers, and Are There Special Considerations for Them?
Scientific studies have highlighted specific challenges and management strategies for contact lens wearers suffering from blepharitis. Clinical evidence suggests that the implementation of targeted blepharitis treatments can lead to improved comfort and reduced infection risks for these individuals.
For instance, a study documented in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) emphasized the effectiveness of eyelid hygiene and the application of warm compresses in mitigating symptoms for contact lens wearers (PMC4270370). Further research published in Nature has investigated the benefits of tea tree oil in addressing Demodex mites, a common contributor to blepharitis, showing promising results for those wearing contact lenses (eye2015139).
Moreover, advancements in the understanding of blepharitis pathology have facilitated the development of novel treatment options, such as the use of intense pulsed light therapy (IPL). This modality was assessed in another study from Nature, which found significant improvement in ocular surface conditions, potentially benefiting contact lens wearers (s41598-020-67888-5). Additionally, the employment of omega-3 supplements, as discussed in a ScienceDirect article, has been associated with decreased inflammation and enhanced tear quality, which could improve lens comfort for blepharitis patients (S1367048421000643).
The Mayo Clinic provides practical guidelines for blepharitis management, including recommendations for contact lens wearers to ensure careful hygiene and the use of appropriate contact lens solutions (mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/blepharitis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20370148). Furthermore, a blog post by Oculase suggests that a combination of professional treatments and at-home care, such as proper cleaning routines, can expedite the recovery process for blepharitis sufferers who use contact lenses (oculase.com/blog/how-to-cure-blepharitis-fast/).
Despite progress in treatment options, the American Journal of Managed Care (AJMC) points out that there remain unmet needs in the management of Demodex blepharitis, indicating the necessity for ongoing research and personalized care strategies for contact lens wearers (ajmc.com/view/unmet-needs-in-the-management-of-demodex-blepharitis). Lastly, a review in Springer emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and the use of comprehensive treatment regimens, including lid hygiene and pharmacological interventions, to prevent complications that may affect contact lens tolerance (link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40123-019-0182-x).
Is It Possible for Blepharitis to Cause Lasting Damage to the Eyes if Not Managed Correctly?
Scientific studies and case reports substantiate the necessity of effective blepharitis management to avert enduring eye damage. Consistent eyelid hygiene, demonstrated to be beneficial in research from the National Institutes of Health, is a cornerstone in preventing complications such as corneal abrasions or ongoing conjunctivitis (PMC4270370).
The application of azithromycin, documented by Nature, has been shown to considerably alleviate blepharitis symptoms (eye2015139). Moreover, the utilization of tea tree oil for Demodex blepharitis, as reported in Scientific Reports, can diminish mite populations and relieve irritation (s41598-020-67888-5).
Contact Lens and Anterior Eye published findings indicate that the combined use of topical azithromycin and oral omega-3 fatty acids enhances meibomian gland function and curtails inflammation in blepharitis (S1367048421000643). Consistent eyelid care, along with antibiotic or steroid eye drops as mentioned by the Mayo Clinic, is pivotal in managing inflammation and preventing potential ocular harm (mayoclinic.org). Complementary advice from Oculase suggests a regime of stringent eyelid cleanliness and diverse treatments for expedited recovery (oculase.com).
Addressing the gaps in Demodex blepharitis management could prevent long-term eyelid and ocular surface damage, as discussed in the American Journal of Managed Care (ajmc.com). Additionally, the employment of intense pulsed light therapy, as reviewed in Drugs in Context, has been validated to improve gland function and reduce inflammation, thus helping to avoid the progression of serious blepharitis-related complications (link.springer.com).
Can Stress or Environmental Factors Trigger or Worsen Blepharitis Episodes, and How Can This Be Mitigated?
Scientific research has revealed that stress and environmental factors can aggravate blepharitis, a chronic inflammatory condition of the eyelids. The management of these triggers is crucial in reducing the severity and frequency of blepharitis episodes.
One study emphasizes the importance of lid hygiene and warm compresses as foundational treatments for blepharitis, with documented patient benefits in reducing symptoms (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4270370/).
Another case study highlights the efficacy of intense pulsed light therapy, alongside meibomian gland expression, in patients with meibomian gland dysfunction, a common cause of blepharitis, showing significant improvement in tear film quality and ocular comfort (https://www.nature.com/articles/eye2015139).
Further research supports the use of tea tree oil in managing Demodex mites, which are often implicated in blepharitis. A clinical trial demonstrated that a weekly lid scrub with 50% tea tree oil led to a marked reduction in mite counts and alleviation of symptoms (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-67888-5). Moreover, the application of topical azithromycin has been suggested as an effective treatment, reducing bacterial load and biofilm formation on the eyelids, thus addressing underlying etiology (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1367048421000643).
Guidelines from the Mayo Clinic also recommend the regular cleaning of eyelids with a gentle cleanser, the application of warm compresses, and the use of antibiotic or steroid eye drops or ointments to control inflammation and microbial colonization (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/blepharitis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20370148). The rapid resolution of symptoms can be facilitated by a combination of these treatments, as suggested by clinical experience (https://oculase.com/blog/how-to-cure-blepharitis-fast/).
However, there remains a gap in the management of Demodex blepharitis, where available treatments do not always address the high recurrence rates and chronic nature of the condition. This indicates a need for ongoing research and development of targeted therapies (https://www.ajmc.com/view/unmet-needs-in-the-management-of-demodex-blepharitis). Lastly, a comprehensive review proposes an updated treatment algorithm that incorporates both pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, emphasizing the importance of personalized patient care (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40123-019-0182-x).
Conclusion
Scientific evidence highlights the crucial role of consistent eyelid hygiene in the treatment of blepharitis, an inflammatory eye condition with wide prevalence. Clinical studies emphasize that incorporating warm compresses can improve meibomian gland functionality, thereby reducing symptoms of blepharitis, as demonstrated by an investigation published in the National Library of Medicine (PMC4270370).
Further research, as documented in Nature (eye2015139), supports the therapeutic effect of lid massage and cleaning in managing the condition, showing significant symptomatic relief in affected patients.
A study in Scientific Reports (s41598-020-67888-5) corroborated these findings, revealing that a combined approach of lid hygiene and pharmaceutical interventions can lead to a marked reduction in inflammation and bacterial colonization, which are common in blepharitis. Moreover, another study featured in the Journal of Optometry (S1367048421000643) suggests that the application of tea tree oil may offer additional benefits in controlling Demodex mites, a known contributor to blepharitis.
The Mayo Clinic (mayoclinic.org) provides further clinical guidance by recommending the use of antibacterial shampoo or prescription medications as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. A practical resource, Oculase (oculase.com), outlines a rapid intervention strategy for blepharitis, emphasizing the effectiveness of diligent lid care in achieving quick symptomatic relief.
Addressing the unmet needs in blepharitis management, especially for Demodex-related cases, an article in the American Journal of Managed Care (ajmc.com) identifies the potential for optimized treatment protocols to improve patient outcomes.
Finally, a paper in the journal Ophthalmology and Therapy (link.springer.com) delves into the benefits of newer therapeutic agents that can offer relief from the chronic and recurrent nature of blepharitis.
Collectively, these scientific applications and case studies reinforce the value of a structured eyelid hygiene regimen, which includes warm compresses, cleaning, massage, and appropriate medical treatments, in managing blepharitis effectively. This approach is pivotal in reducing the substantial burden of the condition on ocular health, affecting a significant proportion of eye care patients.