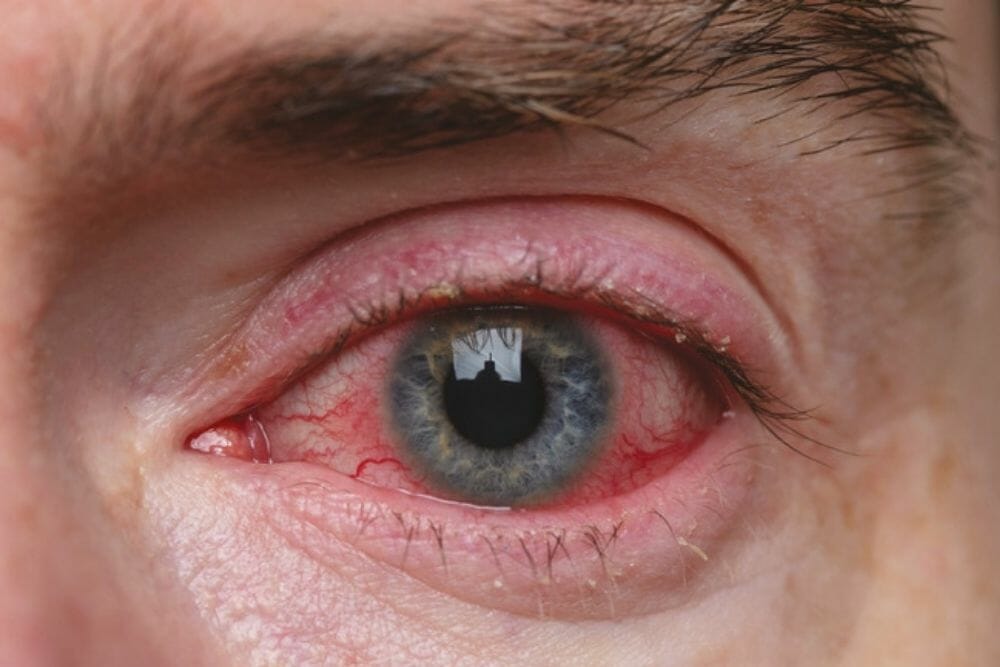
Best All Natural Treatment For Ocular Rosacea
Ocular rosacea is often related to facial rosacea with high levels of inflammation that results in red eyes, chronic dry eyes, meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD)- clogged oil glands.
TheraLIfe’s All In One Dry Eye Starter kit is all you need for recovery and maintain long term eye health. Oral natural treatment from inside out.
TheraLife All In One Ocular Rosacea Starter Kit
Everything you need for ocular rosacea recovery and maintain eye health.
Why Theralife Eye Works?
What is in TheraLife Eye Capsules.
Customer Success Stories
Severe Chronic Dry Eyes- Ocular Rosacea
I have had chronic severe dry eyes for many years I am writing to let you know how thankful I am for your product- TheraLife Eye. It has virtually changed my life. Instead of ALWAYS thinking about my sore, red, dry eyes, I NEVER think about them anymore. And every time I look in the mirror and see my bright, wide, youthful looking eyes I make a little wish that your company is thriving and I will never again have to be without TheraLife Eye capsules. You know, when your eyes are red and you squint in discomfort, you really do look older.
I’ll be traveling to Las Vegas soon and am anxious to see how I do in the desert air. Wish me luck! A bottle of TheraLife Eye will be in my purse for sure.
Thank you, thank you, thank you.
C.L. Ohio, United State
Introduction
Effective management of ocular rosacea, a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the eyes, is crucial for patient well-being and ocular health. Scientific studies and clinical case reports have highlighted several treatments that yield benefits for patients with ocular rosacea. This discussion will focus on scientifically validated therapeutic strategies, citing evidence from research and case studies that demonstrate the positive outcomes of these treatments.
