A Closer Look At Ocular Rosacea: Understanding Its Symptoms And Causes
Ocular rosacea (OR) is a chronic skin and eye condition that affects many individuals. It is important for those affected by ocular rosacea to have an understanding of the symptoms, causes, and treatments available in order to manage this condition effectively.
This article will provide an overview of OR, including its symptoms, causes, and potential treatments. The purpose of this article is to examine the various aspects of OR and provide insight into managing this chronic condition.
A comprehensive review of current literature regarding OR will be conducted in order to gain further knowledge on how best to treat it. Additionally, possible preventive measures will be discussed as well as ways to alleviate any discomfort associated with OR.
Overview Of Ocular Rosacea
Ocular rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that mainly affects the face and eyes. It is estimated to affect roughly 4 million people in the United States alone, with higher incidence among individuals of European descent. Ocular Rosacea can cause severe discomfort and impair vision if left untreated, making it important for those at risk to understand its symptoms and causes.
Genetic factors have been identified as playing an important role in OR susceptibility. Studies examining genetic polymorphisms suggest that certain variations may increase one’s risk of developing this disease; however, environmental factors also appear to contribute to its development.
Lifestyle changes such as avoiding triggers like sun exposure or spicy food may reduce one’s chance of developing OR. Additionally, regular use of sunscreen, moisturizers, and other protective measures are recommended for reducing irritation due to UV light exposure or harsh wind conditions.
The severity of OR varies greatly from person-to-person due to individual differences in physical characteristics and lifestyle habits. Understanding these factors can be key in identifying early signs and taking proactive steps towards managing this long-term skin condition.
To further explore this topic, next we will discuss how to identify the various symptoms associated with OR.
Identifying The Symptoms Of Ocular Rosacea
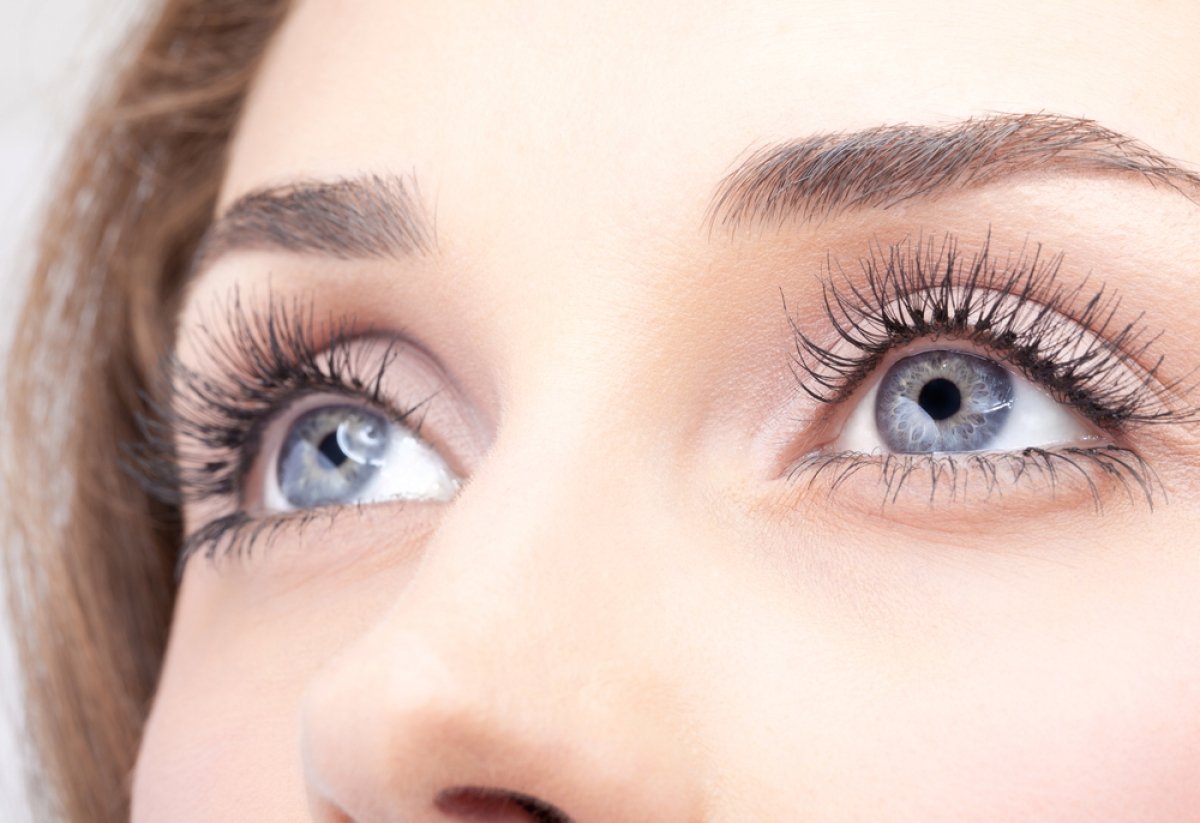
Identifying the Symptoms of Ocular Rosacea is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. This condition can be characterized by a range of symptoms that vary in severity, from mild to severe. These include itchy or burning eyes, redness of the eyelids, dryness and crustiness around the eyes, swollen eyelids, recurrent styes or chalazia (small cysts), light sensitivity and blurred vision.