- A study in the Arquivos Brasileiros de Oftalmologia evaluated the effectiveness of oral tetracycline and topical corticosteroid treatment in ocular rosacea patients, showing significant improvement in symptoms and corneal health.
- Research published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found that the use of oral doxycycline, a tetracycline derivative, was beneficial in treating ocular rosacea, particularly in reducing ocular inflammation.
- A study from the Archives of Ophthalmology indicated that omega-3 fatty acid supplements could help alleviate the symptoms of ocular rosacea by reducing inflammation and improving tear film stability.
- The American Journal of Ophthalmology reported on the efficacy of cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion in treating ocular rosacea, noting improvements in ocular surface disease and tear function.
- A case study in JAMA Dermatology documented the successful use of oral isotretinoin in a patient with ocular rosacea, leading to a significant reduction in ocular inflammation and discomfort.
- The American Journal of Ophthalmology also highlighted the positive effects of azithromycin eye drops in treating ocular rosacea, resulting in improved meibomian gland function and decreased inflammation.
- A study featured in Advances in Therapy presented a case where topical azithromycin therapy was used effectively to treat ocular rosacea, offering another potential treatment option.
- Research from the Ophthalmology journal showed that low-dose oral erythromycin could be an effective treatment for children with ocular rosacea, providing symptomatic relief.
- Clinical and Experimental Optometry published a study on the long-term management of ocular rosacea with lid hygiene and topical metronidazole, demonstrating improvements in ocular surface health.
- A study in the Clinical Ophthalmology journal supported the use of oral ivermectin for ocular rosacea treatment, particularly in cases resistant to other therapies.
- Pediatric ophthalmology research documented in Cornea indicated that children with ocular rosacea could benefit from treatments such as lid hygiene, topical antibiotics, and systemic therapy, leading to improved clinical outcomes.
- A study in the British Journal of Dermatology highlighted the potential of brimonidine tartrate gel for reducing facial erythema associated with ocular rosacea.
- The American Journal of Ophthalmology discussed the positive impact of topical cyclosporine therapy in ocular rosacea patients, noting improvements in ocular surface discomfort and visual function.
- The Dermatologic Surgery journal provided evidence for the use of intense pulsed light therapy, which can reduce symptoms and improve the quality of life for ocular rosacea patients.
- Lastly, a review in Current Opinion in Ophthalmology emphasized the importance of recognizing and treating ocular rosacea early, including the use of topical and oral antibiotics, to prevent long-term complications.
These treatments, backed by scientific research and case studies, have shown to significantly improve symptoms and quality of life in patients with ocular rosacea, underscoring their value in clinical practice.
Key Takeaways
In investigating ocular rosacea treatments, scientific studies have consistently demonstrated the effectiveness of various interventions in improving ocular health and reducing symptoms.
Warm compresses, a mainstay in meibomian gland dysfunction care, have been found to be beneficial in ocular rosacea as well. They enhance meibomian gland secretions and alleviate eyelid inflammation, a finding supported by case studies (Stewart et al., 1992; Arthritis Rheum).
The therapeutic role of topical cyclosporine was corroborated in a case series where it lessened corneal involvement and heightened patient comfort in those with ocular rosacea, showcasing its viability as a treatment option (Perry et al., 2006; Am J Ophthalmol).
Oral doxycycline’s anti-inflammatory properties have been proven effective in a clinical trial, resulting in a marked reduction in ocular rosacea symptoms and corneal fluorescein staining, highlighting its importance in treatment regimens (Frucht-Pery et al., 1993; Arch Ophthalmol). Azithromycin, both topically and orally administered, has also produced favorable results, diminishing signs and symptoms of the condition (Bakar et al., 2009; Adv Ther; Luchs, 2008; J Ocul Pharmacol Ther).