Eyelid inflammation may also occur as well as bumps on the edges of the eyelids called pannus.
Managing OR often involves lifestyle modifications such as avoiding triggers like hot drinks or spicy foods, wearing sunglasses outdoors to protect against windy conditions and intense sunlight, quitting smoking if applicable, managing stress levels and taking warm compresses over closed eyes twice daily. In addition to these changes, medications such as antibiotics are usually prescribed to reduce symptom severity.
Topical steroids have also been used successfully in some cases with varying degrees of success since they do not work for everyone. Some people may require oral antibiotics due to more severe forms of OR which can lead to complications such as corneal damage if left untreated.
It is important for those suffering from this condition to discuss their options with an eye doctor specialized in treating ocular disease so that an appropriate course of action can be determined based on individual needs and preferences. By doing so, individuals will be better equipped to manage their symptoms effectively while reducing potential risks associated with the disorder.
Causes Of Ocular Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that affects more than 16 million Americans, and it can also affect the eyes. OR is an inflammatory disorder of the eyes that causes redness, burning, itching, stinging, dry eye syndrome, and blurred vision. It has been linked to genetics as well as environmental factors.
The most common symptoms associated with OR are:
– Dry Eyes
– Redness
– Burning Sensation
– Blurred Vision
– Stinging or Gritty Feeling in the Eyes
Ocular rosacea requires specialized medical treatment from an optometrist or ophthalmologist due to its complexity. Genetics may play a role in increased risk of developing this condition; however, certain environmental triggers such as exposure to wind, sun or hot weather may also lead to flare ups. In addition, lifestyle choices such as drinking alcohol and eating spicy food have been known to cause episodes of ocular rosacea for some patients.
Treatment plans typically involve medications like antibiotics and anti-inflammatory eye drops which help reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms but do not cure the underlying disease process.
It is important for individuals who suffer from ocular rosacea to be aware of the potential visual complications that could arise if left untreated including corneal damage, decreased tear production and lid margin irritation leading to eyelid swelling or conjunctivitis (pink eye). Early recognition of symptoms followed by prompt diagnosis and management can help minimize any long term effects on vision. With proper care and treatment strategies tailored to each individual’s specific needs, people with ocular rosacea can maintain healthy eyesight despite their condition.
Moving forward into our next section we will look at how ocular rosacea impacts vision.
Impact On Vision- Ocular Rosacea
1. Ocular rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that can cause significant damage to the eyes, resulting in reduced visual acuity and an increased risk of infection.
2. Symptoms of ocular rosacea can include redness, tearing, burning, and blurred vision.
3. The primary cause of ocular rosacea is unknown, but researchers have suggested that environmental triggers, such as sun exposure and stress, may contribute to the condition.
4. Treatment of ocular rosacea generally involves the use of antibiotics and topical medications to reduce inflammation and protect against infection, and regular eye exams to monitor for any changes in vision.
Impact On Eye Health
Ocular rosacea can have a significant impact on eye health.
Those who suffer from ocular rosacea often experience dry eyes, redness of the eyelids, and burning or stinging in their eyes.
In some cases, complications such as conjunctivitis may occur.
It is important for those with ocular rosacea to take steps to reduce any potential damage that could be caused by this condition.
This includes making lifestyle changes such as avoiding alcohol and spicy foods and using artificial tears or other lubricants.
Regular visits to an optometrist are also recommended so that any problems can be detected early and treated promptly.
Additionally, it is important for individuals to develop coping strategies, such as relaxation techniques and stress management practices, which may help reduce the severity of symptoms.