Intense pulsed light therapy has emerged as a significant advance, reducing inflammatory load and telangiectasia associated with ocular rosacea and contributing to symptom relief (Craig et al., 2020; Clin Exp Optom). Low-dose isotretinoin, traditionally used for severe acne, has shown effectiveness in treating refractory ocular rosacea, significantly improving meibomian gland function and ocular surface health (Sobolewska et al., 2014; J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol).
Pediatric cases of ocular rosacea have been managed with tailored approaches, combining lid hygiene, topical antibiotics, and systemic therapy, emphasizing the need for individualized treatment strategies (Tisma et al., 2007; Cornea). The addition of omega-3 fatty acid supplements has been spotlighted for its significant symptom reduction and improvement in ocular surface disease index (Kangari et al., 2013; Int J Ophthalmol).
The scientific literature endorses a comprehensive approach to ocular rosacea treatment, with each therapy providing a distinct mechanism to combat the disease. These studies and case reports collectively offer strong evidence for the benefits of diverse treatment strategies, enhancing the lives of those affected by this chronic condition.
Warm Compress Application
Applying a warm compress to the eyelids is a fundamental and effective treatment for alleviating symptoms of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD). This non-invasive heat therapy method is instrumental in mitigating the blockage of meibomian glands by melting the waxy substances within the ducts, thereby restoring normal secretion. Regular application of a warm compress can significantly improve gland function and patient comfort.
The effectiveness of a warm compress largely depends on the consistent delivery of sufficient heat. Therefore, the selection of compress materials is crucial. Recent advancements have led to the development of specially designed compresses that maintain a steady temperature, optimizing the therapeutic effect. These compresses, often gel pack-based or bead-filled, can be reheated multiple times, ensuring uniform heat distribution across the eyelid area.
Patient education on the correct use of warm compresses is paramount. Individuals should be instructed on the appropriate temperature, which is typically around 40-45 degrees Celsius, and the duration of application, generally recommended for 10-15 minutes, one to two times daily. It is essential to counsel patients on monitoring the heat level to prevent skin irritation or burns.
Integrating heat therapy as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for MGD fosters patient engagement and leads to improved ocular health outcomes.
Eyelid Hygiene Routines
Scientific investigations have recognized the significance of targeted treatments for ocular rosacea, an inflammatory eye condition that can severely affect the meibomian glands and ocular surface. A study published in ‘Arquivos Brasileiros de Oftalmologia’ highlighted that ocular hygiene with warm compresses and eyelid cleaning was beneficial in reducing symptoms of ocular rosacea, corroborating the traditional approaches to eyelid hygiene in managing Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD) (SciELO).
Further scientific evidence from a case study in ‘Dermatology’ described the successful management of ocular rosacea using oral doxycycline, which reduced inflammation and ocular discomfort (ScienceDirect, pii/S0190962213004349). Similarly, a study in ‘Ophthalmology’ found that topical cyclosporine A was effective in treating ocular rosacea by improving tear production and reducing corneal damage (ScienceDirect, pii/S0161642097300153).
Research published in ‘Survey of Ophthalmology’ provided insights into the benefits of azithromycin, both in topical and oral forms, for treating the ocular manifestations of rosacea, enhancing patient comfort and quality of life (ScienceDirect, pii/S0039625717300012). Moreover, a clinical trial reported in ‘JAMA Dermatology’ demonstrated that tetracycline could alleviate ocular symptoms in rosacea patients (JAMA Network).
A study in ‘Experimental Eye Research’ further supported the use of omega-3 fatty acids as a dietary supplement to improve ocular surface inflammation common in rosacea patients (ScienceDirect, pii/S152918391000655X). Metronidazole gel, according to an article in ‘Advances in Therapy,’ also provided symptomatic relief for ocular rosacea when applied topically (Springer).
The efficacy of topical corticosteroids in managing ocular rosacea was documented in ‘Archives of Ophthalmology,’ suggesting their role in controlling acute inflammatory episodes (ScienceDirect, pii/0039625786900342). An assessment in ‘Clinical & Experimental Optometry’ showed that the combination of oral and topical therapies could offer enhanced outcomes for ocular rosacea patients (Wiley Online Library).
A comprehensive review in the ‘Journal of Ophthalmic & Vision Research’ underscored the multifaceted nature of ocular rosacea treatment, advocating for a personalized approach based on the severity and symptoms in each case (PMC). Pediatric cases of ocular rosacea, as discussed in ‘Cornea,’ require particular attention to diagnosis and treatment due to their unique aspects (LWW, Cornea Journal).
Research in ‘Ophthalmology’ has also emphasized the potential of laser therapy in managing telangiectasias associated with ocular rosacea, thereby improving patient satisfaction and ocular appearance (ScienceDirect, pii/S0161642096304120). An evaluation of low-dose isotretinoin in ‘Clinical and Experimental Dermatology’ indicated its utility in severe ocular rosacea cases resistant to conventional treatments (Europe PMC).
The once-daily treatment with oral ivermectin, documented in ‘Cornea,’ proposed an innovative approach in the treatment regimen for ocular rosacea, showing promising results in reducing inflammatory lesions (LWW, Cornea Journal). The role of brimonidine tartrate gel in managing facial erythema of rosacea, which may complement ocular treatment, was discussed in a study in ‘Therapeutic Advances in Ophthalmology’ (SAGE Journals).
Finally, a study in the ‘British Journal of Dermatology’ underlined the importance of recognizing demodex mites as a contributing factor in ocular rosacea, suggesting that addressing these mites could improve treatment outcomes (OUP). The collaboration between dermatologists and ophthalmologists was advocated in ‘American Journal of Ophthalmology’ to ensure comprehensive care for patients with ocular rosacea (ScienceDirect, pii/S0002939403008900).
Daily Warm Compresses
Implementing daily warm compresses forms a cornerstone of eyelid hygiene routines in managing Meibomian Gland Dysfunction effectively. This simple yet crucial practice supports gland stimulation and tear film optimization, which are vital for ocular comfort and visual function.
Here’s why incorporating warm compresses into your routine can make a significant difference:
- Soothes Eyelids: Reduces discomfort associated with gland blockages.
- Improves Gland Function: Enhances secretion of oils necessary for tear stability.
- Prevents Dryness: Maintains moisture by promoting a healthy tear film.
- Easy to Implement: Can be integrated into daily hygiene with minimal effort.
- Reduces Reliance on Medication: May decrease the need for pharmacological interventions.
As patients adopt warm compresses in their daily regimen, transitioning to lid margin cleaning will further enhance the management of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction.
Lid Margin Cleaning
Complementing the benefits of daily warm compresses, meticulous lid margin cleaning constitutes an essential component of a comprehensive eyelid hygiene regimen to alleviate symptoms of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction.
This process involves the use of lid scrubs, which are specially formulated to remove debris and bacterial biofilms that can exacerbate this condition. An evidence-based approach recommends patients gently clean the eyelid margins with these scrubs, using a side-to-side motion at the base of the eyelashes to ensure thorough cleansing.
Additionally, it is crucial to select hygienic cosmetics that are non-irritating and free from oils that can block the meibomian glands.
Patient education on proper eyelid hygiene and the judicious use of appropriate products is fundamental to managing and improving the symptoms associated with Meibomian Gland Dysfunction.
Prescription Medications
For patients with Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD), several prescription medications can effectively target the underlying inflammation and improve tear film quality. When considering these treatment options, it is imperative to weigh the prescription benefits against potential drug interactions, ensuring a patient-centered approach to care. These medications are often used when initial conservative treatments, such as warm compresses and eyelid hygiene, have not provided sufficient relief.
- Topical Cyclosporine: An immunomodulatory agent that can decrease corneal damage and increase tear production.
- Oral Tetracyclines: Such as doxycycline, these antibiotics also possess anti-inflammatory properties beneficial for MGD.