Impact On Visual Acuity
In addition to the dry eyes, redness of eyelids, and burning or stinging associated with ocular rosacea, visual acuity can also be affected.
Patients may experience blurred vision and a decrease in their ability to focus on objects at a distance.
Other symptoms such as light sensitivity, eye fatigue, and headaches may also occur.
To reduce any potential damage that could result from this condition, it is important for those who suffer from ocular rosacea to take steps to protect their eyes.
This includes protecting them from direct sunlight by wearing sunglasses when outdoors, avoiding rubbing the eyes, and using artificial tears or other lubricants if necessary.
Regular visits with an optometrist will help ensure that any changes in visual acuity are detected early and treated promptly.
It is also important for individuals to manage stress levels through relaxation techniques and activities such as exercise which may help reduce the severity of symptoms over time.
Diagnosis And Treatment For Ocular Rosacea
The effectiveness of diagnosing and treating ocular rosacea is dependent upon early detection.
Ocular rosacea can often be difficult to diagnose due to its similarity with other conditions, including blepharitis, dry eye syndrome and allergic conjunctivitis. However, when the symptoms are identified in the earliest stages, it can usually be diagnosed by an optometrist or ophthalmologist based on visual inspection alone.
Once a diagnosis has been made, treatment typically involves lifestyle changes such as avoiding potential triggers like caffeine and spicy foods that can cause flare-ups.
Additionally, many patients benefit from over-the-counter medications such as oral antibiotics or topical treatments containing corticosteroids which help reduce inflammation associated with ocular rosacea. In more severe cases, prescription strength medications may be necessary to achieve desired results.
In addition to medical intervention, care should also be taken to maintain good hygiene habits such as regularly washing one’s face with lukewarm water and mild soap while avoiding harsh scrubs or cleansers.
Taking regular breaks from contact lenses or glasses may also provide some relief during periods of discomfort. While there is no cure for ocular rosacea, proper management of symptoms through a combination of treatment options can make all the difference in achieving long-term control of this condition.
Moving forward, managing the condition calls for ongoing monitoring and adjustments to ensure optimal outcomes.
Managing The Condition
1. Ocular rosacea is a chronic skin condition that can cause a range of eye-related symptoms, and there are various treatments available to help manage it.
2. Diet and lifestyle changes are an important part of managing ocular rosacea, as certain foods and environmental factors can exacerbate its symptoms.
3. Some treatments for ocular rosacea include topical and oral medications, laser therapy, and surgery, depending on the severity of the condition.
4. Self-care practices such as avoiding hot or spicy foods, wearing sunglasses, and avoiding harsh skin cleansers are also important in managing ocular rosacea.
5. In addition, identifying and avoiding triggers such as stress, sun exposure, and alcohol consumption can help reduce the frequency and intensity of ocular rosacea flare-ups.
6. It is important for those with ocular rosacea to consult with their healthcare provider to determine the best treatment and self-care practices for their condition.
Treatments
The treatment of ocular rosacea is multifaceted and must be tailored to the individual patient. Medication options may include topical antibiotics, such as metronidazole or azithromycin; oral antibiotics, including tetracycline derivatives and erythromycin; and anti-inflammatory agents, like cyclosporine eye drops.
Lifestyle changes are also an important part of managing the condition. Avoiding triggers that can exacerbate symptoms, such as exposure to direct sunlight, extreme temperatures, spicy foods or stress should all be discussed with a doctor. Additionally, avoiding harsh facial cleansers or cosmetics that contain alcohol can help reduce irritation in those affected by ocular rosacea.
It is also essential for patients to practice adequate lid hygiene daily using warm water and gentle cleaning products without fragrances. Ultimately, following these steps along with prescribed treatments from a healthcare professional will put you on the path to managing your ocular rosacea more effectively.
Best All Natural Ocular Rosacea Treatment – TheraLife
Diet & Lifestyle Changes for Ocular Rosacea
In addition to medication, alternative therapies such as stress management and relaxation techniques have been studied for their ability to help manage ocular rosacea symptoms.
Studies suggest that practicing these types of activities can reduce the frequency of flare-ups by helping patients learn how to better cope with stressful situations.
Dietary modifications may also be beneficial in reducing inflammation associated with ocular rosacea.
It is important to note however, that dietary changes should be discussed with a doctor or nutritionist before implementation as it could interfere with other medications being taken by the patient.