- Topical Steroids: Short-term use can significantly reduce inflammation but require monitoring for possible side effects.
- Topical Azithromycin: An antibiotic that can help manage bacterial colonization and reduce eyelid inflammation.
- Omega-3 Supplements: While available over-the-counter, a prescription-grade formulation may offer a more targeted dose for managing MGD.
It is critical for healthcare providers to stay abreast of the latest evidence-based research to optimize treatment regimens for MGD, always considering individual patient histories and the potential for adverse reactions when prescribing these medications.
Nutritional Supplements
In addition to prescription medications, incorporating nutritional supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids has shown promise in the management of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD). Omega benefits extend to improving the quality of meibum, the oily substance secreted by these glands, which is crucial for a healthy tear film and ocular surface. Clinical trials suggest that a regular intake of omega-3 supplements can reduce inflammation associated with MGD, subsequently alleviating symptoms like eye irritation and dryness.
Furthermore, increasing antioxidant intake through dietary supplements is also advocated for its role in ocular health. Antioxidants help combat oxidative stress, a factor implicated in the pathogenesis of various eye conditions, including MGD. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants contribute to the preservation of meibomian gland function and support overall eye wellness.
Patient-centered care in MGD management involves a comprehensive approach, integrating both pharmacological treatments and nutritional optimization. Healthcare providers should counsel patients on the potential advantages of these supplements, underlining the importance of quality sources and appropriate dosages as part of a tailored treatment strategy.
It is imperative for patients to discuss with their healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure compatibility with their individual health needs and existing treatments.
Pulsed Light Therapy
Among the emerging treatments for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD), pulsed light therapy stands out due to its non-invasive approach targeting the underlying inflammation of the eyelids. This therapy uses intense pulsed light to deliver specific wavelengths which have been shown to reduce the inflammation that contributes to MGD. The efficacy of pulsed light therapy depends on the precise calibration of light parameters, which are adjusted to maximize therapeutic benefit while minimizing potential side effects.
To further elucidate the advantages of pulsed light therapy, consider the following:
- Tailored light parameters: The treatment allows for customization according to individual patient needs, ensuring optimal outcomes.
- Reduction in reliance on medications: Patients may experience a decrease in the need for topical or oral medications.
- Quick treatment sessions: Procedures are typically fast, allowing for minimal disruption to patients’ daily lives.
- Enhanced gland function: Improved meibomian gland performance leads to better tear film stability and ocular comfort.
- Long-term benefits: Studies have indicated sustained improvements in MGD symptoms following a course of treatment.
By addressing both the symptoms and causes of MGD, pulsed light therapy represents a significant step forward in management strategies.
Transitioning from this innovative therapy, let’s explore the in-office procedures that complement such advanced treatments in the continuum of care for MGD.
In-Office Procedures
In the clinical management of ocular rosacea, specific in-office procedures have demonstrated substantial benefits in scientific studies and case reports.
Thermal pulsation treatment, an innovative approach that applies heat and pressure, has been evidenced to significantly enhance Meibomian Gland function, leading to improved patient comfort and symptomatology, as reported in a variety of clinical trials and research articles.
Concurrently, manual expression of the Meibomian Glands, conducted by eye care specialists, has been validated as an effective technique to alleviate gland blockages, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the tear film and overall ocular surface health.
These procedures are supported by empirical evidence highlighting their efficacy in the treatment regimen for patients with ocular manifestations of rosacea.
Thermal Pulsation Treatment
One effective in-office procedure for managing Meibomian Gland Dysfunction is thermal pulsation treatment. This method applies controlled heat and pressure to the eyelids to clear blocked meibian glands. It harnesses advanced technologies to improve patient experiences by providing a targeted approach that addresses the root cause of the dysfunction.
- Precision: Utilizes exact temperature control for optimal efficacy.
- Safety: Designed with built-in mechanisms to protect delicate eye structures.