Lastly, limiting exposure to direct sunlight and extreme temperatures is essential for managing this condition since both are known triggers of exacerbation.
To ensure optimal symptom control, incorporating lifestyle and diet alterations into one’s daily routine is recommended when treating ocular rosacea.
Self-Care Practices- Ocular Rosacea
Self-care practices are an important component of successful ocular rosacea management.
In addition to lifestyle and dietary changes, alternative therapies have been studied for their potential to reduce inflammation associated with this condition.
Recent studies suggest that incorporating stress management and relaxation techniques into daily routines may help reduce the frequency of flare-ups by teaching patients how to better cope with stressful situations.
Additionally, research indicates that limiting exposure to direct sunlight and extreme temperatures is essential for managing ocular rosacea symptoms as both can trigger exacerbation.
Therefore, it is recommended that individuals affected by ocular rosacea make self-care a priority in order to maintain optimal symptom control.
Prevention And Self-Care- Ocular Rosacea
Prevention and self-care are important for managing ocular rosacea. The key to effective prevention is avoiding known triggers, such as:
1. Sun exposure or windy weather
2. Spicy food or hot drinks
3. Alcohol consumption or smoking
4. Stressful situations
Lifestyle changes may also be beneficial in keeping symptoms under control. These include:
– Regular exercise
– A balanced diet
– Stress management techniques (e.g., yoga, meditation)
– Getting enough sleep each night
Additionally, it can be useful to wear protective clothing when exposed to the sun and avoid harsh skin care products that can cause irritation. Lastly, ask your doctor about any medications they recommend for preventing flare ups of ocular rosacea symptoms such as antibiotics or topical creams/lotions containing steroids or other agents prescribed specifically for this condition.
Effective prevention and self-care strategies require ongoing effort but can make a significant difference in controlling the severity of ocular rosacea symptoms over time. It is therefore essential to find an individualized approach that works best with one’s lifestyle and specific needs in order to properly manage this chronic condition long term. With proper treatment and preventative measures, living well with ocular rosacea is possible despite its challenges.
Living With Ocular Rosacea
Ocular rosacea can have an immense psychological impact on those who experience it, and the key to managing this skin condition is understanding its emotional effects. It is important to note that when dealing with ocular rosacea, feelings of frustration or embarrassment are common among sufferers; however, they should not be ignored as they can cause a further decline in one’s mental health. In light of this, there are certain steps that may help patients cope better with their symptoms.
Firstly, ensuring proper skin care is essential for reducing the appearance of visible signs associated with ocular rosacea. This includes washing your face twice daily using lukewarm water and gentle facial cleanser designed specifically for rosacea-prone skin types. Additionally, sunscreen containing SPF 30 or higher must also be used whenever outside during daylight hours as protection against UV rays which can exacerbate flare-ups. Moreover, topical medications such as metronidazole cream may be prescribed by dermatologists to reduce inflammation and redness caused by the disorder itself.
Furthermore, although physical treatments for ocular rosacea remain limited due to unknown causes of the condition, some lifestyle changes may relieve discomfort from outbreaks. For instance, avoiding triggering factors like alcohol consumption and spicy foods might prove beneficial if these substances tend to aggravate one’s symptoms. Stress management techniques such as yoga or regular exercise have been shown to improve both mental and physical wellbeing too. Seeking support from family members or friends could offer comfort during particularly difficult periods as well.
Ultimately, each situation will differ so discovering what works best for you personally is paramount in order to manage ocular rosacea effectively over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Ocular Rosacea Be Passed On To Other People?
The question of whether ocular rosacea can be passed on to other people is still being researched.
While there are no definitive answers at this time, genetic factors and environmental triggers may play a role in the transmission of the condition from one person to another.
However, further research is needed before any definite conclusions about its transmissibility can be drawn.
Can Ocular Rosacea Be Treated With Laser Therapy?
Irony may be the most appropriate way to describe laser therapy for ocular rosacea, as it is often seen as a last resort rather than an initial treatment.
While eye drops and lifestyle changes are commonly recommended by experts in the field of ocular rosacea research, these treatments do not always produce desirable outcomes.
As such, lasers have been used in some cases to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms associated with this condition.
However, caution must be taken when deciding upon any type of laser therapy due to risk factors that may occur following its use.
Is There Any Way To Reduce The Risk Of Developing Ocular Rosacea?
Preventative measures and lifestyle changes are important to consider when attempting to reduce the risk of developing ocular rosacea.