- Efficiency: Typically completed in a single session, offering convenience.
- Patient Comfort: Adjustments can be made to enhance the individual’s experience.
- Evidence-Based: Supported by clinical studies demonstrating its effectiveness in improving gland function.
Manual Gland Expression
Manual gland expression is a hands-on technique performed by eye care professionals to relieve blockages from the meibomian glands. This procedure is critical for patients with Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD), as it aids in restoring the normal flow of oils into the tear film. During professional consultation, the eye care provider conducts a thorough gland evaluation, assessing the functionality and structure of the meibomian glands.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Assess gland functionality and blockages through gland evaluation. |
| 2 | Apply gentle pressure to the eyelid to express contents of the glands. |
| 3 | Monitor patient’s comfort and response to expression. |
| 4 | Provide patient-centered care and instructions for post-procedure care. |
A meticulous approach to manual gland expression can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve ocular surface health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Meibomian Gland Dysfunction Affect Contact Lens Wearers Differently, and What Special Precautions Should They Take?
The management of Meibomian gland dysfunction in contact lens wearers is enhanced through evidence-based treatments for ocular rosacea. Scientific studies have demonstrated that tailored treatment regimens, such as the use of anti-inflammatory medications and antibiotics, significantly improve tear film stability and reduce symptoms of dryness and irritation.
Case studies highlight the effectiveness of incorporating oral tetracyclines, which have been shown to provide measurable benefits in ocular surface health for those affected by ocular rosacea. Furthermore, the application of thermal pulsation therapy is a novel approach with promising results in restoring Meibomian gland function.
With these specialized treatments, contact lens wearers with ocular rosacea can achieve improved comfort and a decreased risk of complications, underscoring the importance of adopting strategies informed by clinical research to maintain optimal ocular health.
Can Meibomian Gland Dysfunction Be Completely Cured, or Is It a Chronic Condition Requiring Ongoing Management?
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD), a common component of ocular rosacea, requires ongoing management rather than a one-time cure.
Scientific applications and case studies have demonstrated the benefits of various treatments for ocular rosacea, which also positively impact MGD. For instance, the use of oral tetracyclines has shown efficacy in managing ocular symptoms of rosacea, including MGD (ScienceDirect [1], JAMA Dermatology [5], SpringerLink [7], Wiley Online Library [9], LWW [14], SAGE Journals [16]).
Topical cyclosporine has been reported to improve ocular signs and symptoms (ScienceDirect [6], PubMed Central [10]), and azithromycin therapy, specifically with a once-daily regimen, has been effective as well (LWW [14], ScienceDirect [17]).
A study on children with ocular rosacea revealed that early diagnosis and aggressive treatment are crucial for preventing vision-threatening complications (LWW [11]).
Furthermore, low-dose doxycycline has been recognized for its anti-inflammatory properties, providing symptomatic relief for ocular rosacea sufferers (ScienceDirect [4], Karger [19], LWW [20]).
Collectively, these treatments underscore the importance of a sustained, evidence-based therapeutic strategy to manage MGD within the broader context of ocular rosacea.
[1] ScienceDirect. Doxycycline and ocular rosacea: A long-term, low-dose approach.[4] ScienceDirect. Low-dose doxycycline and ocular rosacea.[5] JAMA Dermatology. Oral tetracyclines and ocular rosacea.[6] ScienceDirect. Topical cyclosporine and its benefits for ocular rosacea.[7] SpringerLink. Oral tetracyclines: A therapeutic review for ocular rosacea.[9] Wiley Online Library. Management of ocular rosacea with tetracyclines.[10] PubMed Central. Cyclosporine in the treatment of ocular rosacea.[11] LWW. Evaluation and treatment of children with ocular rosacea.[14] LWW. Once daily azithromycin in the treatment of adult ocular rosacea.[16] SAGE Journals. The impact of ocular rosacea treatment on quality of life.[17] ScienceDirect. Azithromycin for ocular rosacea.[19] Karger. Anti-inflammatory properties of doxycycline and ocular rosacea.[20] LWW. Ocular rosacea: Current understanding and therapy options.Are There Any Environmental or Lifestyle Factors That Can Exacerbate Meibomian Gland Dysfunction, and What Steps Can Be Taken to Mitigate These Effects?
Environmental and lifestyle factors, such as prolonged computer use and unbalanced dietary habits, can exacerbate meibomian gland dysfunction, which is often associated with ocular rosacea. Scientific studies have shown that incorporating certain treatments can offer significant benefits for those with ocular rosacea.
For instance, the use of oral omega-3 fatty acid supplements has been documented to improve ocular symptoms and meibomian gland function in patients with ocular rosacea, suggesting a link between diet and ocular surface inflammation (ScienceDirect, 2013; PubMed, 2015).
Moreover, effective management strategies for ocular rosacea include environmental modifications, such as taking regular screen breaks to encourage blinking and adjusting workstation ergonomics to reduce eye strain. These strategies can help to alleviate some symptoms of meibomian gland dysfunction, which is a key component of ocular rosacea (ScienceDirect, 1993; JAMA Dermatology, 1961; ScienceDirect, 2010).
Clinical case studies have demonstrated the success of these treatments, with patients experiencing reduced symptoms and improved quality of life after following recommendations for dietary changes and environmental controls (Springer, 2009; Wiley Online Library, 2020; LWW Journals Cornea, 2007).
These findings underscore the importance of a holistic approach to managing ocular rosacea that includes both medical treatment and lifestyle adaptations to support ocular health and mitigate the severity of symptoms associated with meibomian gland dysfunction (ScienceDirect, 1996; Europe PMC, 2003; LWW Journals Cornea, 2014; SAGE Journals, 2020; BJD, 2021; ScienceDirect, 2003; Karger, 1986; LWW Journals Ophthalmology, 2020).
How Does Meibomian Gland Dysfunction Impact Sleep Quality, and Are There Any Recommended Treatments or Adjustments to Improve Sleep?
Meibomian gland dysfunction, often associated with ocular rosacea, can negatively impact sleep quality due to its symptomatic dry eye discomfort, leading to nocturnal disturbances. Scientific evidence has shown that treatments for ocular rosacea, which often include measures to alleviate meibomian gland dysfunction, can improve sleep quality.
For instance, a study demonstrated that the use of oral doxycycline, an antibiotic with anti-inflammatory properties, significantly reduced ocular symptoms and improved sleep (ScienceDirect, pii/S0190962213004349). In addition, implementing lid hygiene and warm compresses has been advocated to relieve symptoms and enhance sleep by promoting healthy meibomian gland function (ScienceDirect, pii/S0039625717300012; ScienceDirect, pii/S0161642097300153).
Moreover, case studies have suggested that omega-3 fatty acids may be beneficial, potentially due to their anti-inflammatory effects, which help in restoring eyelid health and thus ameliorate sleep disturbances (ScienceDirect, pii/S152918391000655X; PubMed, PMC4458660). Furthermore, the application of topical cyclosporine has shown promise in improving meibomian gland function, thereby contributing to better sleep quality for patients with ocular rosacea (Springer, 10.1007/s12325-009-0037-2).
In children with ocular rosacea, tailored approaches such as the use of topical corticosteroids and oral erythromycin have displayed effectiveness in managing symptoms, which is vital for ensuring restful sleep (LWW, 2007/01000). Similarly, low-dose oral antibiotics have been effective in adult cases, significantly improving ocular signs and symptoms, which can be extrapolated to imply a potential for improved sleep (ScienceDirect, pii/S0161642096304120).
Are There Any Specific Exercises or Activities That Can Promote Better Eye Health and Potentially Reduce the Symptoms of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction?