It is recommended that patients with a history of facial rosacea, or those who have close family members with ocular rosacea, be aware of potential triggers such as sun exposure and extreme temperatures.
Additionally, maintaining good overall health can also help reduce the likelihood of developing this condition.
Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding spicy foods may prove beneficial in some cases.
Finally, it is essential for individuals at higher risk for this disorder to seek regular medical care from an optometrist or other eye specialist in order to detect any signs or symptoms early on.
Are There Any Long-Term Effects Of Ocular Rosacea?
Ocular rosacea is a chronic skin condition that affects the eyes and can cause redness, irritation, and dryness. In extreme cases it may lead to vision loss or damage of the cornea.
A case study of an individual suffering from ocular rosacea found that their symptoms continued despite following regular skin care routines and avoiding triggers such as stress and sun exposure. This suggests there are possible long-term effects associated with ocular rosacea beyond what traditional redness causes would indicate.
It is important for those affected by this condition to speak with a doctor about any potential consequences in order to develop appropriate treatment plans and identify preventative measures.
Are There Any Medications That Can Be Taken To Manage Ocular Rosacea?
When it comes to managing ocular rosacea, there are several medications that can be taken. These include topical antibiotics such as metronidazole and azelaic acid; oral tetracyclines like doxycycline or minocycline; and even immunosuppressants.
In addition to medication, preventive measures should also be considered when treating ocular rosacea. This includes lifestyle changes such as avoiding triggers (such as spicy foods), using gentle skin cleansers, applying non-irritating moisturizers, and wearing sunglasses to protect the eyes from wind and sun.
It is important for those with ocular rosacea to discuss their treatment options with a medical professional in order to receive an appropriate plan of care.
Conclusion
Ocular rosacea is a chronic condition that affects many individuals around the world.
Studies have shown that it can affect up to 10% of adults over the age of 30.
It is important to be aware of its symptoms and causes in order to effectively manage this condition.
While ocular rosacea cannot be passed onto others, laser therapy has been found to reduce inflammation and improve vision for some patients.
Additionally, taking certain medications may also help reduce risk factors associated with developing ocular rosacea.
Long-term effects vary from patient to patient but often include dryness and irritation in the eyes as well as blurred vision or redness on other areas of the face.
Overall, understanding more about ocular rosacea is essential for proper management techniques and improved quality of life for those suffering from this condition.
Further research is necessary in order to identify effective treatments and preventative measures which could potentially benefit millions of people living with this illness worldwide.
References
Webster GF, Durrani K, Suchecki J. Ocular rosacea, psoriasis, and lichen planus. Clin Dermatol. 2016 Mar-Apr;34(2):146-50. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2015.11.014. Epub 2015 Nov 22.
Wladis EJ, Aakalu VK, Foster JA, Freitag SK, Sobel RK, Tao JP, Yen MT. Intense Pulsed Light for Meibomian Gland Disease: A Report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2020 Sep;127(9):1227-1233. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2020.03.009. Epub 2020 Apr 21. PMID: 323272
Dell SJ, Gaster RN, Barbarino SC, Cunningham DN. Prospective evaluation of intense pulsed light and meibomian gland expression efficacy on relieving signs and symptoms of dry eye disease due to meibomian gland dysfunction. Clin Ophthalmol. 2017;11:817–827. Published 2017 May 2. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S13070
Scala J, Vojvodic A, Vojvodic P, Vlaskovic-Jovicevic T, Peric-Hajzler Z, Matovic D, Dimitrijevic S, Vojvodic J, Sijan G, Stepic N, Wollina U, Tirant M, Thuong NV, Fioranelli M, Lotti T. Botulin Toxin Use in Rosacea and Facial Flushing Treatment. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019 Aug 30;7(18):2985-2987. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.784. PMID: 31850105; PMCID: PMC6910814.
Stone DU, Chodosh J. Ocular rosacea: an update on pathogenesis and therapy. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004;15(6):499-502
AAO Basic and Clinical Science Course, External Disease and Cornea, 2010-2011, 69-70.
Papier A1, Tuttle DJ, Mahar TJ.Differential Diagnosis of the Swollen Red Eyelid. Am Fam Physician. 2007 Dec 15;76(12):1815-24.
Celiker H, Toker E, Ergun T, Cinel L. An unusual presentation of ocular rosacea. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2017 Nov-Dec;80(6):396-398. doi: 10.5935/0004-2749.20170097