In scientific studies and case reports, treatments for ocular rosacea have shown significant benefits for patients.
A study published in the Brazilian Journal of Ophthalmology reported that intense pulsed light therapy, along with meibomian gland expression, resulted in reduced symptoms and improved meibomian gland functionality.
Another study highlighted in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology showed that oral doxycycline improved ocular rosacea symptoms more effectively than topical metronidazole.
The use of topical cyclosporine, as noted in the Archives of Ophthalmology, demonstrated improvements in ocular rosacea signs and symptoms, and a study in Survey of Ophthalmology indicated that azithromycin, both oral and topical, could be beneficial.
The effectiveness of oral tetracycline therapy was documented in JAMA Dermatology, revealing it as a reliable treatment option.
A clinical trial published in Cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology discussed the positive effects of oral omega-3 fatty acids in ocular rosacea patients, while Advances in Therapy reported improvements with oral azithromycin therapy.
A study in the American Journal of Ophthalmology found that topical metronidazole was useful in managing ocular rosacea.
The benefits of once-daily low-dose doxycycline were presented in Cornea, and the European Journal of Ophthalmology described the advantages of brimonidine gel in reducing ocular rosacea erythema.
The British Journal of Dermatology showcased that minocycline could provide relief for rosacea-related ocular manifestations.
A case series in the American Journal of Ophthalmology emphasized the potential of oral isotretinoin for severe ocular rosacea. The efficacy of subantimicrobial dose doxycycline was explored in the journal Cornea, offering an alternative with fewer side effects.
Finally, the Current Opinion in Ophthalmology review summarized various treatments, including lid hygiene and artificial tears, as part of a comprehensive management strategy for ocular rosacea.
Conclusion
In the scientific exploration of ocular rosacea treatment, a variety of interventions have demonstrated efficacy in enhancing ocular health and mitigating symptoms.
The application of warm compresses, traditionally recommended for meibomian gland dysfunction, has also shown benefits in managing ocular rosacea by improving meibomian gland secretions and reducing eyelid inflammation (Stewart et al., 1992; Arthritis Rheum).
Moreover, the effectiveness of topical cyclosporine has been validated in a case series, where it reduced corneal involvement and improved subjective comfort in patients with ocular rosacea (Perry et al., 2006; Am J Ophthalmol).
A clinical trial indicated that oral doxycycline, by virtue of its anti-inflammatory properties, effectively treats ocular rosacea, leading to a significant decrease in symptoms and corneal fluorescein staining (Frucht-Pery et al., 1993; Arch Ophthalmol). Additionally, azithromycin, both in topical and oral forms, has yielded positive outcomes in reducing signs and symptoms of the condition (Bakar et al., 2009; Adv Ther; Luchs, 2008; J Ocul Pharmacol Ther).
Intense pulsed light therapy, a more recent technological advancement, has demonstrated its potential in reducing the inflammatory load and telangiectasia associated with ocular rosacea, further contributing to symptom relief (Craig et al., 2020; Clin Exp Optom). Low-dose isotretinoin, typically used for severe acne, has also been reported to be effective in treating refractory ocular rosacea, providing substantial improvement in meibomian gland function and ocular surface health (Sobolewska et al., 2014; J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol).
Moreover, children with ocular rosacea have been successfully managed with a combination of lid hygiene, topical antibiotics, and systemic therapy, emphasizing the importance of a tailored approach in pediatric cases (Tisma et al., 2007; Cornea). The integration of omega-3 fatty acid supplements has been highlighted as well, showing a marked reduction in symptoms and an improved ocular surface disease index (Kangari et al., 2013; Int J Ophthalmol).
Overall, the scientific literature supports a multifaceted approach to the treatment of ocular rosacea, with each therapy offering a unique mechanism to combat the disease. The collective evidence from these studies and case reports presents a compelling case for the benefits of various treatment strategies, improving the quality of life for those affected by this chronic condition.